4 Easy Circles, Part 2
If the two smallest circles are congruent, and the radius of the largest circle can be expressed as c a − b , where a , b , c are coprime positive integers and c is a square-free, submit a + b + c .

The answer is 81108.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
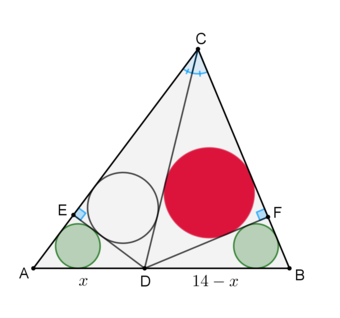 △
A
B
C
is a compound of a
1
5
-
9
-
1
2
and a
1
3
-
5
-
1
2
right triangle sharing a common side of length
1
2
, which is the height from C of
△
A
B
C
.
△
A
B
C
is a compound of a
1
5
-
9
-
1
2
and a
1
3
-
5
-
1
2
right triangle sharing a common side of length
1
2
, which is the height from C of
△
A
B
C
.
Thus,
sin
A
=
1
5
1
2
=
5
4
,
cos
A
=
1
5
9
=
5
3
,
sin
B
=
1
3
1
2
and
cos
B
=
1
3
5
.
Let A D = x . Then, D B = 1 4 − x .
Moreover, E D = A D ⋅ sin A ⇒ E D = 5 4 x , E A = A D ⋅ cos A ⇒ E A = 5 3 x
For the incircle of the right △ E A D we have
r = 2 1 ( E A + E D − A D ) = 2 1 ( 5 3 x + 5 4 x − x ) = 5 x ( 1 ) Working similarly on right △ F D B , F D = B D ⋅ sin B ⇒ F D = ( 1 4 − x ) 1 3 1 2 F B = B D ⋅ cos B ⇒ F B = ( 1 4 − x ) 1 3 5
r = 2 1 ( F D + F B − B D ) = 2 1 ( 1 4 − x ) ( 1 3 1 2 + 1 3 5 − 1 ) = 1 3 2 ( 1 4 − x ) ( 2 ) Combining ( 1 ) and ( 2 ) we get 5 x = 1 3 2 ( 1 4 − x ) ⇔ x = 2 3 1 4 0 Using this value, we find F D = 2 3 1 6 8 and F B = 2 3 7 0 Hence, by Pythagorean theorem on right △ C D F ,
C D = F D 2 + C F 2 = ( 2 3 1 6 8 ) 2 + ( 1 3 − 2 3 7 0 ) 2 ⇒ C D = 2 3 8 0 6 6 5
Finally, for the inradius R of right △ C D F ,
R = 2 1 ( F D + C F − C D ) = 2 1 ( 2 3 1 6 8 + 2 3 2 2 9 − 2 3 8 0 6 6 5 ) ⇒ R = 4 6 3 9 7 − 8 0 6 6 5 Doing analogous calculations for the inradius R ′ of △ C D E we find R ′ = 4 6 3 7 3 − 8 0 6 6 5 Since R ′ < R , the largest circle is the incircle of △ C D F .
For the answer, a = 3 9 7 , b = 8 0 6 6 5 , c = 4 6 , thus, a + b + c = 8 1 1 0 8 .
We note that a 13-14-15 triangle is made up of a 3-4-5 right triangle and a 5-12-13 right triangle sharing an altitude of 1 2 . Therefore △ A D E is a 3-4-5 right triangle and △ B D F is a 5-12-13 right triangle.
Let D B = x ; then F B = 1 3 5 x and D F = 1 3 1 2 x . If r is the radius of the two congruent incircles, then
r = 2 1 ( F B + D F + D B ) 2 1 F B ⋅ D F = 1 3 2 x
Similarly, A D = 1 4 − x , A E = 5 3 ( 1 4 − x ) . E D = 5 4 ( 1 4 − x ) , and
r = 2 1 ( A E + E D + A D ) 2 1 A E ⋅ E D = 5 1 4 − x
Therefore r = 1 3 2 x = 5 1 4 − x ⟹ x = 2 3 1 8 2 = D B , D F = 1 3 1 2 D B = 2 3 1 6 8 , F B = 1 3 5 D B = 2 3 7 0 , and C F = 1 3 − F B = d f r a c 2 2 9 2 3 . The radius of the largest circle,
R = 2 1 ( D F + C F + C D ) 2 1 D F ⋅ C F = D F + C F + D F 2 + C F 2 D F ⋅ C F = 4 6 3 9 7 − 8 0 6 6 5
The required answer is a + b + c = 3 9 7 + 8 0 6 6 5 + 4 6 = 8 1 1 0 8 .
Draw altitude C G . Since the 1 3 - 1 4 - 1 5 triangle is a 9 - 1 2 - 1 5 right triangle combined with a 5 - 1 2 - 1 3 right triangle at side 1 2 , C G = 1 2 .
Now △ A G C ∼ △ A E D and △ B G C ∼ △ B F D by AA similarity, so let A E = 3 m , E D = 4 m , A D = 5 m , and r △ A E D = m (because it is similar to a 9 - 1 2 - 1 5 or 3 - 4 - 5 triangle, which has an inradius of r = 2 1 ( 3 + 4 − 5 ) = 1 ) and let B F = 5 n , D F = 1 2 n , D B = 1 3 n , and r △ B F D = 2 n (because it is similar to a 5 - 1 2 - 1 3 triangle, which has an inradius of r = 2 1 ( 5 + 1 2 − 1 3 ) = 2 ).
From segment addition, A B = A D + D B = 5 m + 1 3 n = 1 4 , and since the two smallest circles are congruent, r △ A E D = r △ B F D = m = 2 n .
Solving 5 m + 1 3 n = 1 4 and m = 2 n gives m = 2 3 2 8 and n = 2 3 1 4 .
That means D F = 1 2 n = 2 3 1 6 8 , F C = B C − B F = 1 3 − 5 n = 2 3 2 2 9 , C D = D F 2 + F C 2 = ( 2 3 1 6 8 ) 2 + ( 2 3 2 2 9 ) 2 = 2 3 8 0 5 5 4 , and the radius of the largest circle is r = 2 1 ( D F + F C − C D ) = 4 6 3 9 7 + 8 0 6 6 5 , so that a = 3 9 7 , b = 8 0 6 6 5 , c = 4 6 , and a + b + c = 8 1 1 0 8 .