Algebra 02
2 1 ( a + b α + c α 2 + d α 3 ) + 2 1 ( a + b β + c β 2 + d β 3 )
If α and β are roots to the equation 6 x 2 − 6 x + 1 = 0 , and the value of the expression above can be expressed as p a + q b + r c + s d for integers p , q , r and s , find the value of p ⋅ q r ⋅ s .
The answer is 6.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions

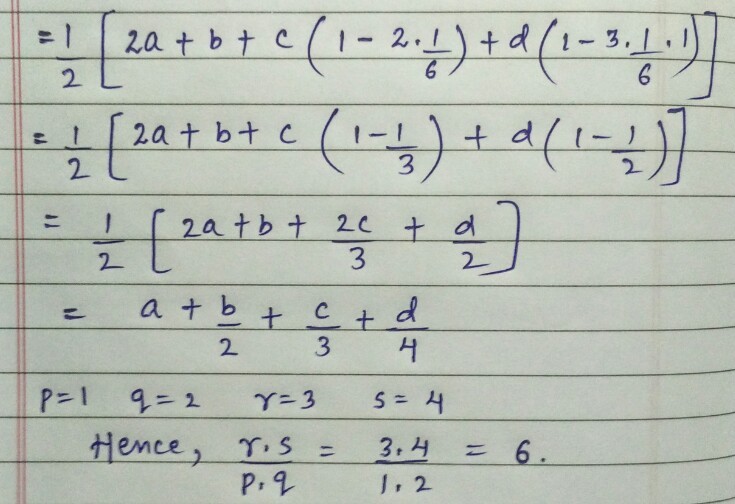
That Calligraphy Kills me everytime.
Nice solution man
Woah! Nice problem + solution again!
Newton's sums made it easy !!
We will first start by finding the roots of the equation : 6 x 2 − 6 x + 1 = 0 and we do so by the "Quadratic formula" : x = 2 a − b ± b 2 − 4 a c where a = 6 , b = − 6 , c = 1
we therefore get that the two roots are 6 3 + 3 , 6 3 − 3 and we can say that α = 6 3 + 3 , β = 6 3 − 3 now the problem is simple , all we have to do is rearrange the equation , and equate coefficients : 2 1 ( a + b α + c α 2 + d α 3 ) + 2 1 ( a + b β + c β 2 + d β 3 ) = a + 2 1 b ( α + β ) + 2 1 c ( α 2 + β 2 ) + 2 1 d ( α 3 + β 3 ) and this equation can be written as : p a + q b + r c + s d therefore by equating coefficients one finds : p 1 = 1 , q 1 = 2 α + β , r 1 = 2 α 2 + β 2 , s 1 = 2 α 3 + β 3 and by computing these values one finds : p = 1 , q = 2 , r = 3 , s = 4 Therefore p . q r . s = 1 ∗ 2 3 ∗ 4 = 2 1 2 = 6