A Question of Area
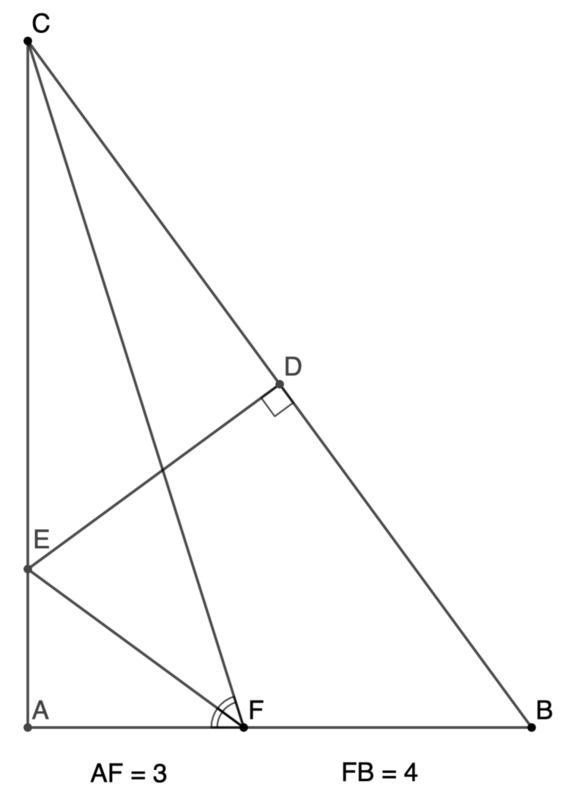
In △ A B C , E D is the perpendicular bisector of C B and E F bisects ∠ A F C . A F and F B have lengths 3 and 4 respectively. Express the area of △ A B C as c a b , where a , b , and c are positive integers and b is square-free, and submit a + b + c .
The answer is 100.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Plot this figure on the Cartesian plane with coordinates A ( 0 , 0 ) , F ( 3 , 0 ) , B ( 7 , 0 ) , E ( 0 , k ) , C ( 0 , h ) , where h > k > 0 .
Since E D is the perpendicular bisector of C B , then D ( 2 7 , 2 h ) .
The equation of the straight line C B is 7 x + h y = 1 ⇔ y = − 7 h x + h . So its gradient m C B = − 7 h .
Also the gradient of the straight line E D is m E D = 0 − 2 7 k − 2 h = 7 h − 2 k .
Since E D and C B are perpendicular to each other, m E D ⋅ m C B = − 1 , or 7 h − 2 k = h 7 ( 1 )
And because E F bisects ∡ A F C , ∡ C F B tan − 1 3 h 3 h h = = = = ∡ E F A 2 ⋅ tan − 1 3 k tan [ 2 ⋅ tan − 1 3 k ] = 9 − k 2 6 k 9 − k 2 1 8 k
Substitute h into ( 1 ) and solve the equation yields ( h , k ) = ( ± 7 , ∓ 3 7 ) , ( ± 9 1 , ∓ 1 3 6 3 ) .
But since h > k > 0 , then the only solution is ( h , k ) = ( 9 1 , 1 3 6 3 ) .
Therefore, the area of the triangle A B C is 2 1 ⋅ 7 ⋅ h = 2 7 9 1 . The answer is 7 + 9 1 + 2 = 1 0 0 .
Let's find an algebraic expression for the area. If A F = x and F B = y , then the following program suggests that
△ A B C = 2 ( x + y ) 3 x 2 + 4 x y + y 2 = 2 7 9 1 ⟹ 7 + 9 1 + 2 = 1 0 0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
|
1 2 |
|
We note that △ B D E and △ C D E are congruence. Hence B E = C E . Let ∠ E F A = ∠ C F E = θ and t = tan θ . Then A E = 3 tan θ = 3 t and A C = 3 tan 2 θ = 1 − t 2 6 t . By Pythagorean theorem ,
B E 2 ⟹ B E A C − A E 1 − t 2 6 t − 3 t 1 − t 2 3 t ( 1 + t 2 ) 3 t ( 1 + t 2 ) 9 t 6 + 1 8 t 4 + 9 t 2 1 3 t 4 − 9 8 t 2 + 4 9 ( t 2 − 7 ) ( 1 3 t 2 − 7 ) t ⟹ t = A E 2 + A B 2 = ( 3 t ) 2 + 7 2 = 9 t 2 + 4 9 = 9 t 2 + 4 9 = 9 t 2 + 4 9 = 9 t 2 + 4 9 = 9 t 2 + 4 9 = ( 1 − t 2 ) 9 t 2 + 4 9 = 9 t 6 + 3 1 t 4 − 8 9 t 2 + 4 9 = 0 = 0 = ± 7 , ± 1 3 7 = 1 3 7 Since B E = C E = A C − A E Squaring both sides Since θ < 4 5 ∘
The area of △ A B C , [ A B C ] = 2 1 A B ⋅ A C = 2 1 ⋅ 7 ⋅ 1 − t 2 6 t = 1 − 1 3 7 2 1 1 3 7 = 2 7 9 1 . Therefore a + b + c = 7 + 9 1 + 2 = 1 0 0 .