Almost equal
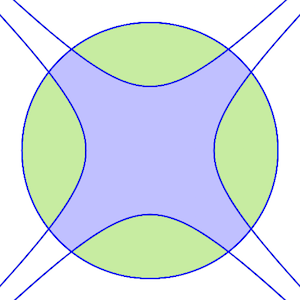
The shaded areas in the image are defined by a circle of radius r and the hyperbolas x 2 − y 2 = ( 2 r ) 2 and y 2 − x 2 = ( 2 r ) 2 .
Find the value of the quotient blue area green area .
The answer is 1.04387.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
My calculations got f ed up.
Log in to reply
Yes, computation is tough.
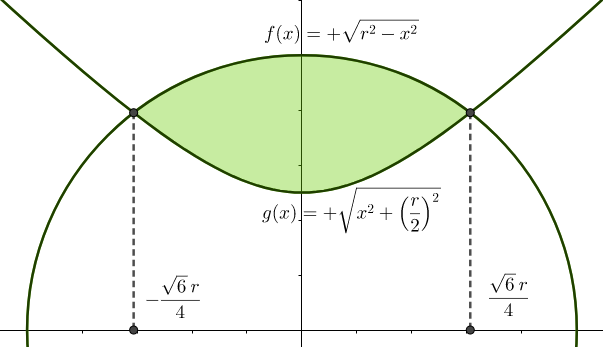
The green area is four times the value of the integral:
∫ − 4 6 r 4 6 r [ f ( x ) − g ( x ) ] d x = 2 × ∫ 0 4 6 r ( r 2 − x 2 − x 2 + ( 2 r ) 2 ) d x = = 2 × [ 2 1 x r 2 − x 2 + r 2 arcsin r x − 2 1 x x 2 + ( 2 r ) 2 − ( 2 r ) 2 sinh − 1 r 2 x ] 0 4 6 r = 0 . 4 0 1 1 3 r 2 ⟹ green area = 4 × 0 . 4 0 1 1 3 r 2 = 1 . 6 0 4 5 1 r 2
blue area = π r 2 − green area = 1 . 5 3 7 0 8 r 2
The desired ratio is blue area green area = 1 . 5 3 7 0 8 r 2 1 . 6 0 4 5 1 r 2 = 1 . 0 4 3 8 7
This is a replicated rectangular hyperbola. As noted elsewhere, it is sufficient to work in the lower octant of the first quadrant and that any radius could be chosen. I used a radius of 1. By working in polar coordinates, the green area can be computed in one integral, with the hyperbola being at r = 2 1 sec ( 2 θ ) , the circle being at r = 1 and 0 ≤ θ ≤ 2 1 cos − 1 ( 4 1 ) , which is the angle at which the hyperbola meets the circle. green = 8 ∫ 0 2 1 cos − 1 ( 4 1 ) ∫ 2 1 sec ( 2 θ ) 1 r d r d θ ⇒ 2 arccos 4 1 − arctanh 5 3 . The answer: π − green green ≈ 1 . 0 4 3 8 7 1 8 9 0 8 8 0 9 8 .
I thought almost equal area implies their quotient to be close to 1. Then i thought circle implies pi. Pi/3=1.0472 - correct.
Close enough to pass... A fortunate coincidence!
Due to symmetry, we only need to consider the firs half quadrant of the graph, where the ratio A blue A green is the same.
We know that the point P , where the circle intersects the hyperbola, satisfies the system of equations below.
⎩ ⎨ ⎧ Hyperbola: Circle: x 2 − y 2 = 4 r 2 x 2 + y 2 = r 2 . . . ( 1 ) . . . ( 2 )
From ( 1 ) + ( 2 ) : 2 x 2 = 4 5 r 2 ⟹ x = 8 5 r . Since x 2 + y 2 = r 2 , ⟹ y = 8 3 r and P ( 8 5 r , 8 3 r ) .
Then the green area is given by:
A green = ∫ 2 r 8 5 r x 2 − 4 r 2 d x + ∫ 8 5 r r r 2 − x 2 d x = 2 r ∫ 2 r 8 5 r ( r 2 x ) 2 − 1 d x + r ∫ 8 5 r r 1 − ( r x ) 2 d x = 4 r 2 ∫ 0 tan − 1 2 3 sec θ tan 2 θ d θ + r 2 ∫ tan − 1 3 5 2 π cos 2 ϕ d ϕ = 4 r 2 sec θ tan θ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ 0 tan − 1 2 3 − 4 r 2 ∫ 0 tan − 1 2 3 sec 3 θ d θ + 2 r 2 ∫ tan − 1 3 5 2 π ( 1 + cos 2 ϕ ) d ϕ = 8 1 5 r 2 − 4 r 2 [ 2 sin θ sec 2 θ + 2 1 ∫ sec θ d θ ] 0 tan − 1 2 3 + 2 r 2 [ ϕ + 2 1 sin 2 ϕ ] tan − 1 3 5 2 π = 8 1 5 r 2 − 1 6 1 5 r 2 − 8 r 2 ln ( tan θ + sec θ ) ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ 0 tan − 1 2 3 + 4 π r 2 − 2 r 2 tan − 1 3 5 − 1 6 1 5 r 2 = 1 6 r 2 ( 4 π − ln ( 4 + 1 5 ) − 8 tan − 1 3 5 ) ≈ 0 . 2 0 0 5 6 4 2 0 1 r 2 Let r 2 x = sec θ ⟹ d x = 2 r sec θ tan θ d θ Let r x = sin ϕ ⟹ d x = r cos ϕ d ϕ By integration by parts By reduction formula
Then A blue A green = 8 π r 2 − A green A green ≈ 0 . 3 9 2 6 9 9 0 8 2 r 2 − 0 . 2 0 0 5 6 4 2 0 1 r 2 0 . 2 0 0 5 6 4 2 0 1 r 2 ≈ 1 . 0 4 4