A Special Square
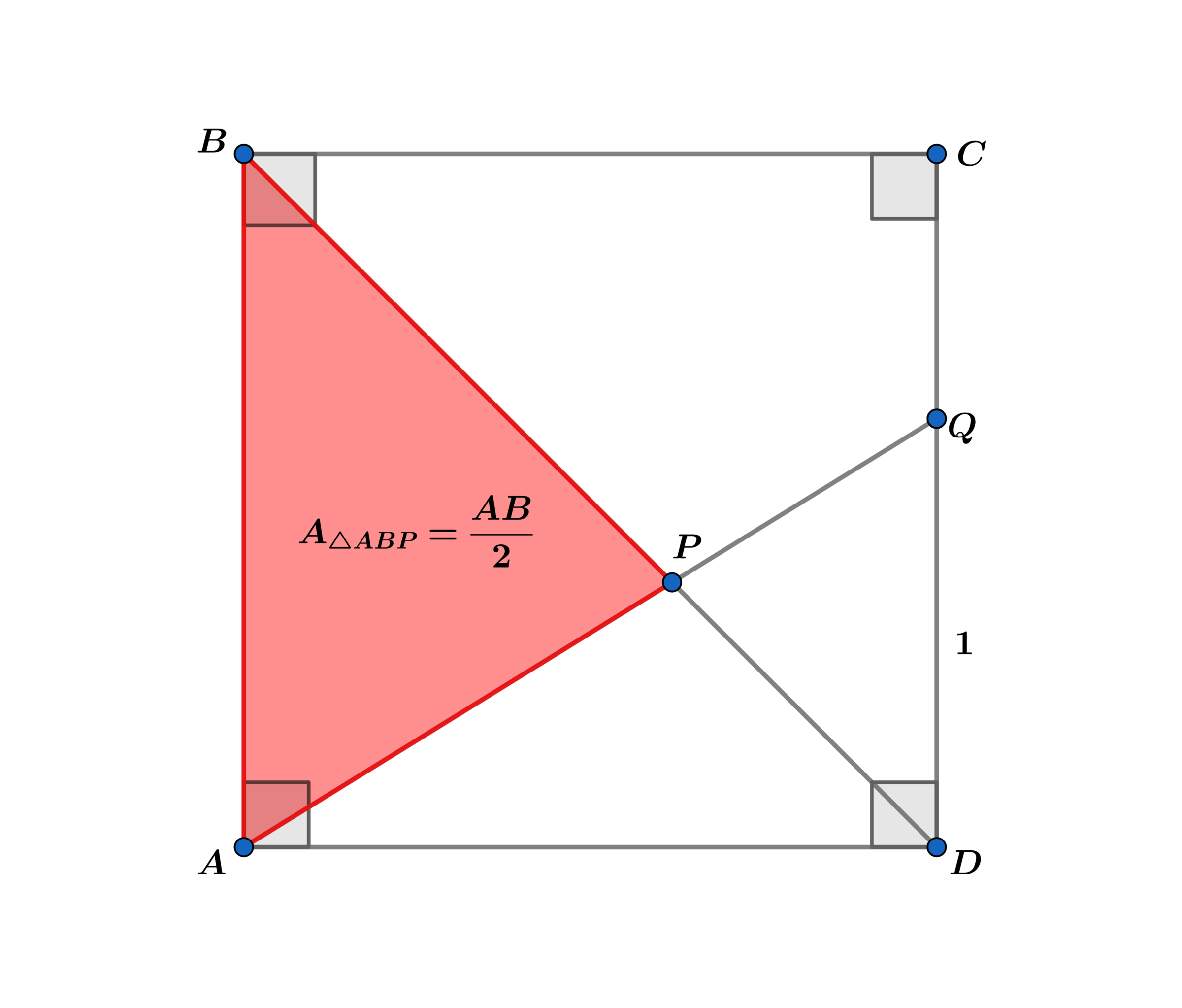
In square A B C D , B D and A Q intersect at P with Q D = 1 and the area A △ A B P = 2 A B .
Find the side of the above square.
