Alt-Center
The figure shows a unit circle with two perpendicular chords of lengths 1 . 5 and 1 . 5 1 . 5 .
The ratio of the blue area to the grey area is equal to A π − B A π + B .
If A and B are coprime positive integers, find A + B .
The answer is 9.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
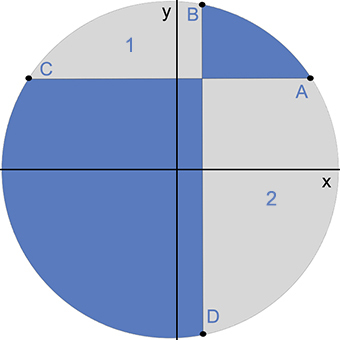 Let's consider the circle as
x
2
+
y
2
=
1
, so that
y
(
x
)
=
1
−
x
2
. Points coordinates are*:
Let's consider the circle as
x
2
+
y
2
=
1
, so that
y
(
x
)
=
1
−
x
2
. Points coordinates are*:
A ( 2 1 2 3 , 8 5 )
B ( 3 2 5 , 4 3 2 3 )
C ( − 2 1 2 3 , 8 5 )
D ( 3 2 5 , − 4 3 2 3 )
We can evaluate the area of 1 as:
A r e a ( 1 ) = ∫ − 2 1 2 3 3 2 5 1 − x 2 − 8 5 .
Now, to calculate the area of
2
, let's rotate anticlockwise** of
2
π
radiants the entire circle. The situation is described in the second picture.
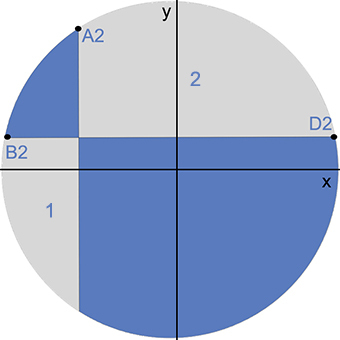 A
2
(
−
8
5
,
2
1
2
3
)
A
2
(
−
8
5
,
2
1
2
3
)
B 2 ( − 4 3 2 3 , 3 2 5 )
D 2 ( 4 3 2 3 , 3 2 5 )
The area of 2 can be calculated
A r e a ( 2 ) = ∫ − 8 5 4 3 2 3 1 − x 2 − 3 2 5 d x .
Let's define W the white area and B the blue area. We have:
W = A r e a ( 1 ) + A r e a ( 2 ) = ∫ − 2 1 2 3 3 2 5 1 − x 2 − 8 5 d x + ∫ − 8 5 4 3 2 3 1 − x 2 − 3 2 5 d x = 8 1 ( 4 π + 5 ) Since the radius R = 1 ,
B = π − W = π − 8 1 ( 4 π + 5 ) = 8 1 ( 4 π − 5 )
The ratio is 4 π − 5 4 π + 5 , so A = 4 , B = 5 . Eventually, A + B = 9 .
*: A x = 2 1 2 3 , so that A y = y ( A x ) = 1 − 8 3 = 8 5 . B y = 4 3 2 3 = 1 − B x 2 , so that B x = 3 2 5
**: To rotate the points I multilpied the rotation matrix ( sin θ cos θ cos θ − sin θ ) , θ = 2 π by the respective points.
The circle with its four sections is re-drawn above, with the two secants aligned with the horizontal and vertical directions, with the longer secant being horizontal, and the shorter secant being vertical. We will take the origin of the coordinate system to be at the center of the circle. Then the intersection point of the two secants is ( a , b ) . From the length conditions we can deduce the values of a and b , we have
1 . 5 = 2 1 − a 2 ⇒ a = − 8 5
and
1 . 5 1 . 5 = 2 1 − b 2 ⇒ b = − 3 2 5
Next, we identify the four points of intersection between the secants and the circle with the radian angle each makes with the positive x-axis as t 1 , t 2 , t 3 , t 4 . Since the given circle is a unit circle, we have
sin t 1 = sin t 3 = b and cos t 2 = cos t 4 = a
It follows that cos t 1 = 1 − b 2 and cos t 3 = − 1 − b 2 and sin t 2 = 1 − a 2 and sin t 4 = − 1 − a 2
Next, to find the blue area, we form the 2D vector from the intersection point ( a , b ) to a point on the circumference of the circle.
r ( t ) = ( x ( t ) , y ( t ) ) = ( cos t , sin t ) − ( a , b )
Differentiating with respect to t ,
r ′ ( t ) = ( x ′ ( t ) , y ′ ( t ) ) = ( − sin t , cos t )
Now the area is given by this formula which follows from Green's Theorem.
Blue Area = 2 1 ( ∫ t 1 t 2 x ( t ) y ′ ( t ) − y ( t ) x ′ ( t ) d t + ∫ t 3 t 4 x ( t ) y ′ ( t ) − y ( t ) x ′ ( t ) d t )
Plugging in the expression for r ( t ) and r ′ ( t ) , and simplifying, the above expression reduces to
Blue Area = 2 1 ( ( t 2 − t 1 ) + ( t 4 − t 3 ) − a ( sin t 2 − sin t 1 + sin t 4 − sin t 3 ) + b ( cos t 2 − cos t 1 + cos t 4 − cos t 3 ) )
We note that t 1 + t 3 = π and t 2 + t 4 = 2 π . Therefore, the expression becomes,
Blue Area = 2 1 ( π − a ( 1 − a 2 − b − 1 − a 2 − b ) + b ( a − 1 − b 2 + a + 1 − b 2 ) )
Simplifying, we get
Blue Area = 2 1 ( π + 4 a b ) = 2 1 ( π + 4 8 5 3 2 5 )
= 2 1 ( π + 4 5 ) = 8 4 π + 5
It follows that the gray area is π ( 1 ) 2 − 8 4 π + 5 = 8 4 π − 5
Hence the ratio of the areas is 4 π − 5 4 π + 5 ; therefore, A = 4 and B = 5 , making the answer 4 + 5 = 9 .