A Pentagon Problem.
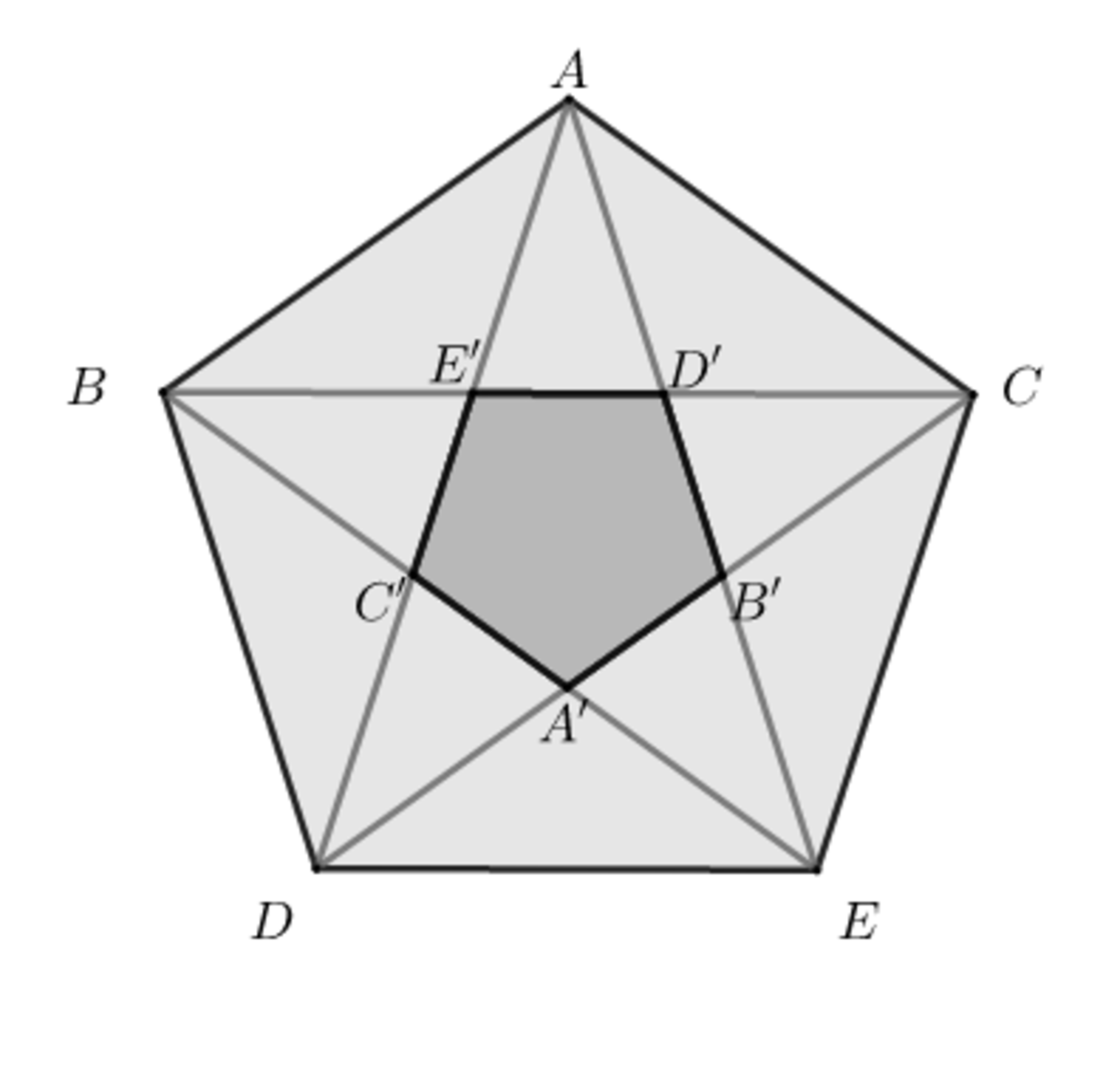
A B C D E is a regular pentagon . A ′ B ′ C ′ D ′ E ′ is the pentagon inscribed in A B C D E 's diagonals.
Find similarity ratio of A B C D E to A ′ B ′ C ′ D ′ E ′ .
