Ancient Sum
n = 1 ∑ 2 5 n ( n + 1 ) ( n + 2 ) 2 n − 1
If the summation above equals to E M for coprime positive coprime integer, then find the value of M + E .
The answer is 1177.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Moderator note:
It's great that you recognized we could use partial fractions to approach this problem!
Bad calculation three times !! . Up voted your solution. Can you please explain your method after "Let S=...." ........Any way my approach...
f
(
n
)
=
n
=
1
∑
2
5
n
(
n
+
1
)
(
n
+
2
)
2
n
−
1
.
n
(
n
+
1
)
(
n
+
2
)
2
n
−
1
=
n
(
n
+
1
)
(
n
+
2
)
5
(
n
+
1
)
−
3
(
n
+
2
)
=
n
(
n
+
2
)
5
−
n
(
n
+
1
)
3
=
{
2
n
5
−
2
(
n
+
2
)
5
}
−
{
n
3
−
n
+
1
3
}
∴
f
(
n
)
=
−
n
=
1
∑
2
5
2
n
1
+
n
=
1
∑
2
5
n
+
1
3
−
n
=
1
∑
2
5
2
(
n
+
2
)
5
=
−
2
1
∗
n
=
1
∑
2
n
1
−
2
1
∗
n
=
3
∑
2
5
n
1
+
{
3
∗
n
=
2
∑
2
n
1
+
3
∗
n
=
3
∑
2
5
n
1
+
3
∗
n
=
2
6
∑
2
6
n
1
}
−
2
5
∗
n
=
3
∑
2
5
n
1
−
2
5
∗
n
=
2
6
∑
2
7
n
1
=
−
2
1
−
4
1
+
{
2
3
+
2
6
3
}
−
2
5
∗
2
6
1
−
2
5
∗
2
7
1
=
7
0
2
4
7
5
m
+
n
=
1
1
7
7
Log in to reply
I did the same. But calculation got wrong.
Log in to reply
In the first two attempts I got my calculation wrong , in the last one with utmost care , I did it and got it right :) :)
There is a typo in the second line of your solution.
Moderator note:
This is how I done it! You don't have to completely express the fraction as partial fractions, as long as its in the form of a n + 1 − a n .
Did the exact same
n ( n + 1 ) ( n + 2 ) 2 n − 1 = n A + n + 1 B + n + 2 C ⇒ 2 n − 1 = A ( n + 1 ) ( n + 2 ) + B ( n 2 + 2 n ) + C ( n 2 + n ) = A ( n 2 + 3 n + 2 ) + B ( n 2 + 2 n ) + C ( n 2 + n ) ⇒ 2 A = − 1 , 3 A + 2 B + C = 2 , A + B + C = 0 ⇒ A = 2 − 1 , → B = 3 → C = 2 − 5 . The rest is similar to Surya Prakash's solution.
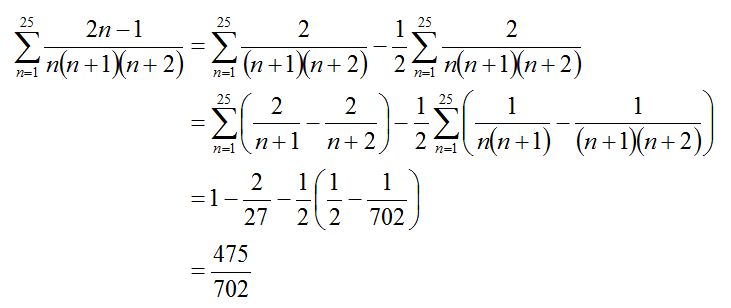
n = 1 ∑ 2 5 ( n ) ( n + 1 ) ( n + 2 ) 2 n − 1 = n = 1 ∑ 2 5 2 n − 1 + n + 1 3 + 2 ( n + 2 ) − 5 = n = 1 ∑ 2 5 2 n − 1 + n = 1 ∑ 2 5 n + 1 3 + n = 1 ∑ 2 5 2 ( n + 2 ) − 5
Let S = ∑ n = 1 2 5 n 1 .
So,
= 2 − 1 ( S ) + 3 ( S + 2 6 1 − 1 ) − 2 5 ( S + 2 7 1 + 2 6 1 − 2 1 − 1 ) = 7 0 2 4 7 5
So, M = 4 7 5 and E = 7 0 2 .
Therefore, M + E = 1 1 7 7 .