A Geometry Problem.
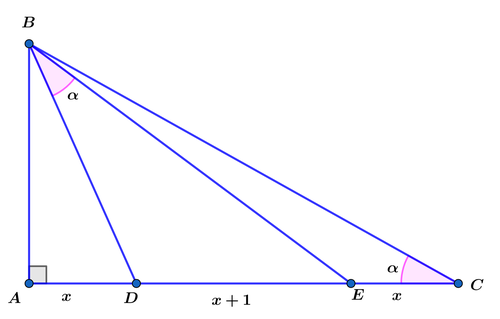
In the right △ A B C above, A D = E C = x , D E = x + 1 and m ∠ D B E = m ∠ B C A = α . Find the value of x for which the area A △ D B E = x 2 − 1 .
The answer is 3.369924.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
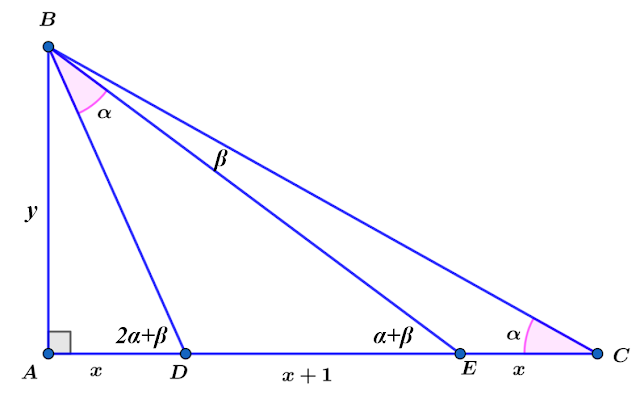
Since A △ A D E = x 2 − 1 , it follows that x > 1 .
Referring to the figure we have
x y = tan ( 2 α + β ) = 1 − tan α ⋅ tan ( α + β ) tan α + tan ( α + β ) = 1 − ( 3 x + 1 ) ( 2 x + 1 ) y 2 3 x + 1 y + 2 x + 1 y
Hence,
x 1 = 1 − ( 3 x + 1 ) ( 2 x + 1 ) y 2 3 x + 1 1 + 2 x + 1 1 ⇔ y 2 = x 2 + 3 x + 1 ⇒ y = x 2 + 3 x + 1 Now we have an equation for x :
A △ A D E = x 2 − 1 ⇔ 2 1 y ⋅ ( x + 1 ) = x 2 − 1 ⇔ x 2 + 3 x + 1 ⋅ ( x + 1 ) = 2 ( x − 1 ) ( x + 1 ) ⇔ x 2 + 3 x + 1 = 2 ( x − 1 ) ⇒ x 2 + 3 x + 1 = 4 x 2 − 8 x + 4 ⇔ 3 x 2 − 1 1 x + 3 = 0 ⇔ x > 1 x = 6 1 1 + 8 5 ≈ 3 . 3 6 9 9
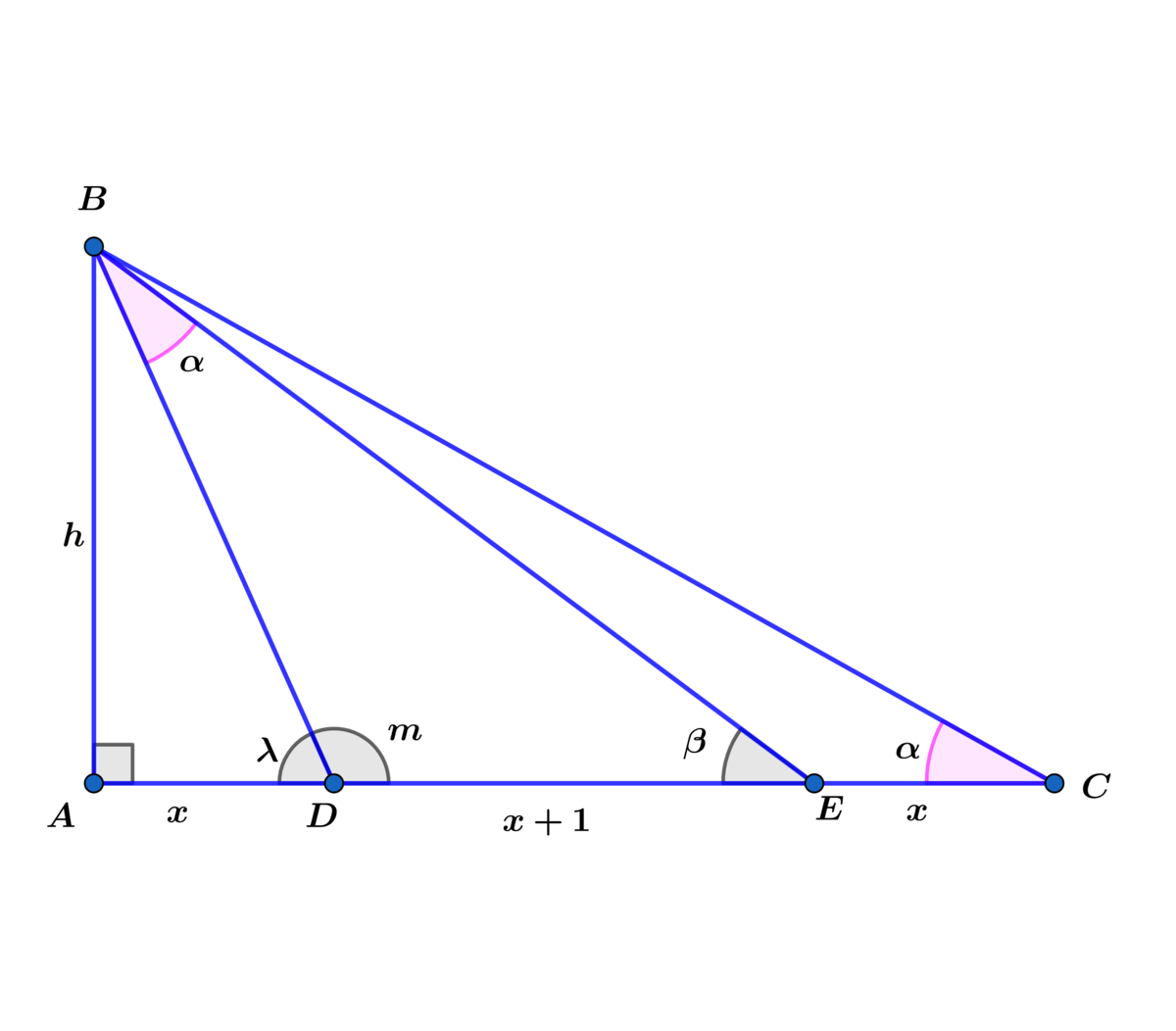
m = 1 8 0 − ( α + β ) = 1 8 0 − λ ⟹ λ = α + β
⟹ tan ( λ ) = x h = tan ( α + β ) , where tan ( β ) = 2 x + 1 h and tan ( α ) = 3 x + 1 h