The answer is 1.61803.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
I provided two solutions:
Solution using coordinate geometry:
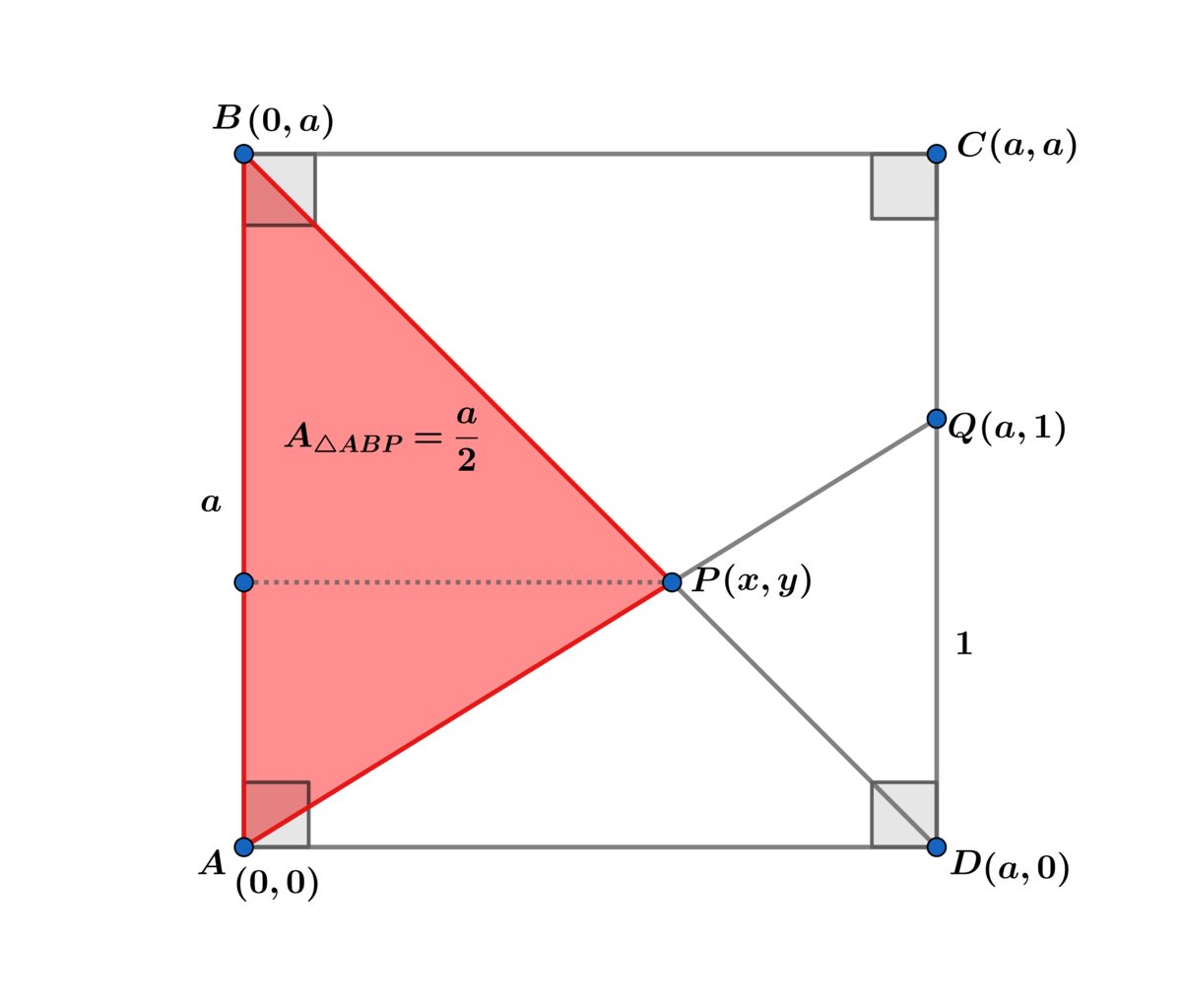
For B D : y = a − x and for A Q : y = a 1 x ⟹ x = a + 1 a 2 ⟹
A △ A B P = 2 ( a + 1 ) a 3 = 2 a ⟹ a ( a 2 − a − 1 ) = 0 a > 0 ⟹
a = 2 1 + 5 ≈ 1 . 6 1 8 0 3 .
