A geometry problem by Hosam Hajjir
A cube on a table has edge length 24. A plane intersects the cube's four vertical edges at points A, B, C, and D such that point A is a vertex of the cube, as shown. The heights of points B and C are shown to be 7 and 12, respectively.
Calculate the volume of the portion of the cube that lies underneath the cutting plane.
The answer is 3456.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
Let side length L be equal to 2 4 . Let point A be the origin.
Plane normal vector and plane equation:
N = ( 2 4 , 0 , 7 ) × ( 2 4 , 2 4 , 1 2 ) = ( − 1 6 8 , − 1 2 0 , 5 7 6 ) N x x + N y y + N z z = 0 z = − N z N x x − N z N y y = α x + β y
Volume under cutting plane:
V = ∫ 0 L ∫ 0 L z d x d y = ∫ 0 L ∫ 0 L ( α x + β y ) d x d y = 2 L 3 ( α + β ) = 3 4 5 6
@Hosam Hajjir the last sentence is a little misleading because the volume under the plane isn't a cube.
Log in to reply
Thanks for that. I've updated the problem in accordance with your remark.
The red solid is bounded by a plane ( π parallel to the base of the cube at a height 1 2 above it, and the cutting plane A B C D .
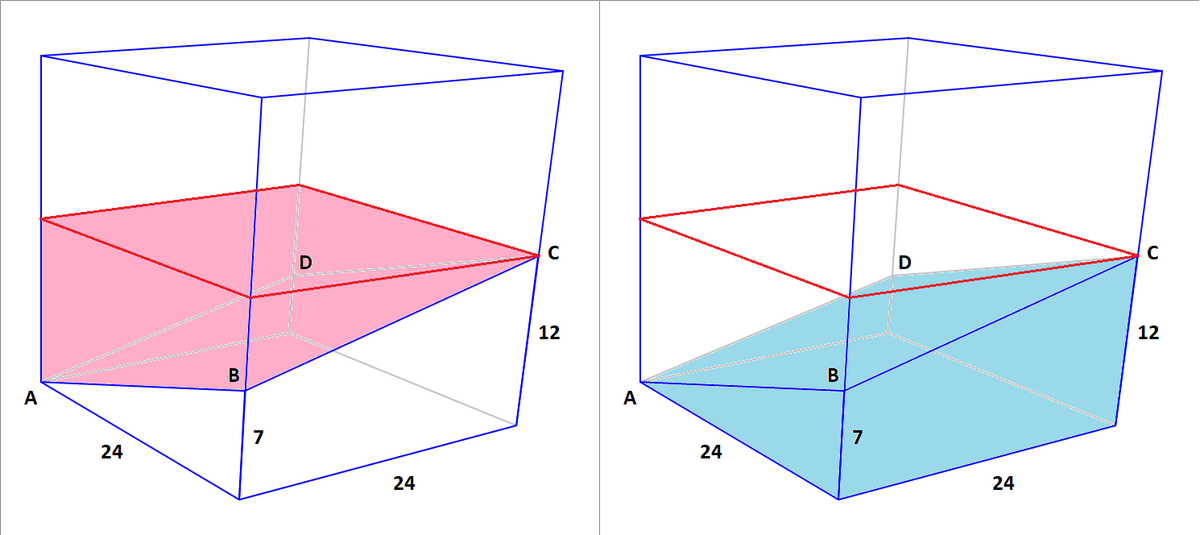
The volume of the blue solid is equal to the volume of the red solid; joined together they form a cuboid of dimensions 2 4 × 2 4 × 1 2 , so the answer is V = 2 2 4 ⋅ 2 4 ⋅ 1 2 = 3 4 5 6
To convince yourself that the volumes are the same, note that point D is at height 5 above the base of the cube. This can be proved by considering the equation of the plane A B C D , or just by noting that the lines A C and B D intersect at their midpoints at the centre of A B C D .
It follows that point A is 1 2 below π , point B is 5 below it, point C is on π , and point D is 7 below it - ie the red solid has exactly the same measures and angles as the blue solid, so they do indeed have the same volume. (They are mirror images of each other)
z = ax + by, origin at A. When x =24, y = 0, z = 7. When x = 24, y = 24, z =12, so a = 7/24, b = 5/24, V = integral from 0 to 24, integral from 0 to 24 of z= 7/24x + 5/24Y = 3456.
Since A B and C D are on opposite faces of the cube and on the same plane, they are parallel, and by the same argument so are A D and B C . Therefore, A B C D is a parallelogram.
The average height of the truncated cube would be the height at the centroid of this parallelogram, and since the centroid of a parallelogram is the midpoint of one of its diagonals, this height can be calculated by finding the average of the heights at A and C , which is 2 0 + 1 2 = 6 .
Therefore, the volume of the truncated cube is V = 2 4 ⋅ 2 4 ⋅ 6 = 3 4 5 6 .