A geometry problem by Deepansh Jindal
The diagonals and of the regular hexagon are divided by the inner points and , respectively, so that . Determine the value of if and are collinear.
Give your answer correct to 2 decimal places.
The answer is 0.57.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
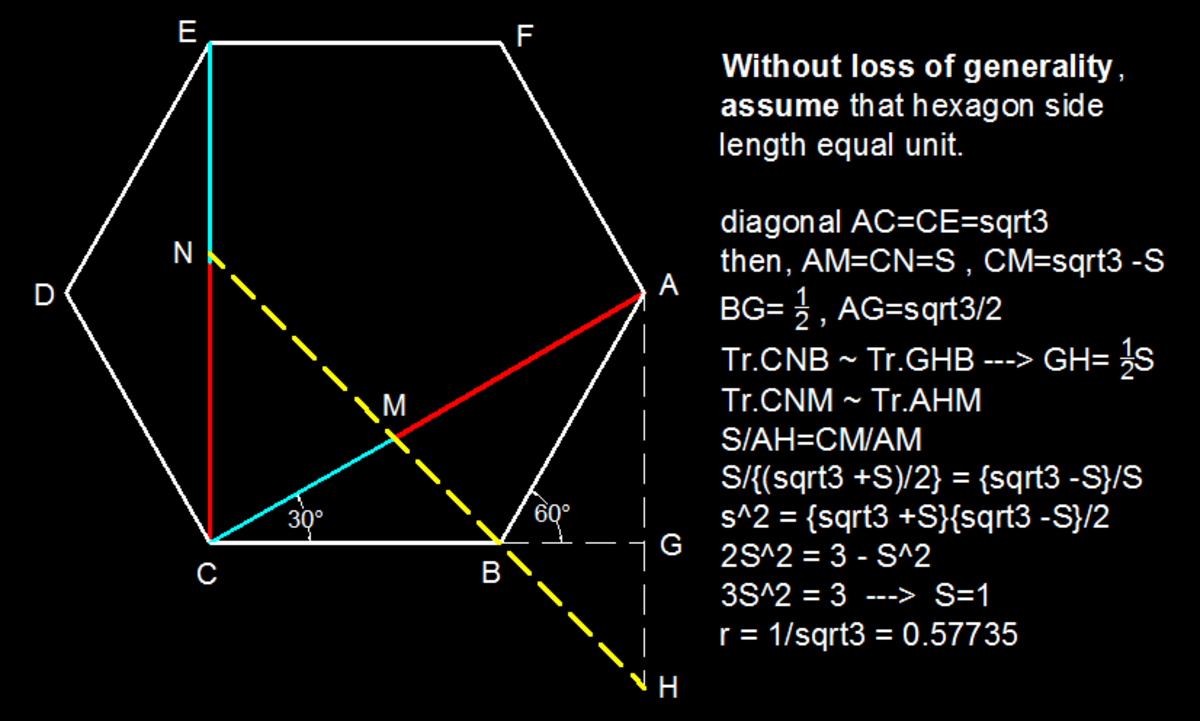
Suppose X is the intersection of A C and B E . X is the mid-point of A C .
Since B , M , and N are collinear, then by Menelaus Theorem ,
N E C N ⋅ B X E B ⋅ M C X M = 1 .
Suppose the side length of the hexagon is 1 . Then A C = C E = 3 .
N E C N = C E − C N C N = 1 − C E C N C E C N = 1 − r r
B X E B = 2 1 2 = 4
M C X M = A C − A M A M − A X = 1 − A C A M A C A M − A C A X = 1 − r r − 2 1
Substituting them into the first equation yields
1 − r r ⋅ 1 4 ⋅ 1 − r r − 2 1 = 1
3 r 2 = 1
Hence r = 3 3 ≈ 0 . 5 7