Solution using similar triangles:
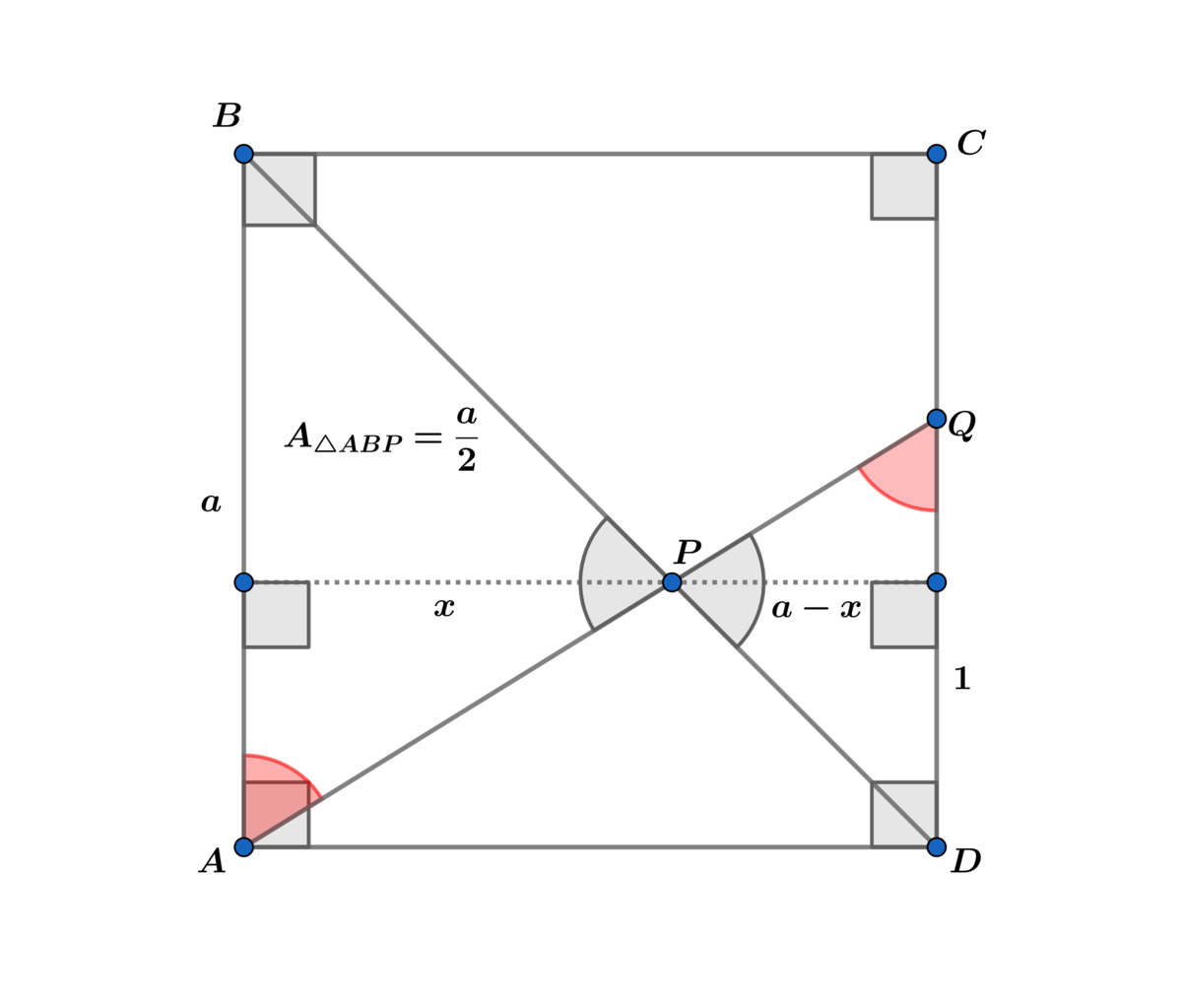
Since vertical angles are congruent and A B ∥ C D ⟹ alternate interior angles are congruent ⟹ △ A B P ∼ △ D P Q ⟹
1 a = a − x x ⟹ x = a + 1 a 2 ⟹ A △ A B P = 2 ( a + 1 ) a 3 = 2 a
⟹ a ( a 2 − a − 1 ) = 0 a > 0 ⟹ a = 2 1 + 5 ≈ 1 . 6 1 8 0 3 .
A △ A B D 2 a 2 a 3 a 3 − 2 a 2 + 1 ( a − 1 ) ( a 2 − a − 1 ) ⟹ a A △ A B P + A △ A D P = 2 a + 2 a − 2 a 1 = 2 a 2 − 1 = 0 = 0 = 2 1 + 5 ≈ 1 . 6 1 8 Multiply both sides by 2 a Since a > 1 φ , the golden ratio.