A geometry problem by Swapnil Nikam
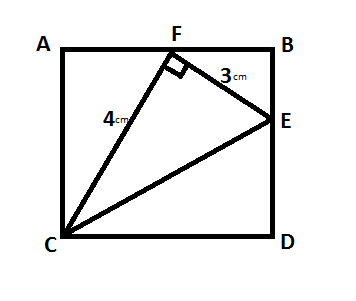 In the given figure ABDC is a square and ΔCFE is right angled triangle with sides CF=4cm and FE=3cm.
Find area of square ABDC.
In the given figure ABDC is a square and ΔCFE is right angled triangle with sides CF=4cm and FE=3cm.
Find area of square ABDC.
The answer is 15.06.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
how the two triangles are similar can u please tell?
Log in to reply
Note that ∠ C F A = 9 0 − ∠ E F B , since ∠ C F E = 9 0 degrees.
But this means that ∠ F E B = ∠ C F A and ∠ A C F = ∠ E F B . Thus the two right-angled triangles C A F and F B E are similar.
L e t ∠ A C F = ∠ E F B = θ G i v e n A C = A F + F B 4 c o s θ = 4 s i n θ + 3 c o s θ θ = t a n − 1 ( 1 / 4 ) = 1 4 . 0 3 6 N o w A C = 4 c o s θ = 4 c o s ( 1 4 . 0 3 6 ) = 3 . 8 8 0 5 H e n c e A r e a = A C x A C = 3 . 8 8 0 5 2 = 1 5 . 0 5
This problem is solved using Pitagoras theorem all over the place and a system of equations.
First we obtain the hypotenuse of the inner triangle
4 2 + 3 2 = 2 5 , so CE=5
If we name the segments
a = AF b = FB c = BE d = ED
and if we name any of the square sides 's'
We have the following 5 equations (for those 5 variables)
- s=a+b
- s=c+d
- s 2 + d 2 = 2 5
- s 2 + a 2 = 1 6
- b 2 + c 2 = 9
This equation system will yield 4 possible sets of solutions, we'll discard those with negative values and when we pick the one in which all variables are positive (because these are segments of a square and a triangle and they can't possibly be negative)
the value of s for that set is s = 1 6 / 1 7
s 2 = 1 5 . 0 5 8
Let A C = y and A F = x . We are then wanting to find the value of y 2 . Now, since triangles C A F and F B E are similar right-angled triangles, we have that
(i) x 2 + y 2 = 1 6 , and
(ii) y 4 = y − x 3 ⟹ 4 ( y − x ) = 3 y ⟹ x = 4 y .
Substituting this last result into equation (i) yields
( 4 y ) 2 + y 2 = 1 6 ⟹ y 2 = 1 7 1 6 2 = 1 5 . 0 6 to 2 decimal places.