A geometry problem by Alan Enrique Ontiveros Salazar
In a right triangle with sides a , b and hypotenuse c , find the length of the segment that bisects the right angle, in terms of a and b .
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
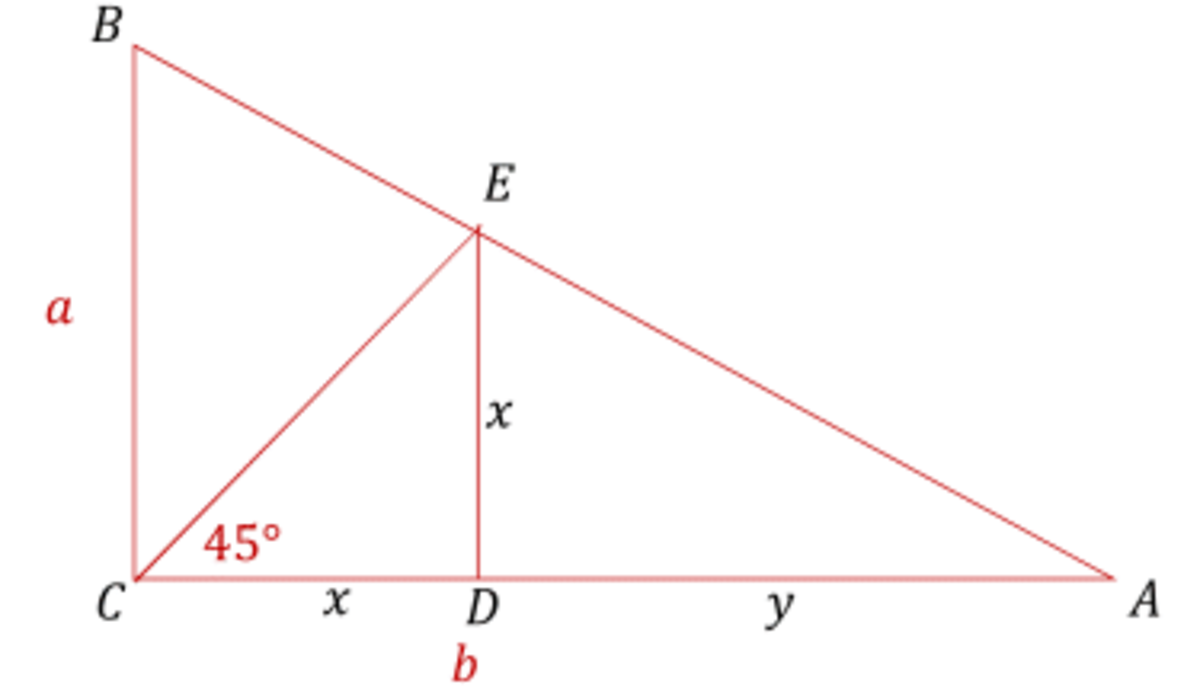 Draw
E
D
parallel to
B
C
dividing
b
so that
b
=
x
+
y
, which makes
y
=
b
−
x
.
Draw
E
D
parallel to
B
C
dividing
b
so that
b
=
x
+
y
, which makes
y
=
b
−
x
.
From the similarity of △ B C A and △ E D A we have b a = y x = b − x x .
Solving for x we get x = a + b a b .
C E = 2 x = a + b 2 a b .
Let the angle bisector be s .
The area of the whole triangle is 2 1 a b ; the area of the smaller triangles are 2 1 a s sin 4 π and 2 1 b s sin 4 π .
It is then easy to see that
2 1 a b = 2 1 a s sin 4 π + 2 1 b s sin 4 π
After a bit of simplification:
a b = 2 1 a s + 2 1 b s = 2 s ( a + b )
Dividing both sides by 2 a + b gives a formula for s :
s = a + b 2 a b