A Collision Problem
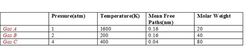 The above table gives data about three Ideal gas samples taken in separate equal volume containers.
The above table gives data about three Ideal gas samples taken in separate equal volume containers.
-
Calculate the ratio of collision frequencies ( Z 1 1 ) (in the form of A:B:C) for the three gases. Let the ratio be j : k : l .
-
Calculate the number of collision by one molecule per second ( Z 1 ). Let the ratio be m : n : o .
Report the answer as j m + n k + o l .
For those who don't know:
-
Z 1 1 is the total number of Bimolecular collisions per unit volume per unit time.
-
Z 1 is the number of collisions made by a single molecule with other molecules per unit time.
The answer is 12.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
A request to any moderator reading this , please let the table that I have made(yes the pic) stay as it is , currently I don't know the Latex code for making a table but I will learn the code and change it on my own .
Thanks for the same :)
The collision frequency for single molecule Z 1 , for all molecules Z 1 1 , mean free path λ and average speed of molecule c are given below:
\(\begin{cases} Z_1 = \sqrt{2}\pi d^2 \overline{c} \left(\dfrac{N}{V}\right) &...(1) \\ Z_{11} = \dfrac{1}{2} Z_1 \left(\dfrac{N}{V}\right) &...(2) \\ \lambda = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}d^2 N} & ...(3) \\ \overline{c} = \sqrt{\dfrac{8k_BT}{\pi m}} & ...(4) \end{cases} \quad \begin{array} {} \text{where } & d = \text{the diameter of molecule} \\ & N = \text{the number of molecules in volume }V \\ & k_B = \text{Boltzmann constant} \\ & T = \text{absolute temperature} \\ & m = \text{molecular mass} \end{array} \)
( 1 ) : Z 1 ∝ d 2 c N Since ( 3 ) : d 2 ∝ λ N 1 ( 4 ) : c ∝ m T ∝ λ 1 m T
⇒ m : n : o = 0 . 1 6 1 2 0 1 6 0 0 : 0 . 1 6 1 4 0 2 0 0 : 0 . 0 4 1 8 0 4 0 0 = 4 : 1 : 4
( 2 ) : Z 1 1 ∝ Z 1 N Since p V = N R T , where p is pressure and R , the universal gas constant ∝ T Z 1 p
⇒ j : k : l = 1 6 0 0 m : 2 0 0 2 n : 4 0 0 4 o = 1 6 0 0 4 : 2 0 0 2 : 4 0 0 1 6 = 1 : 4 : 1 6
⇒ j m + n k + o l = 1 4 + 1 4 + 4 1 6 = 1 2
Let σ A , σ B and σ C be the Collision Diameters of A , B and C .
Let λ be the Mean Free Path i.e the average distance travelled by a molecule between two successive collisions , P be the pressure in atm .
∴ λ = 2 ⋅ π ⋅ σ 2 ⋅ P k ⋅ T ⇒ σ ∝ λ ⋅ P T
∴ σ A : σ B : σ C 0 . 1 6 ⋅ 1 1 6 0 0 : 0 . 1 6 ⋅ 2 2 0 0 : 0 . 0 4 ⋅ 4 4 0 0 = 4 : 1 : 2
Now using this we'll find the rest .
Z 1 1 ∝ m ⋅ T 3 σ 2 ⋅ P 2 ⇒ A : B : C = 2 0 ⋅ 1 6 0 0 3 1 6 × 1 : 4 0 ⋅ 2 0 0 3 1 × 4 : 8 0 ⋅ 4 0 0 3 4 × 1 6 1 : 4 : 1 6 .
⟹ j = 1 , k = 4 , l = 1 6
Z 1 ∝ M T σ 2 ⋅ P
⇒ A : B : C = 2 0 ⋅ 1 6 0 0 1 6 ⋅ 1 : 4 0 ⋅ 2 0 0 1 ⋅ 2 : 8 0 ⋅ 4 0 0 4 ⋅ 4 = 4 : 1 : 4
⟹ m = 4 , n = 1 , o = 4
The final answer is j m + n k + o l = 1 4 + 1 4 + 4 1 6 = 1 2 .