⟹ x h = tan ( α + β ) = 1 − tan ( α ) tan ( β ) tan ( α ) + tan ( β ) = 1 − ( 3 x + 1 ) ( 2 x + 1 ) h 2 3 x + 1 h + 2 x + 1 h = ( 6 x 2 + 5 x + 1 − h 2 5 x + 2 ) h
⟹ x 1 = 6 x 2 + 5 x + 1 − h 2 5 x + 2 ⟹ 6 x 2 + 5 x + 1 − h 2 = 5 x 2 + 2 x
⟹ h 2 = x 2 + 3 x + 1 ⟹ h = x 2 + 3 x + 1
⟹ A △ D B E = 2 1 ( x + 1 ) ( x 2 + 3 x + 1 ) = x 2 − 1 = ( x − 1 ) ( x + 1 ) ⟹
x 2 + 3 x + 1 = 2 ( x − 1 ) ⟹ x 2 + 3 x + 1 = 4 x 2 − 8 x + 4 ⟹
3 x 2 − 1 1 x + 3 = 0 ⟹ x = 6 1 1 ± 8 5 and x > 1 ⟹ x = 6 1 1 + 8 5 ≈ 3 . 3 6 9 9 2 4 .
Since A △ D B A = x 2 − 1 , ⟹ A B = 2 ( x − 1 ) so that A △ D B A = 2 1 A B ⋅ D E = 2 1 ⋅ 2 ( x − 1 ) ( x + 1 ) = x 2 − 1 . The B D = A B 2 + A D 2 = ( 2 ( x − 1 ) ) 2 + x 2 = 5 x 2 − 8 x + 4 . Note that △ B D E and △ B C D are similar, then we have:
D E B D x + 1 5 x 2 − 8 x + 4 5 x 2 − 8 x + 4 3 x 2 − 1 1 x + 3 ⟹ x = B D C D = 5 x 2 − 8 x + 4 2 x + 1 = 2 x 2 + 3 x + 1 = 0 = ⎩ ⎪ ⎨ ⎪ ⎧ 6 1 1 + 8 5 ≈ 3 . 3 6 9 9 2 4 0 7 6 6 1 1 − 8 5 ≈ 0 . 2 9 6 7 4 2 5 9
From A △ D B E = x 2 − 1 ⟹ x > 1 , therefore x ≈ 3 . 3 7 .