Maximizing Volume Given Closed Area
If is the maximum possible volume of a closed cylinder such that its surface area is , what is the value of ?
The answer is 16.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
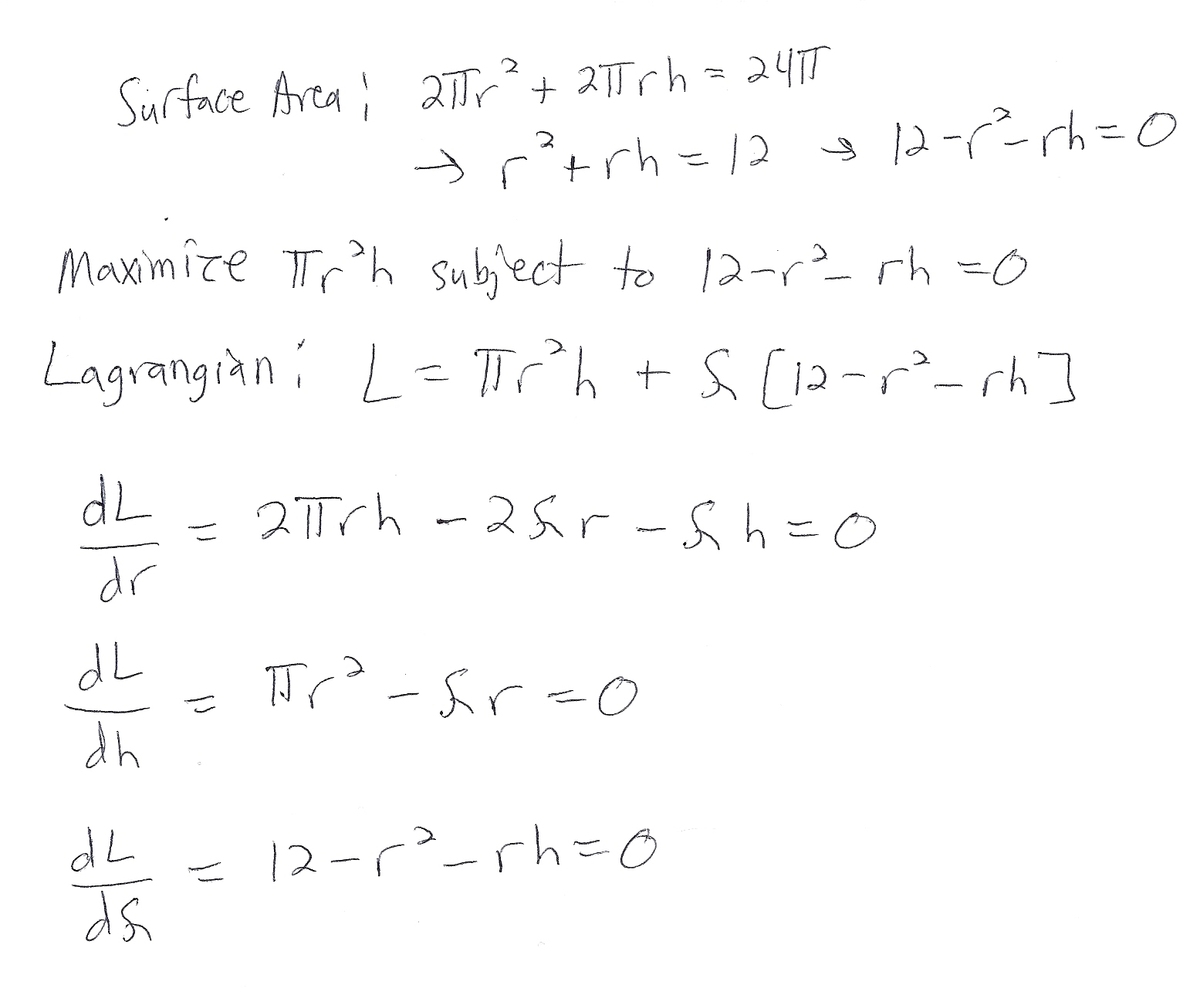

Oh this is nice! I just learned this in my additional math class in high school!
Let S and W denote surface area and the volume of this closed cylinder, respectively.
Recall the relevant formula, the surface area and the volume of a cylinder can be expressed as S = 2 π r ( r + h ) and W = π r 2 h , respectively, where r and h denotes the radius and height of this cylinder.
We are given that S = 2 4 π , so 2 π r ( r + h ) = 2 4 π ⇔ r ( r + h ) = 1 2 ⇔ h = r 1 2 − r .
Substitute this expression into the formula of W gives
W = π r 2 h = π r 2 ( r 1 2 − r ) = π ( 1 2 r − r 3 ) .
When at the crtical point, W ′ = 0 , with W ′ = π ( 1 2 − 3 r 2 ) = 0 , so r 2 = 3 1 2 = 4 ⇒ r = 2 only (we take the positive root only because r represents a measurement of distance).
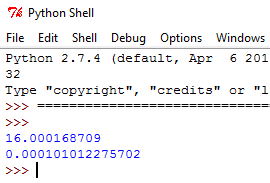
If we substitute the value r = 2 into W , we get W = 1 6 π .
Now, what's left is to prove that W has a maximum value when r = 2 . This can be shown by applying the second derivative test , W ′ ′ = π ( − 6 r ) < 0 when r = 2 .
Since we have shown that W is maximized at r = 2 and is equal to 1 6 π , then V π = 1 6 π ⇒ V = 1 6 . And we're done!
I'm wondering if this question can be solved by applying the arithmetic mean geometric mean inequality or Lagrange multipliers . Thoughts?