Aditya's challenges in Mechanics 2
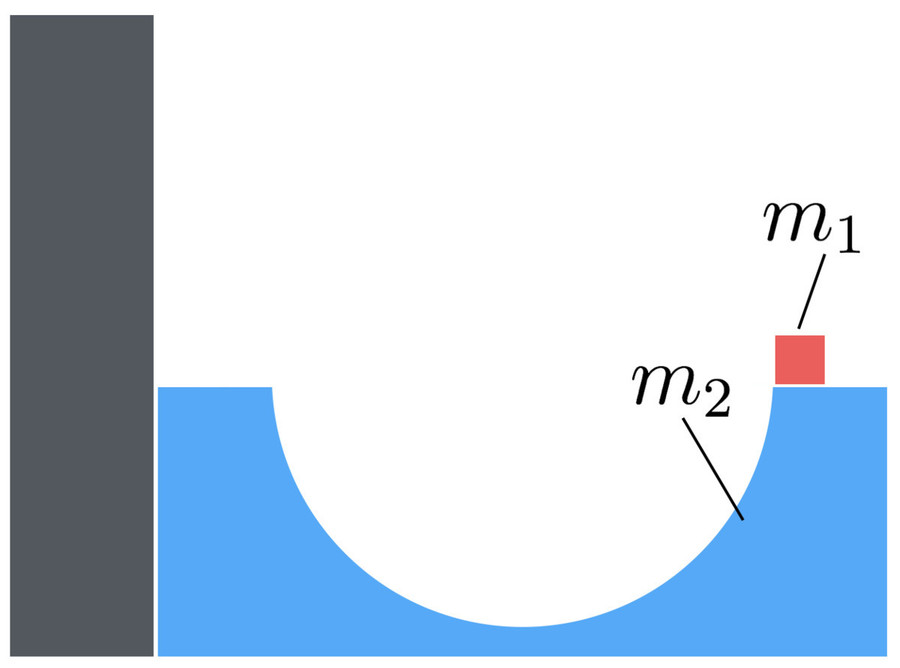
At time zero, the small block is given a slight push so as to slide down the semicircular region of radius . The big block is perfectly smooth and there is no friction with the ground. What is the maximum velocity obtained by the small block during this process?
Details and Assumptions
- , , , .
- The big block is not attached to the wall.
- For geometric purposes, consider the small block as a point particle.
Try more here .
The answer is 13.4164.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Since the only external forces acting on the two blocks are gravity and the normal reaction with the ground, the horizontal component of momentum is conserved. SInce the system is initially at rest, the horizontal component of the centre of mass of the system remains constant. As the small block moves down the surface, the large block will move away from the wall. When the small block reaches the lip of the semicircle, at the side nearest the wall, the system will be instantaneously at rest, and the same motion will repeat, but in the opposite direction, with the smaller block coming to rest at the lip of the semicircle, and the larger block coming to rest just touching the wall, as it was when it started. Thus the maximum speed of the small block on the return trip is the same as the maximum speed of the small block on the outward journey.
Suppose that x is the horizontal distance of the centre of the semicircle on the big block from the wall, and let θ be the angle that the small block makes with the downward vertical. Thus 9 x + ( x + 1 0 sin θ ) remains constant, and so x ˙ = − cos θ θ ˙ Conservation of energy tells us that 2 9 x ˙ 2 + 2 1 [ ( x ˙ + 1 0 cos θ θ ˙ ) 2 + 1 0 0 sin 2 θ θ ˙ 2 ] = 1 0 0 cos θ and hence, using the relationship between x ˙ and θ ˙ , we deduce that θ ˙ 2 = 9 + sin 2 θ 2 0 cos θ If V is the speed of the small block, then V 2 = ( x ˙ + 1 0 cos θ θ ˙ ) 2 + 1 0 0 sin 2 θ θ ˙ 2 = 9 + sin 2 θ 2 0 ( 8 1 + 1 9 sin 2 θ ) cos θ Thus V is maximized when θ = 0 , and so the maximum value of V is 6 5 = 1 3 . 4 1 6 4 .