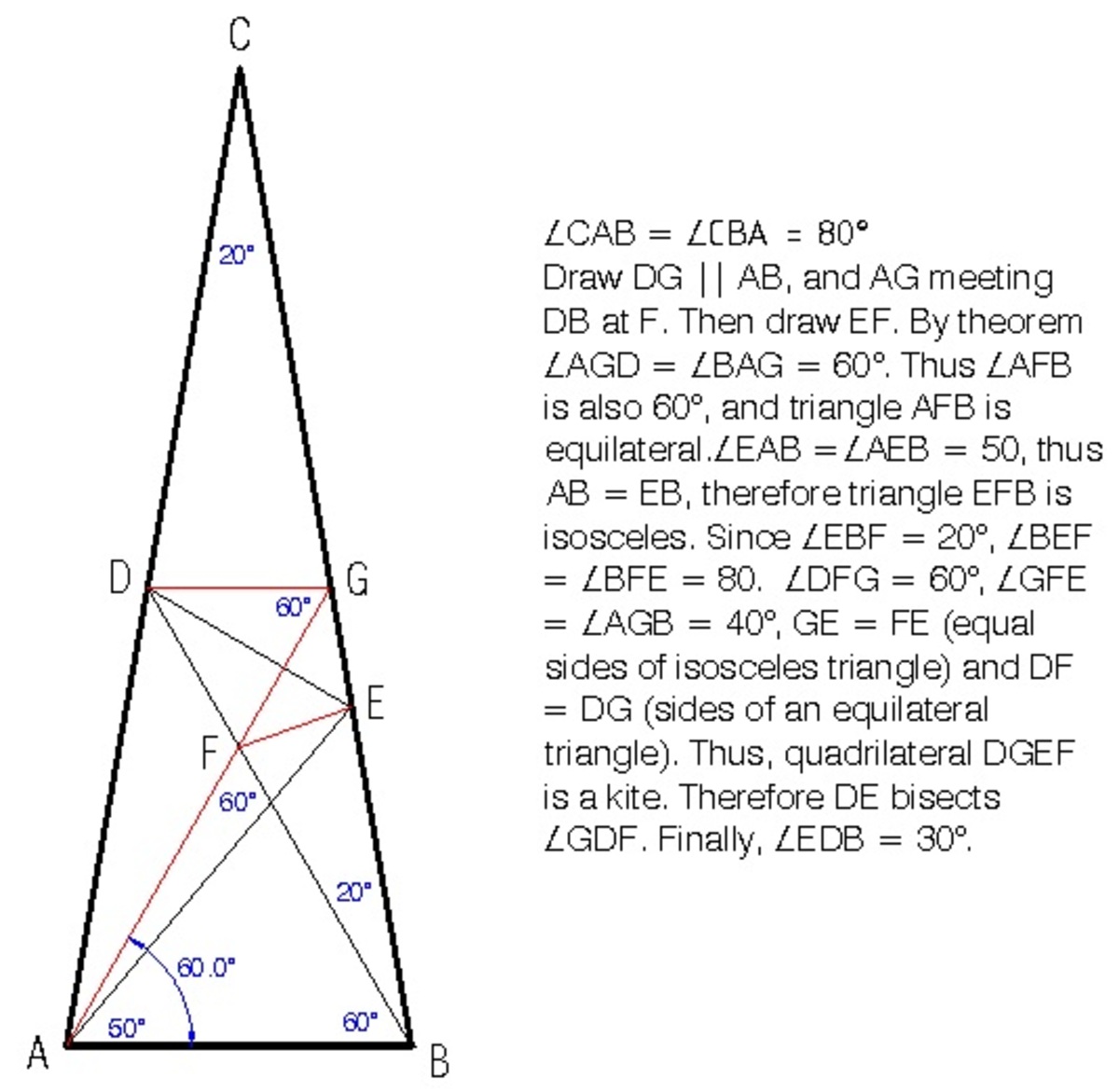
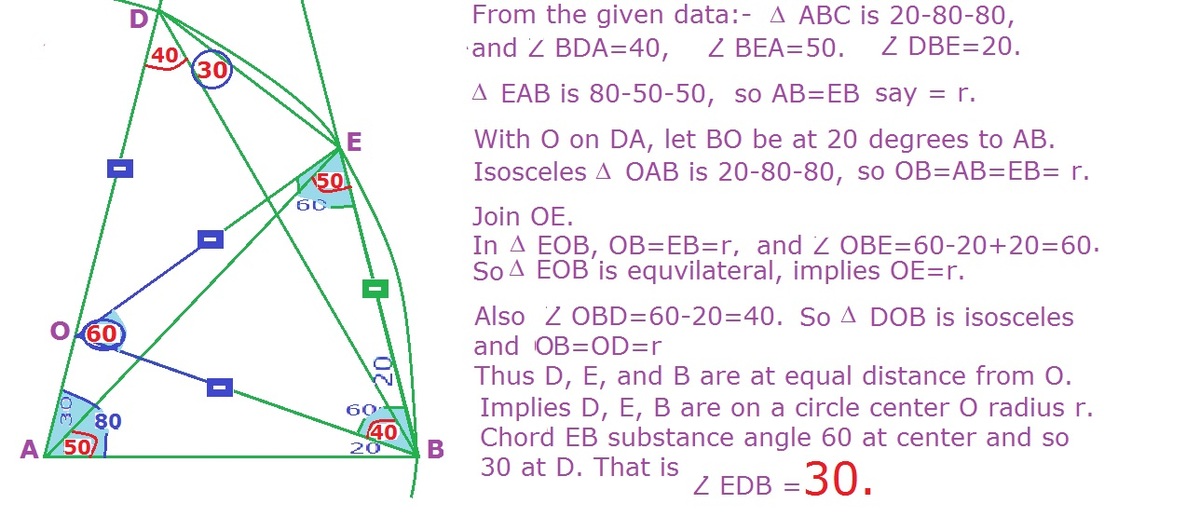
Angles inside a triangle
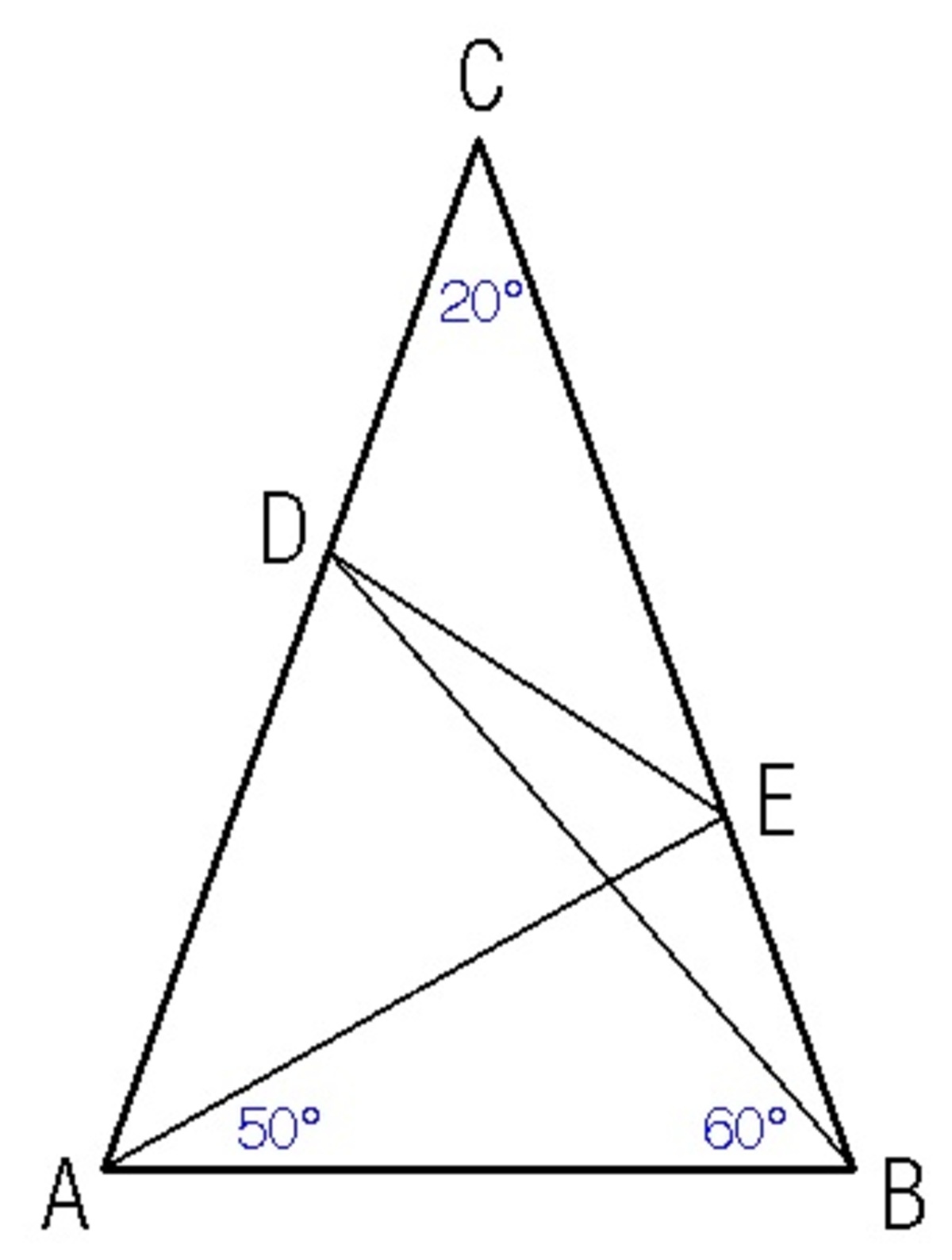 Triangle
A
B
C
is isosceles with
C
A
=
C
B
.
∠
A
B
D
=
6
0
∘
,
∠
B
A
E
=
5
0
∘
, and
∠
C
=
2
0
∘
. Find the measure of
∠
E
D
B
in degrees.
Triangle
A
B
C
is isosceles with
C
A
=
C
B
.
∠
A
B
D
=
6
0
∘
,
∠
B
A
E
=
5
0
∘
, and
∠
C
=
2
0
∘
. Find the measure of
∠
E
D
B
in degrees.
Notes:
- The figure is not drawn to scale.
- Don't draw the figure true to scale and measure angle E D B . You must calculate.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Since △ A B C is isosceles with C A = C B ⟹ ∠ C A B = ∠ C B A = 2 1 8 0 ∘ − 2 0 ∘ = 8 0 ∘ . Therefore, ∠ B E A = 1 8 0 ∘ − 8 0 ∘ − 5 0 ∘ = 5 0 ∘ implies that △ A B E is isosceles with A B = E B . And also ∠ E B D = 8 0 ∘ − 6 0 ∘ = 2 0 ∘ implies that △ B C D is isosceles with B D = C D .
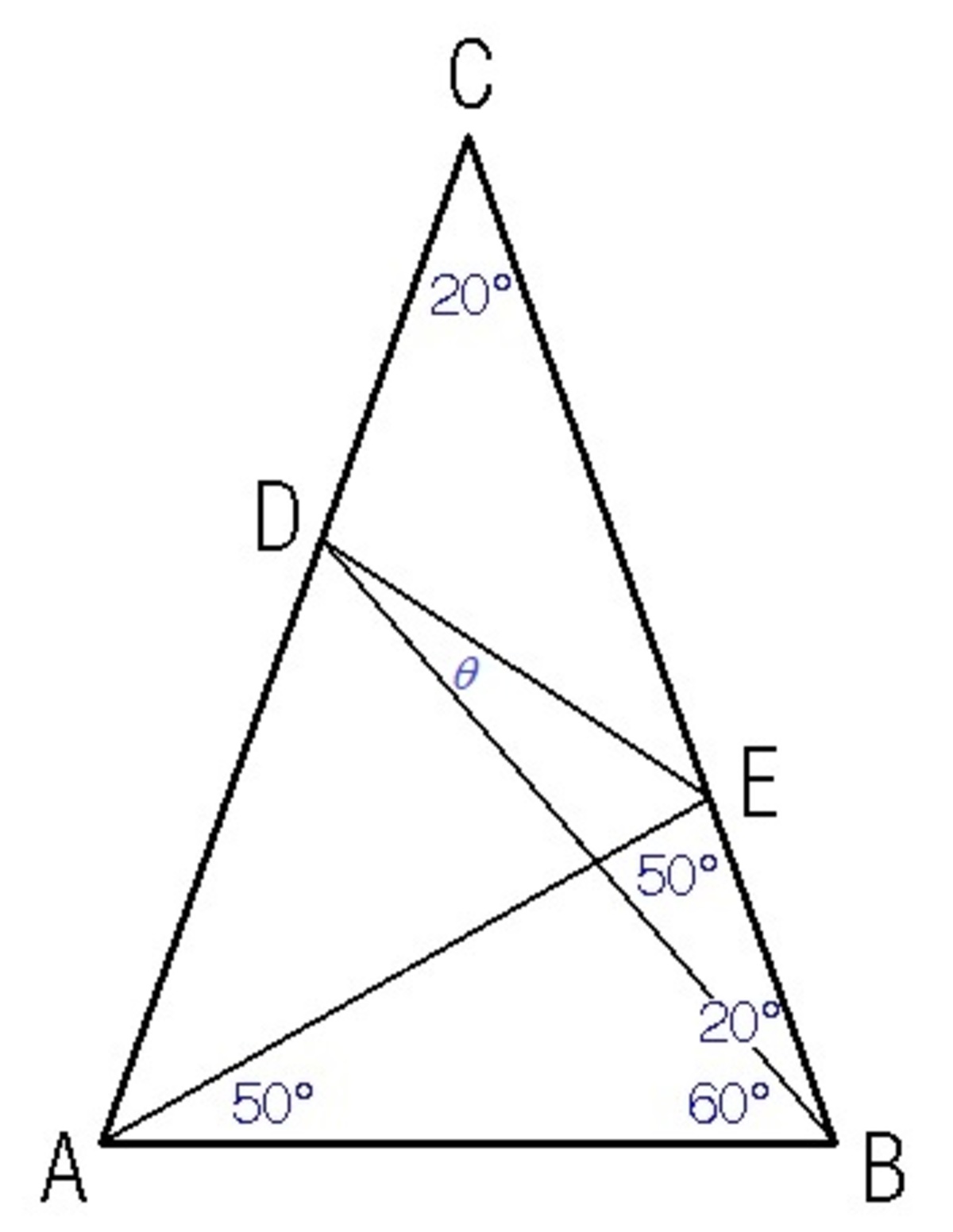
Let ∠ E D B = θ and A B = E B = 1 . Using sine rule on △ A B D :
sin ∠ B A D B D sin 8 0 ∘ B D ⟹ B D = sin ∠ A D B A B = sin 4 0 ∘ 1 = sin 4 0 ∘ sin 8 0 ∘ = 2 cos 4 0 ∘ Note that ∠ A D B = 1 8 0 ∘ − 8 0 ∘ − 6 0 ∘ = 4 0 ∘ Note that sin 8 0 ∘ = 2 sin 4 0 ∘ cos 4 0 ∘
Using sine rule on △ B D E :
E B sin ∠ E D B 1 sin θ 2 cos 4 0 ∘ sin θ cos θ sin θ tan θ ⟹ θ = B D sin ∠ D E B = 2 cos 4 0 ∘ sin ( 1 6 0 ∘ − θ ) = sin ( 2 0 ∘ + θ ) = sin 2 0 ∘ cos θ + cos 2 0 ∘ sin θ = 2 cos 4 0 ∘ − cos 2 0 ∘ sin 2 0 ∘ = 2 cos ( 3 0 ∘ + 1 0 ∘ ) − cos ( 3 0 ∘ − 1 0 ∘ ) sin ( 3 0 ∘ − 1 0 ∘ ) = cos 3 0 ∘ cos 1 0 ∘ − 3 sin 3 0 ∘ sin 1 0 ∘ sin 3 0 ∘ cos 1 0 ∘ − cos 3 0 ∘ sin 1 0 ∘ = 2 3 cos 1 0 ∘ − 2 3 sin 1 0 ∘ 2 1 cos 1 0 ∘ − 2 3 sin 1 0 ∘ = 3 1 = 3 0 ∘ Note that ∠ D E B = 1 8 0 ∘ − 2 0 ∘ − θ = 1 6 0 ∘ − θ Note that sin ( 1 8 0 ∘ − x ) = sin x