A geometry problem by Yan Yau Cheng
In △ A B C , A B = 1 0 and A C = 1 2 , D is a point on line B C such that line A D bisects ∠ B A C , The ratio C D B D can be expressed as q p , where p and q are positive co-prime integers, find the value of p + q
The answer is 11.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
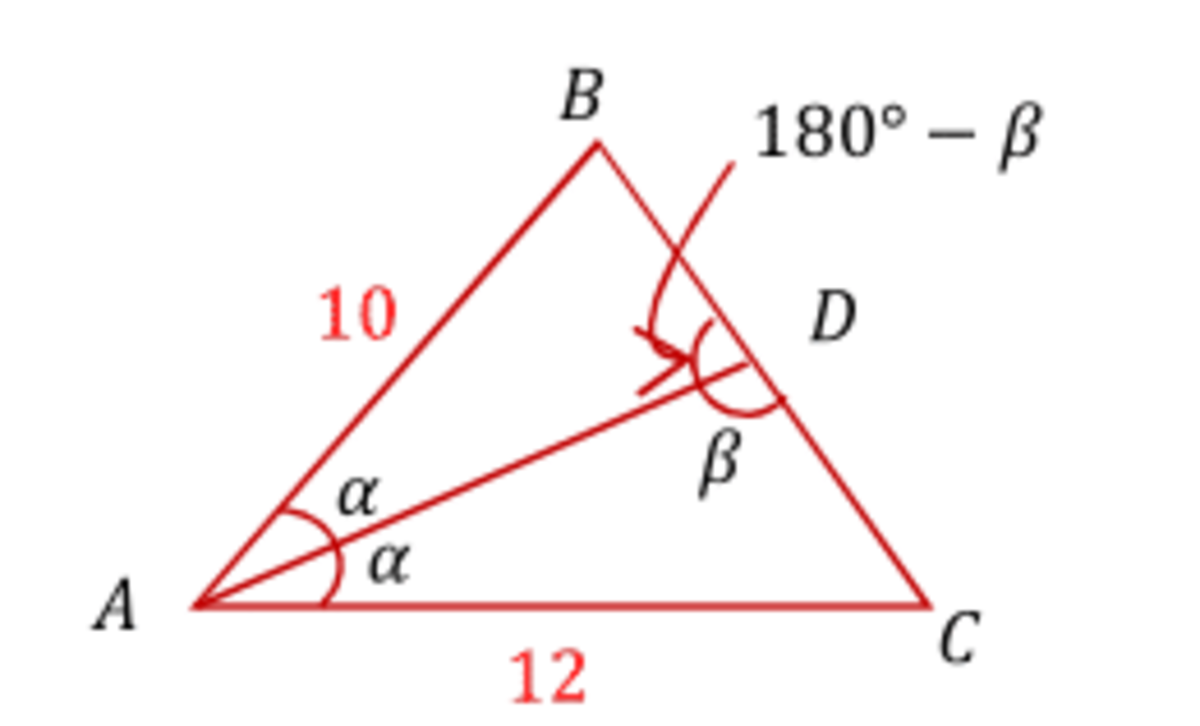 From law of sines in triangle ACD:
sin
α
C
D
=
sin
β
1
2
From law of sines in triangle ACD:
sin
α
C
D
=
sin
β
1
2
Therefore 1 2 C D = sin β sin α
Likewise in triangle ABD: sin α B D = sin ( 1 8 0 ∘ − β ) 1 0 = sin β 1 0
Therefore 1 0 B D = sin β sin α
Putting the two results together: 1 2 C D = 1 0 B D
So that: B D C D = 1 0 1 2 = 5 6
And the answer is 6 + 5 = 1 1
use properties of similarities of triangles
use the angle angle bisector theorem, which according to this question would be-
A C A B = C D B D
⟹ 1 2 1 0 = q p or 6 5 = q p
so, p + q = 1 1