The answer is 2.618.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
5 solutions
Let ∣ D E ∣ = a and ∣ A ′ D ∣ = b then ∣ A ′ E ∣ = ∣ B ′ E ∣ = b
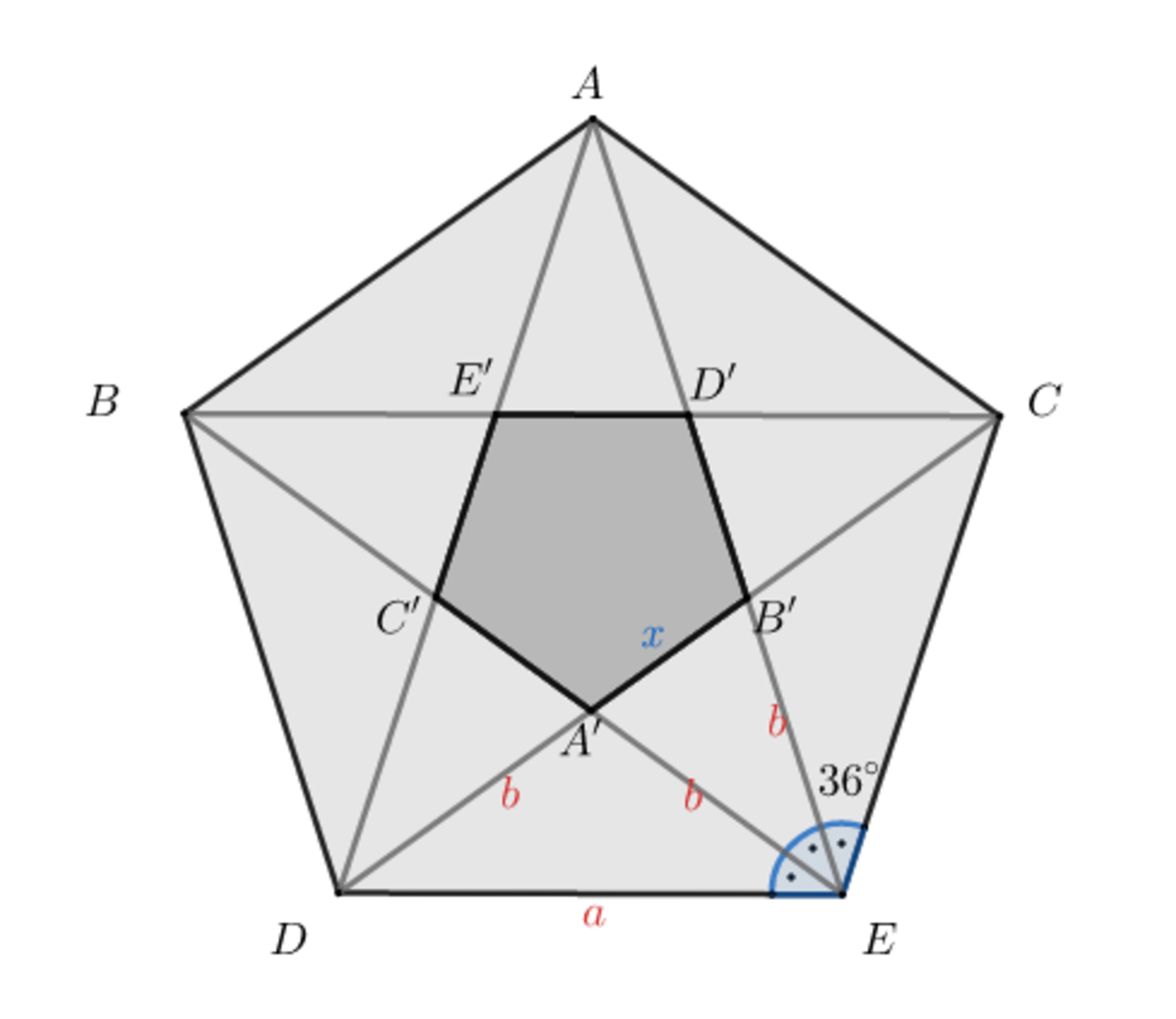
[ A ′ E ] is bisector of ∠ D E B ′ hence b ⋅ b = a ⋅ x ⇒ x = a b 2
If we apply Law of Cosines on △ A ′ B ′ E
( a b 2 ) 2 = 2 ⋅ b 2 − 2 ⋅ b 2 ⋅ c o s 3 6 ° , b 2 s simplifies : a 2 b 2 = 2 − 2 c o s 3 6 °
We want to find similarity ratio that is equal to x a and we know x = a b 2 ,so x a = a b 2 a = b 2 a 2
We got : a 2 b 2 = 2 − 2 c o s 3 6 ° ⇒ b 2 a 2 = 2 − 2 c o s 3 6 ° 1 ≈ 2 . 6 1 8
Let small pentagon side be =1, use bisecting theorem twice to get larger pentagon side =a by following two triangle bisecting Eqs:
x(2x+1)=a(1+x) and a=x^2
a=(1/4)(1+5^0.5)^2
Answer is a= 2.61803
A B = x
E ′ D ′ = y
∠ C ′ E ′ D ′ = 1 0 8 ° (Angles in a regular pentagon.)
