All are 6-digit numbers with the same 6 digits
Given that A is a 6-digit number and that 2 5 A , 3 A , 2 7 A , 4 A and 2 1 1 A are all 6-digit numbers with the same 6 digits as A . Find A .
The answer is 153846.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
6 solutions
Is there a way to optimize?
Am I the only one who thinks that a 6-digit number that satisfies all of this is cool?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
|
If this were to require more calculations, you could reduce the upper bound to 1,000,000*2/11.
I screened as I progressed. I realized that the initial number had to be between 100000 and 181818 and only even integers needed to be tested.
Do [ d1 = Sort [ IntegerDigits [ i ] ] ; j = 2 5 i ; d2 = Sort [ IntegerDigits [ j ] ] ; If [ d1 = d2 , j = 3 i ; d2 = Sort [ IntegerDigits [ j ] ] ; If [ d1 = d2 , j = 2 7 i ; d2 = Sort [ IntegerDigits [ j ] ] ; If [ d1 = d2 , j = 4 i ; d2 = Sort [ IntegerDigits [ j ] ] ; If [ d1 = d2 , j = 2 1 1 i ; d2 = Sort [ IntegerDigits [ j ] ] ; If [ d1 = d2 , Print [ i ] ] ] ] ] ] , { i , 1 0 0 0 0 0 , 1 8 1 8 1 8 , 2 } ] ⟹ 1 5 3 8 4 6 .
A not so brief Python solution :
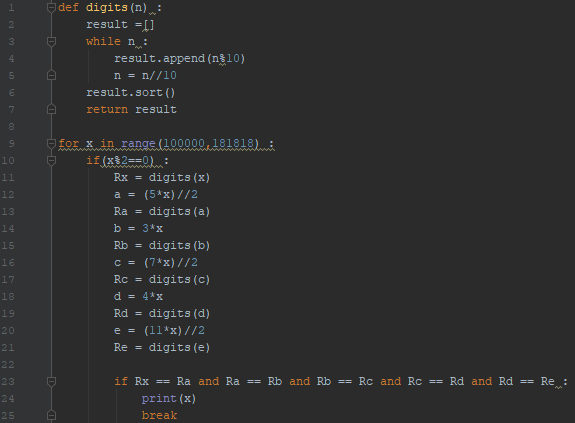
Is there any solution which does not use programming I tried my best but could not find any such solution.
The range is bounded by the minimal 6-digit number (1000000) and the maximal number for which 2 1 1 A is 6-digits (181818). A pythonic solution is implemented below.
1 |
|
I love Python.
Running this program gives the result of 1 5 3 8 4 6 .
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
|
153846
My Java solution: