(9) - Outcoming
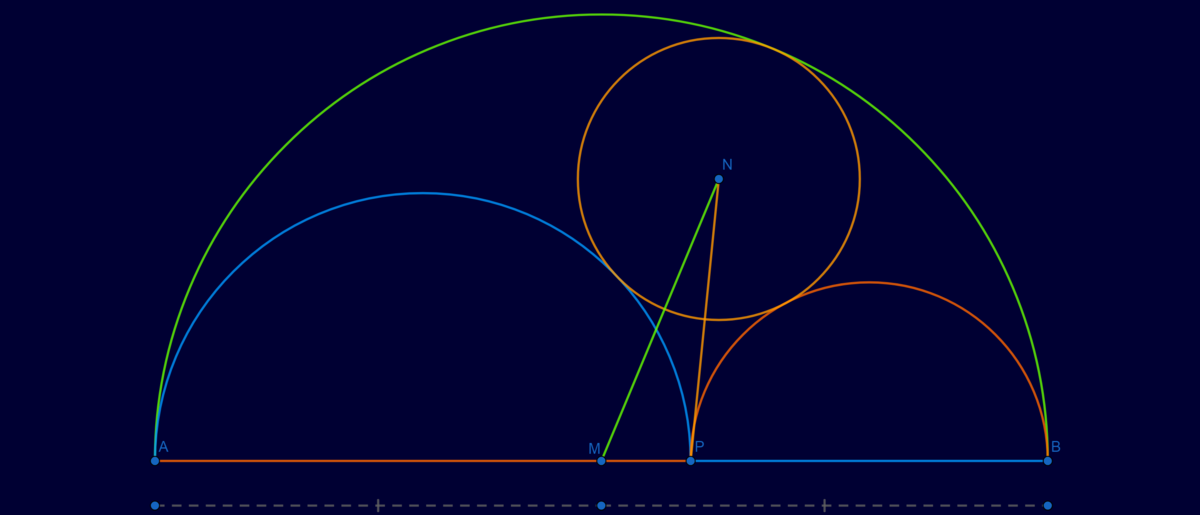
M and N are respectively the center of green semicircle and the light orange circle. If PA BP = 3 2 then MN NP = n m p with p is square-free and g cd ( m , n ) = 1 . Calculate the value of p 2 ( m + n ) .
The answer is 724271.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
There's a minor problem about typing in LaTex that you should check.
@Thành Đạt Lê , if you had used a white background for the figure, I would be able to copy and paste and edit it to use in my solution. Hope that you can do that the next time.
Log in to reply
Are you editing your figure in Paint? If so, you should choose the shade (0, 0, 51) as the background color.
Log in to reply
Here are steps on how to do it:
-
Choose the "Edit Colors" section.
-
Type in the blue box "51" and click OK.
-
Choose the new color as "Color 2".
And just like that, you have just changed the background color to look like mine.
Since P A B P = 3 2 , let B P = 4 and P A = 6 , so that the radius of the red semicircle is r r = 2 , the radius of the blue semicircle is r b = 3 , and the radius of the green semicircle is r g = 5 .
Since the circles are all tangent to each other, the radius of the orange circle can be found by using Destartes' Theorem , r o 1 = 2 1 + 3 1 − 5 1 + 2 2 ⋅ 3 1 − 2 ⋅ 5 1 − 3 ⋅ 5 1 , which solves to r o = 1 9 3 0 .
Let O be the center of the red semicircle. Then O N = r r + r o = 2 + 1 9 3 0 = 1 9 6 5 and O M = r b − r r = 5 − 2 = 3 . Also, M N = r b − r o = 5 − 1 9 3 0 = 1 9 6 5 , M P = r b − 2 r r = 5 − 2 ⋅ 2 = 1 , and O P = r r = 2 .
By the law of cosines on △ M N O , cos O = 2 ⋅ M O ⋅ N O M O 2 + N O 2 − M N 2 = 2 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 1 9 6 8 3 2 + ( 1 9 6 8 ) 2 − ( 1 9 6 5 ) 2 = 1 7 8 .
By the law of cosines on △ P N O , N P = P O 2 + N O 2 − 2 ⋅ P O ⋅ N O ⋅ cos O = 2 2 + ( 1 9 6 8 ) 2 − 2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 1 9 6 8 ⋅ 1 7 8 = 1 9 6 1 0 1 .
Therefore, M N N P = 1 9 6 5 1 9 6 1 0 1 = 6 5 6 1 0 1 , so m = 6 , p = 1 0 1 , and n = 6 5 , which means p 2 ( m + n ) = 1 0 1 2 ( 6 + 6 5 ) = 7 2 4 2 7 1 .
Let M be the origin ( 0 , 0 ) of the x y -plane, the coordinates of N be ( x , y ) , the radius of the light orange be r , A M = 5 , A P = 6 , hence A ( − 5 , 0 ) , P ( 1 , 0 ) , the center of the blue semicircle Q ( − 2 , 0 ) , B P = 4 , hence B ( 5 , 0 ) , the center of orange semicircle R ( 3 , 0 ) . Using Pythagorean theorem we have:
⎩ ⎪ ⎨ ⎪ ⎧ M N 2 = ( x − 0 ) 2 + ( y − 0 ) 2 = ( 5 − r ) 2 Q N 2 = ( x + 2 ) 2 + ( y − 0 ) 2 = ( 3 + r ) 2 R N 2 = ( x − 3 ) 2 + ( y − 0 ) 2 = ( 2 + r ) 2 ⟹ x 2 + y 2 = r 2 − 1 0 r + 2 5 ⟹ x 2 + 4 x + y 2 = r 2 + 6 r + 5 ⟹ x 2 − 6 x + y 2 = r 2 + 4 r − 5 . . . ( 1 ) . . . ( 2 ) . . . ( 3 )
{ ( 2 ) − ( 1 ) : ( 1 ) − ( 3 ) : 4 x = 1 6 r − 2 0 6 x = − 1 4 r + 3 0 ⟹ x = 4 r − 5 ⟹ 3 x = − 7 r + 1 5 . . . ( 4 ) . . . ( 5 )
From 3 ( 4 ) − ( 5 ) : 0 = 1 9 r − 3 0 ⟹ r = 1 9 3 0 . From ( 4 ) : x = 4 × 1 9 3 0 − 5 = 1 9 2 5 .
Now we have:
M N N P = x 2 + y 2 ( x − 1 ) 2 + y 2 = x 2 + y 2 x 2 + y 2 − 2 x + 1 = 1 9 6 5 ( 1 9 6 5 ) 2 − 2 ( 1 9 2 5 ) + 1 = 1 9 6 1 0 1 Recall x 2 + y 2 = ( 5 − r ) 2 = ( 1 9 6 5 ) 2 and x = 1 9 2 5
Then p 2 ( m + n ) = 1 0 1 2 ( 6 + 6 5 ) = 7 2 4 2 7 1 .