Circle With Triangle
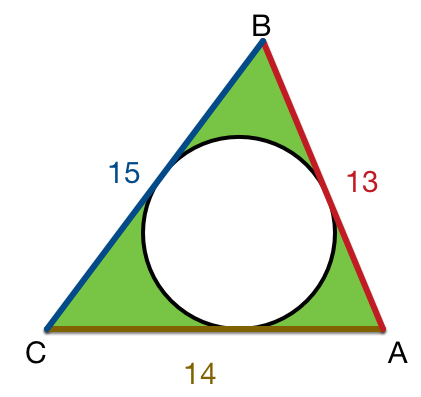
In the figure above triangle A B C with side-lengths A C = 1 4 , A B = 1 3 and B C = 1 5 . The incircle is drawn, which is tangential to all three sides. If the green shaded region is equal to A , find ⌊ A ⌋ .
The answer is 33.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
The area of the green region is equal to the area of the triangle minus the area of the circle. The radius of the inscribed circle can be computed as r = P 2 A where A and P are the area and perimeter of the triangle, respectively. The area of the triangle can be computed using the Heron's Formula. We have
s = 2 a + b + c = 2 1 3 + 1 4 + 1 5 = 2 1
A = s ( s − a ) ( s − b ) ( s − c ) ( s − d ) = 2 1 ( 2 1 − 1 3 ) ( 2 1 − 1 4 ) ( 2 1 − 1 5 ) = 8 4
P = a + b + c = 1 3 + 1 4 + 1 5 = 4 2
So the radius of the inscribed circle is
r = 4 2 2 ( 8 4 ) = 4
Finally, the area of the green region is
A G R E E N = 8 4 − π ( 4 2 ) ≈ 3 3
The question tells us we want to find the area of the shaded region, which is equal to the area of the triangle A B C minus the area of the circle with center O which inscribed the circle. To do so, we need the following information:
( i ) The area of the circle with centre O ,
( ii ) The area of the triangle A B C .
To find ( i ), we need to know the diameter or radius of this circle. However since this circle is inscribed inside the triangle A B C and there is no other information besides that, let us first find ( ii ).
Recall the identity,
Area of triangle = r × semiperimeter of triangle ( 1 )
Where r denotes the inradius of the triangle A B C . In this case, it's the circle with centre O .
Since we are given all the three sides of the triangle already ( A C = 1 4 , A B = 1 3 , B C = 1 5 ), then Heron's formula comes to mind.
( Area of triangle ) 2 = s ( s − a ) ( s − b ) ( s − c )
Where a , b and c denotes the sides of the triangle A B C and s denotes its semiperimeter (half of the perimeter), s = 2 a + b + c = 2 1 3 + 1 4 + 1 5 = 2 1 . And so,
( Area of triangle ) 2 = 2 1 ( 2 1 − 1 3 ) ( 2 1 − 1 4 ) ( 2 1 − 1 5 ) ⇒ Area of triangle = 8 4
(Note that we only take positive value only because it represents an area)
Substituting into the identity, ( 1 ) gives us 8 4 = r × 2 1 ⇒ r = 4 .
To summarize, we managed to calculate:
( i ) The area of the circle with centre O to be π r 2 = 1 6 π ,
( ii ) The area of the triangle A B C to be 8 4 .
Hence the area, A is equal to 8 4 − 1 6 π ≈ 3 3 . 7 3 , and so ⌊ A ⌋ = 3 3 .