A dizzy spiral
The diagram below shows a spiral such that .
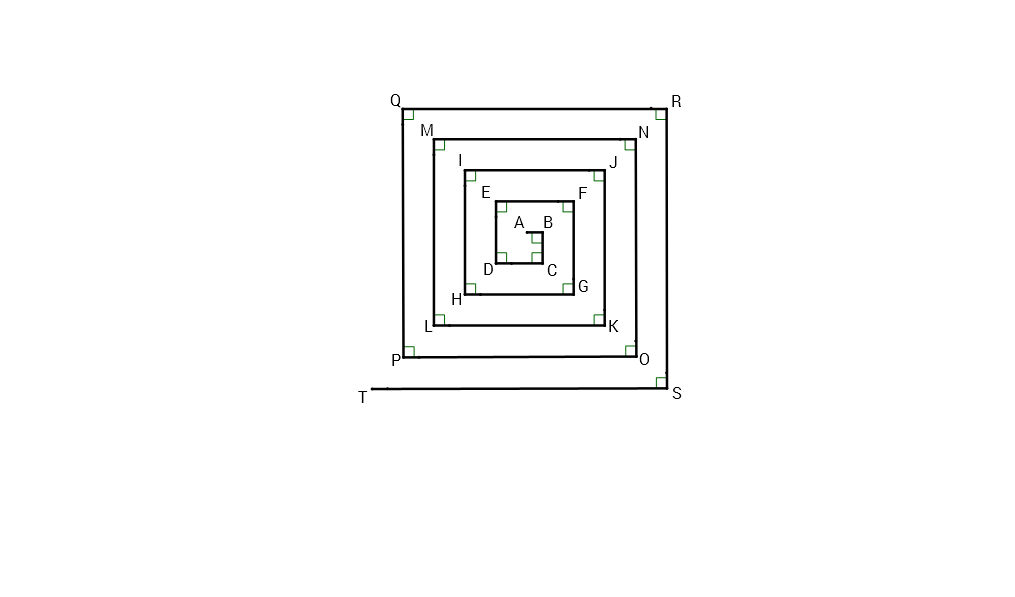
If , , , and , find the area of .
The answer is 40.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Let the spiral to be on the complex plain with A being the origin. Let complex number z 1 = x 1 + y 1 i = A B , z 2 = x 2 + y 2 i = A C , z 3 = x 3 + y 3 i = A D and so on, such that B ( x 1 , y 1 ) , C ( x 2 , y 2 ) , D ( x 3 , y 3 ) and so on.
We note that a turning 9 0 ∘ clockwise is equivalent to multiplying by − i , therefore, we have z n = 1 + 2 ( − i ) + 3 ( − i ) 2 + 4 ( − i ) 3 + ⋯ + n ( − i ) n − 1 = ∑ k = 1 n k ( − i ) k − 1 , which is the sum of an arithmetic-geometrical progression with initial term a = 1 , common difference d = 1 and common ratio r = − i . Therefore,
z n ⟹ z n = 1 + i 1 − n ( − i ) n + ( 1 + i ) 2 ( − i ) ( 1 − ( − i ) n − 1 ) = ( 1 + i ) ( 1 − i ) ( 1 − n ( − i ) n ) ( 1 − i ) + 2 i ( − i ) ( 1 − ( − i ) n − 1 ) = 2 ( − i ) n − 1 ( n + 1 + n i ) − i = 2 ( − i ) n ( − n + ( n + 1 ) i ) ) − i = ⎩ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎨ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎧ − 2 n + 2 n i 2 n + 1 + 2 n − 1 i 2 n − 2 n + 2 i − 2 n + 1 − 2 n + 1 i for n m o d 4 = 0 for n m o d 4 = 1 for n m o d 4 = 2 for n m o d 4 = 3
Now, we have
⎩ ⎪ ⎨ ⎪ ⎧ A E = z 4 = − 2 + 2 i A M = z 1 2 = − 6 + 6 i A T = z 1 9 = − 1 0 − 1 0 i ⟹ E ( − 2 , 2 ) ⟹ M ( − 6 , 6 ) ⟹ T ( − 1 0 , − 1 0 )
From the coordinates, we can find the area of △ E M T as follows:
[ E M T ] = ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ 2 6 + 2 ( − 6 + 2 ) + 2 − 1 0 + 6 ( − 1 0 + 6 ) + 2 2 − 1 0 ( − 2 + 1 0 ) ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ = ∣ 4 ( − 4 ) − 2 ( − 4 ) − 4 ( 8 ) ∣ = ∣ − 1 6 + 8 − 3 2 ∣ = 4 0