An infinite cascade of Π networks
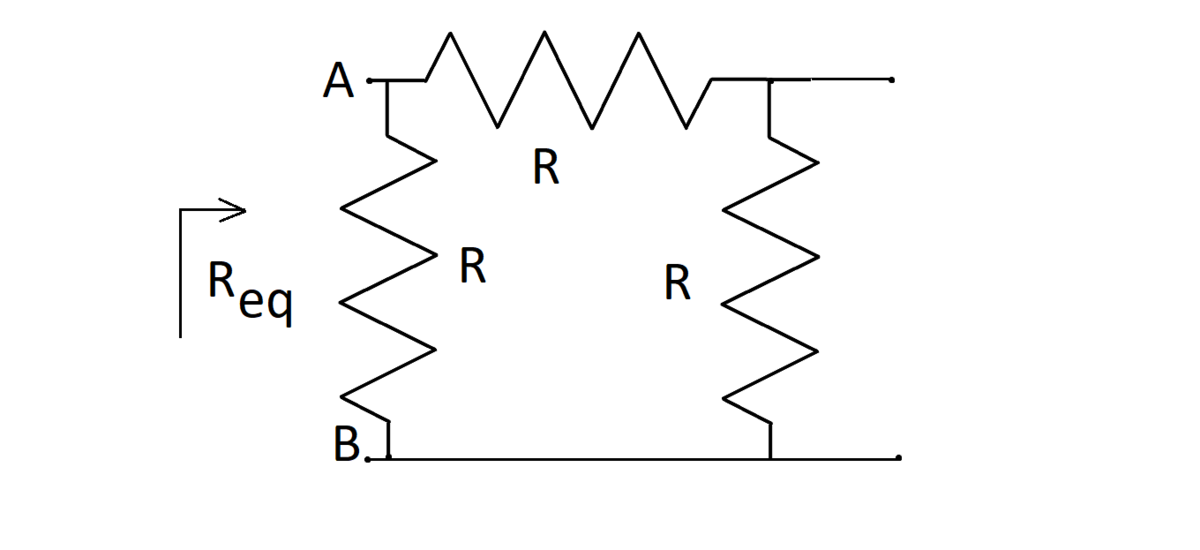
A Π -network of three identical resistors, each with a resistance of R , is shown above. What will be the equivalent resistance between points A and B , as we connect an infinite number of these Π 's (in cascade) to the right? Enter the limiting ratio of the equivalent resistance to R , i.e. find
R R e q ( ∞ )
The answer is 0.57735.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
We have the following recursive relation between R e q ( n + 1 ) and R e q ( n ) ,
R e q ( n + 1 ) = R / / ( R + R / / R e q ( n ) )
where R 1 / / R 2 denotes the equivalent resistance of the parallel connection of R 1 and R 2 , so that R 1 / / R 2 = R 1 + R 2 R 1 R 2
Using this formula in the above recursive equation, we can write,
R + R / / R e q ( n ) = R + R + R e q ( n ) R R e q ( n )
= R + R e q ( n ) R 2 + 2 R R e q ( n )
Therefore,
R e q ( n + 1 ) = R + ( R 2 + 2 R x ( n ) ) / ( R + x ( n ) ) R ( R 2 + 2 R x ( n ) ) / ( R + x ( n ) )
= R 2 + R R e q ( n ) + R 2 + 2 R R e q ( n ) R ( R 2 + 2 R R e q ( n ) )
= 2 R + 3 R e q ( n ) R 2 + 2 R R e q ( n )
Now as n → ∞ , both R e q ( n ) and R e q ( n + 1 ) approach R ∞ , hence,
R ∞ ( 2 R + 3 R ∞ ) = ( R 2 + 2 R R ∞ )
from which,
3 R ∞ 2 = R 2
Hence,
R R ∞ = 3 1 ≈ 0 . 5 7 7 3 5
Let the equivalent resistance of infinite cascade of Π -network be R ∞ . From the figure above, we have:
R ∞ 2 R R ∞ + 3 R ∞ 2 3 R ∞ 2 ⟹ R R ∞ = R ∣ ∣ ( R + R ∣ ∣ R ∞ ) = R ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ( R + R + R ∞ R R ∞ ) = R ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ R + R ∞ R 2 + 2 R R ∞ = R + R + R ∞ R 2 + 2 R R ∞ R ( R + R ∞ R 2 + 2 R R ∞ ) = 1 + R + R ∞ R + 2 R ∞ R + R ∞ R 2 + 2 R R ∞ = 2 R + 3 R ∞ R 2 + 2 R R ∞ = R 2 + 2 R R ∞ = R 2 = 3 1 ≈ 0 . 5 7 7 Multiply both sides by 2 R + 3 R ∞