A line segment from a vertex to the opposite side
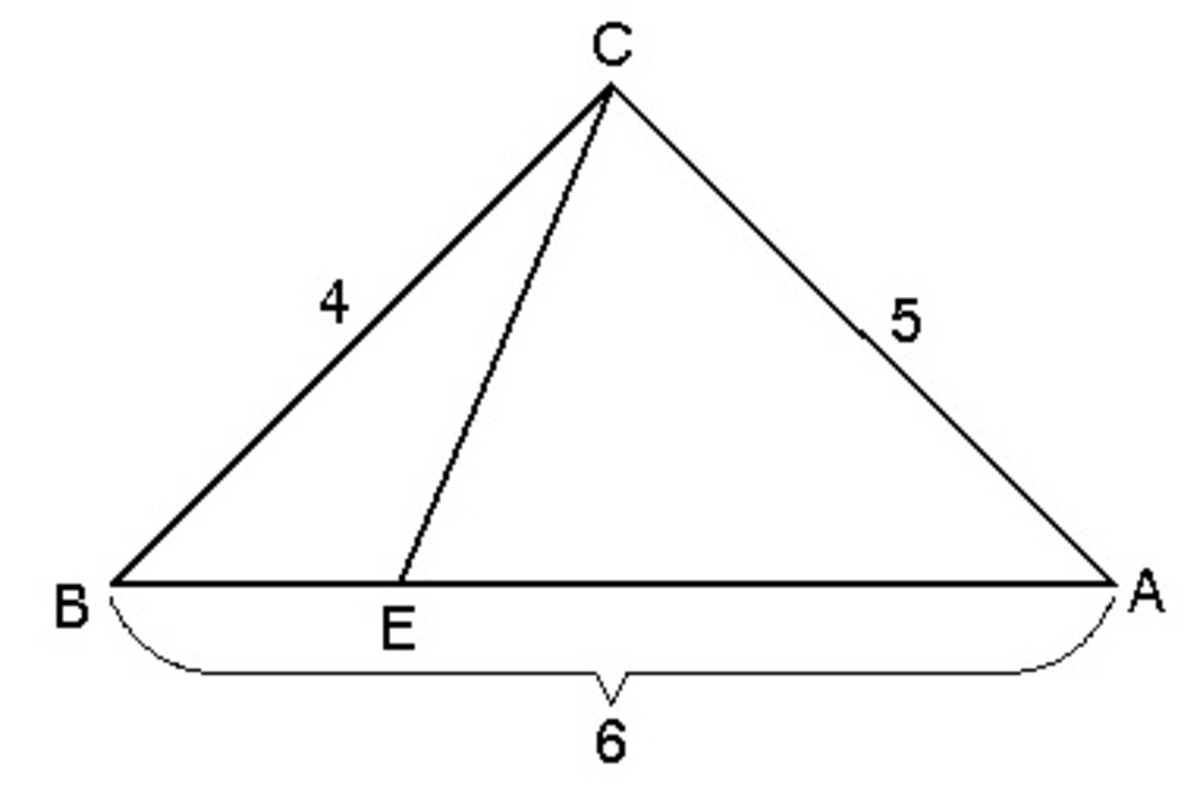 In the triangle shown above, if
C
B
=
4
,
C
A
=
5
,
B
A
=
6
, and
B
E
=
2
1
E
A
, find
C
E
.
