A spherical area bounded by three curves
Taking the unit sphere in the first octant, we define three curves parallel to the x y , x z and y z planes, parametrically, as follows:
p 1 ( t ) = ( sin θ 0 cos t , sin θ 0 sin t , cos θ 0 ) , 0 ≤ t ≤ 2 π
p 2 ( s ) = ( sin θ 0 cos s , cos θ 0 , sin θ 0 sin s ) , 0 ≤ s ≤ 2 π
p 3 ( r ) = ( cos θ 0 , sin θ 0 cos r , sin θ 0 sin r ) , 0 ≤ r ≤ 2 π
If θ 0 = 0 . 8 4 Radians, then find the area bounded by the three curves of the surface on the sphere, (shaded in yellow)
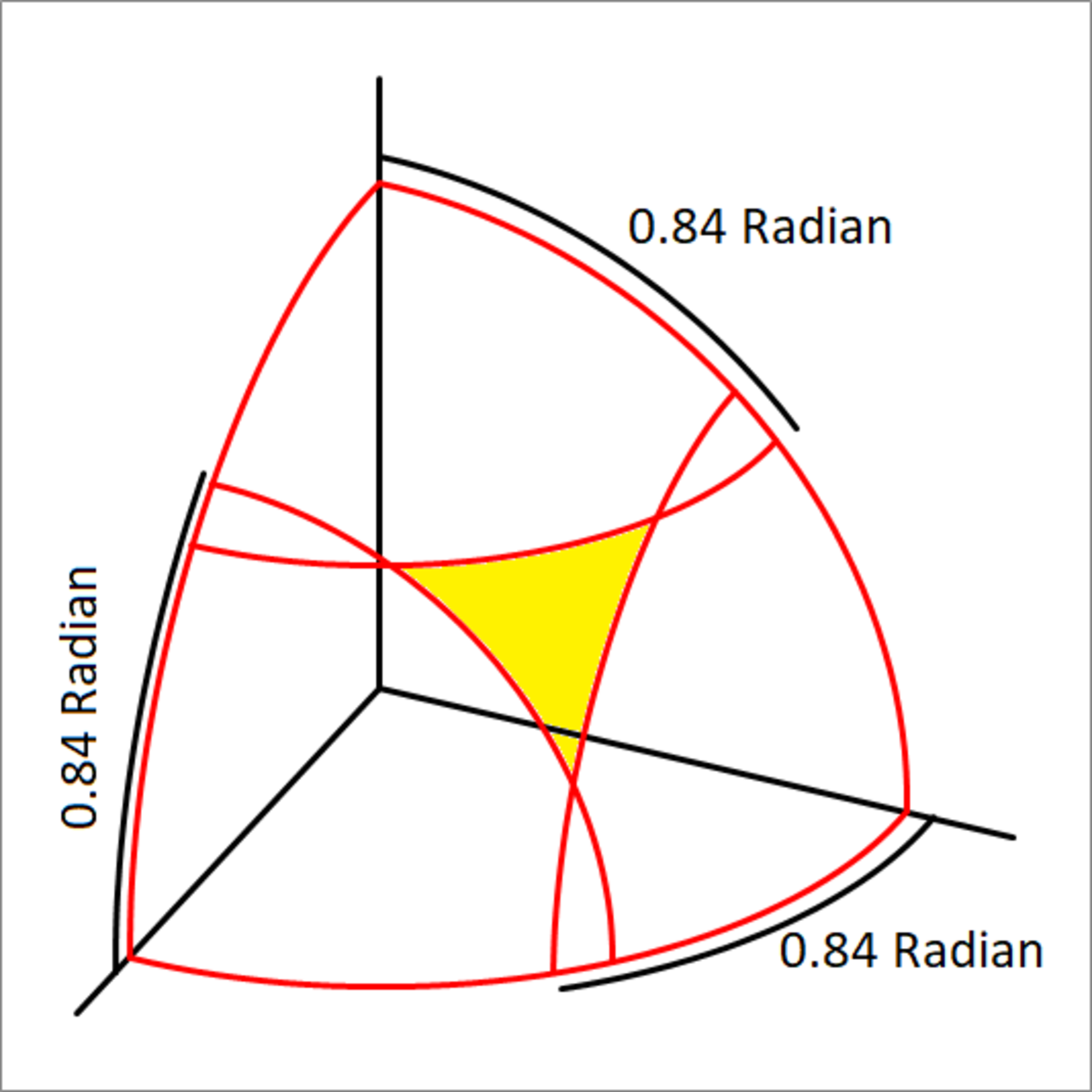
The answer is 0.07746.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
We're going to consider the area shaded in light blue in the figure above. It is 6 1 of the required
area (from symmetry). To compute its area we'll define the green arc as the great arc (center at the origin) and characterised by y = z, and the blue arc as the great arc (center at the origin) characterised by x = y.
Blue Area = ∫ ϕ = 4 π ϕ 1 ∫ θ = θ 0 θ 1 sin θ d θ d ϕ
where ϕ 1 is characterised by sin θ 0 sin ϕ 1 = cos θ 0
Therefore, ϕ 1 = sin − 1 ( cot θ 0 )
And sin θ 1 sin ϕ = cos θ 1 , thus θ 1 = tan − 1 ( sin ϕ 1 )
After integration with respect to θ , the above integral becomes,
Blue Area = ∫ ϕ = 4 π ϕ 1 ( cos θ 0 − cos θ 1 ) d ϕ
Since tan θ 1 = sin ϕ 1 then cos θ 1 = 1 + sin 2 ϕ sin ϕ
Hence, the integral becomes,
Blue Area = cos θ 0 ( ϕ 1 − 4 π ) − ∫ ϕ = 4 π ϕ 1 1 + sin 2 ϕ sin ϕ d ϕ
Substituting sin 2 ϕ = 1 − cos 2 ϕ , the integral becomes,
Blue Area = cos θ 0 ( ϕ 1 − 4 π ) − ∫ ϕ = 4 π ϕ 1 2 − cos 2 ϕ sin ϕ d ϕ
Blue Area = cos θ 0 ( ϕ 1 − 4 π ) − ∫ ϕ = 4 π ϕ 1 2 1 − ( cos ϕ / 2 ) 2 sin ϕ d ϕ
Using the substituting u = 2 cos ϕ , the integral becomes
Blue Area = cos θ 0 ( ϕ 1 − 4 π ) + sin − 1 ( cos ϕ 1 / 2 ) − 6 π
Hence, finally, the required area is 6 times the above expression, and is given by
Area = 6 ( cos θ 0 ( ϕ 1 − 4 π ) + sin − 1 ( cos ϕ 1 / 2 ) − 6 π )