A simple circuit and its modified version
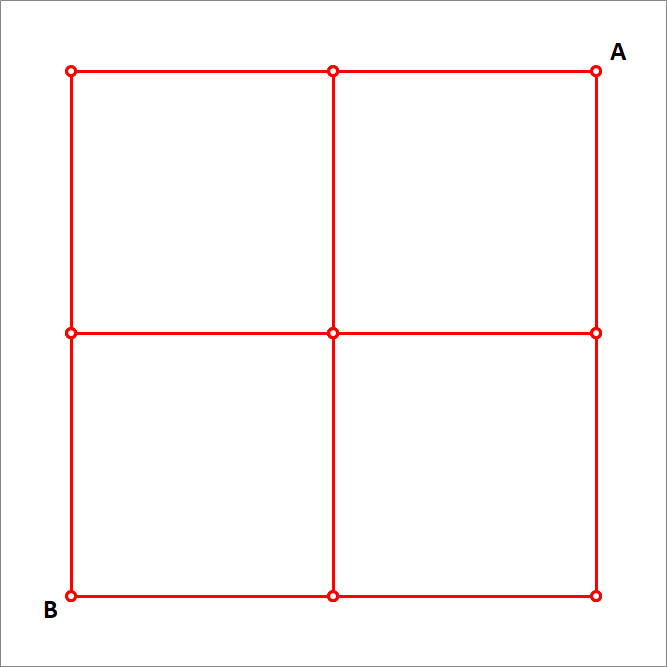
A grid of conducting wires is as shown in the above figure. Each wire segment (between any two nodes) has a resistance of . Find , the equivalent resistance between points and . Next, one of the wires is removed as shown below,
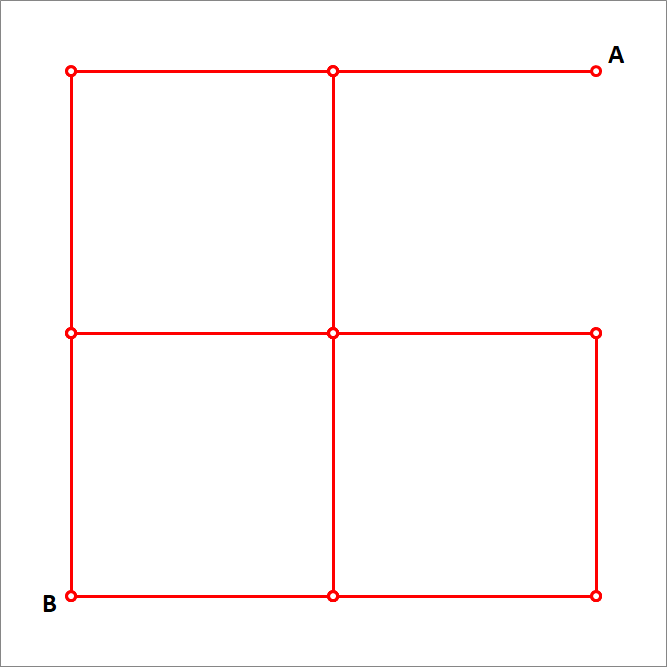
Find , the equivalent resistance between points and for the modified circuit. Calculate the difference, . If this value can be written as , where and are relatively prime positive integers, then find the value of .
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
The 2 × 2 grid circuit is symmetrical between points A and B . Due to this symmetry, the voltages at C and C ′ are the same, those of D , D ′ , and D " , those of E and E ′ are also the same. Therefore, they can be consider as single points of C , D , and E and the equivalent circuit as is on the right. (For convenience, I have use thick red lines to denote resistance and thin black lines as conductors.). Then we have:
R 1 = 1 ∣ ∣ 1 + 1 ∣ ∣ 1 ∣ ∣ 1 ∣ ∣ 1 + 1 ∣ ∣ 1 ∣ ∣ 1 ∣ ∣ 1 + 1 ∣ ∣ 1 = 2 1 + 4 1 + 4 1 + 2 1 = 2 3 Ω
With resistance R A C ′ remove, the circuit can be simplified as the circuit in the middle with R C E = 1 + 1 = 2 Ω and R D E ′ = 1 ∣ ∣ 3 = 1 + 3 1 × 3 = 4 3 Ω . Converting the delta circuit △ C D E into star circuit R C 1 = R C 2 = 2 + 1 + 1 2 × 1 = 2 1 Ω and R C 3 = 2 + 1 + 1 1 × 1 = 4 1 Ω and we get the equivalent circuit on the right.
Then we have
R 2 = 1 + 2 1 + ( 2 1 + 1 ) ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ( 4 1 + 4 3 + 1 ) = 2 3 + 2 3 ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ 2 = 2 3 + 2 3 + 2 2 3 × 2 = 2 3 + 7 6 = 1 4 3 3
Therefore R 2 − R 1 = 1 4 3 3 − 2 3 = 7 6 ⟹ a + b = 6 + 7 = 1 3 .