In the triangle shown above, if
C
B
=
4
,
C
A
=
5
,
B
A
=
6
, and
B
E
=
2
1
E
A
, find
C
E
.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
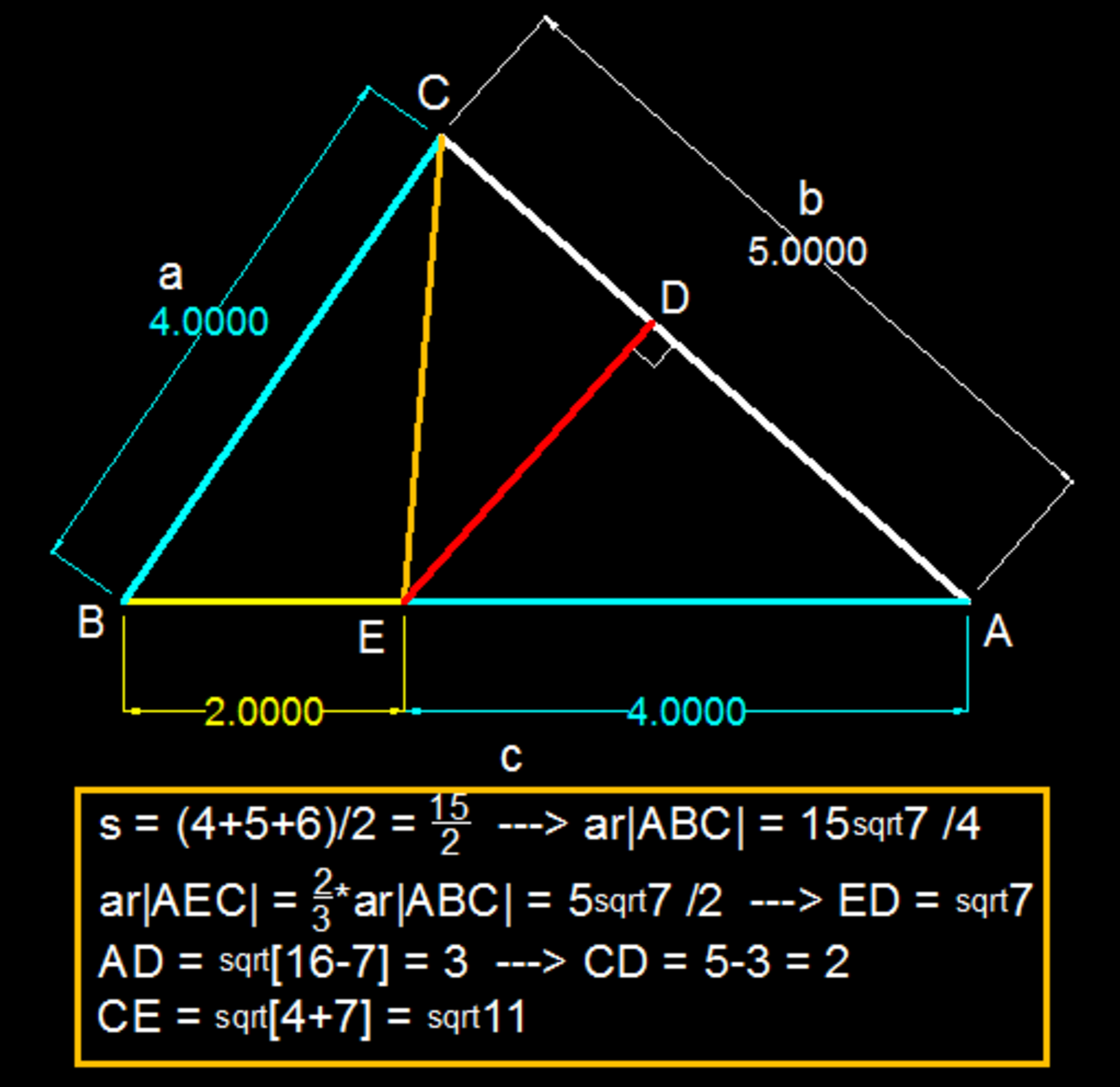
4 solutions
Apply Law of Cosines twice
5^2 = 4^2 + 6^2 - 2 X 4 X 6 X cos B
cos B = 0.5625
BE + EA = 6 : 1.5 EA = 6 : EA = 4 so BE = 2
CE^2 =4^2 + 2^2 - 2 X 4 X 2 X cosB = 11
CE = sqrt(11)
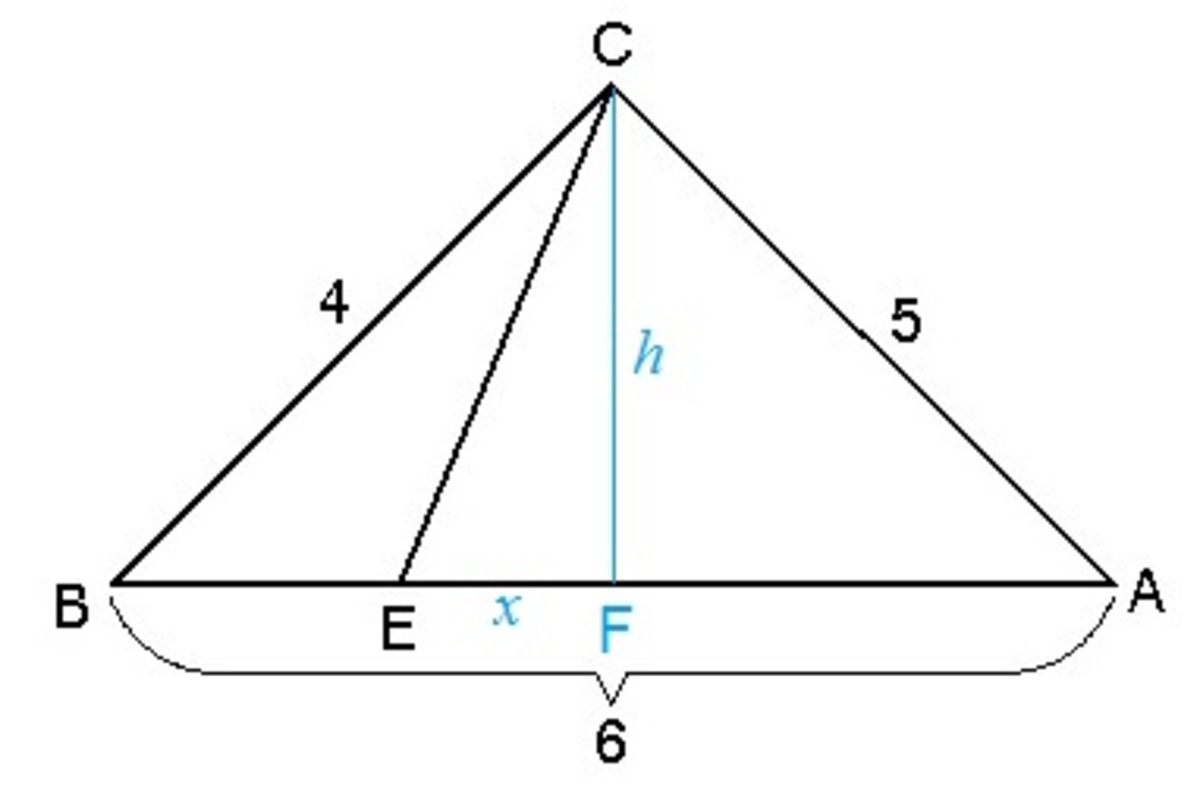
Using Heron's formula ,the area of △ A B C is given by:
[ A B C ] = s ( s − a ) ( s − b ) ( s − c ) = 2 1 5 ( 2 1 5 − 4 ) ( 2 1 5 − 5 ) ( 2 1 5 − 6 ) = 2 1 5 ( 2 7 ) ( 2 5 ) ( 2 3 ) = 4 1 5 7 where s = 2 a + b + c + d
Let C F the altitude from C to A B and its length h and E F = x . Then, we have:
2 1 × A B × C F 2 6 h ⟹ h = [ A B C ] = 4 1 5 7 = 4 5 7
By Pythagorean theorem , we have:
B F 2 ( x + 2 ) 2 ⟹ x = B C 2 − C F 2 = 4 2 − ( 4 5 7 ) 2 = 1 6 8 1 = 4 1 Note that B E = 2 E A = 3 A B = 2
By Pythagorean theorem, we have:
C E 2 ⟹ C E = C F 2 + E F 2 = ( 4 1 5 7 ) 2 + ( 4 1 ) 2 = 1 1 = 1 1
Relevant wiki: Stewart's Theorem