∠ B E ′ A = 1 0 8 ° (Opposite angles.)
∠ A E ′ D ′ = ( 3 6 0 − 2 ∗ 1 0 8 ) / 2 = 7 2 ° (Angles in a circle sum to 360.)
∠ E ′ A D ′ = 1 8 0 − 2 ∗ 7 2 = 3 6 ° (Angles in an isosceles triangle.)
Using the law of sines:
sin 1 0 8 ° x = sin 3 6 ° A E ′
A E ′ = sin 1 0 8 ° x ∗ sin 3 6 °
sin 7 2 ° A E ′ = sin 3 6 ° y
y = sin 7 2 ° A E ′ ∗ sin 3 6 °
Ratio = y x
= sin 7 2 ° sin 1 0 8 ° x ∗ sin 3 6 ° ∗ sin 3 6 ° x
= 0 . 9 5 1 1 0 . 9 5 1 1 x ∗ 0 . 5 8 7 8 ∗ 0 . 5 8 7 8 x
= 0 . 9 5 1 0 . 3 6 3 3 x x
= 0 . 3 8 2 x x
= 1 / 0 . 3 8 2 ≈ 2 . 6 1 8
Let A E ′ = 1 . Then by symmetry, B E ′ = B C ′ = A E ′ = 1 . ∠ B A E ′ = ∠ A B E ′ = 2 1 8 0 ° − 1 0 8 ° = 3 6 ° A B = A E ′ c o s ( 3 6 ° ) + B E ′ c o s ( 3 6 ° ) = 2 c o s ( 3 6 ° ) = 2 s i n ( 5 4 ° ) ⋯ Eq. 1 ∠ C ′ B E ′ = 1 0 8 ° − 3 6 ° − 3 6 ° = 3 6 ° E ′ C ′ = 2 B E ′ s i n ( 1 8 ° ) = 2 s i n ( 1 8 ° ) ⋯ Eq. 2 E ′ C ′ A B = 2 s i n ( 1 8 ° ) 2 s i n ( 5 4 ° ) = s i n ( 1 8 ° ) 3 s i n ( 1 8 ° ) − 4 s i n 3 ( 1 8 ° ) = 3 − 4 s i n 2 ( 1 8 ° ) = 3 − 4 ( 4 5 − 1 ) 2 = 2 3 + 5 = 2 . 6 1 8
Let the side of the small pentagon be 1 and the side of the large pentagon be x . The similarity ratio will then be x .
Since B D ′ = A B = x and E ′ D ′ = 1 , B E ′ = x − 1 . By symmetry, A E ′ = A D ′ = B E ′ = x − 1 .
Since △ A D ′ E ′ ∼ △ B A D ′ , E ′ D ′ A D ′ = A D ′ B A or 1 x − 1 = x − 1 x . This rearranges to x 2 − 3 x + 1 = 0 , which has a solution of x = 2 3 + 5 ≈ 2 . 6 1 8 for x > 1 .
Bonus: The answer is also x = ϕ 2 , where ϕ = 2 1 + 5 , the golden ratio.