Another Circle Problem! (fixed)
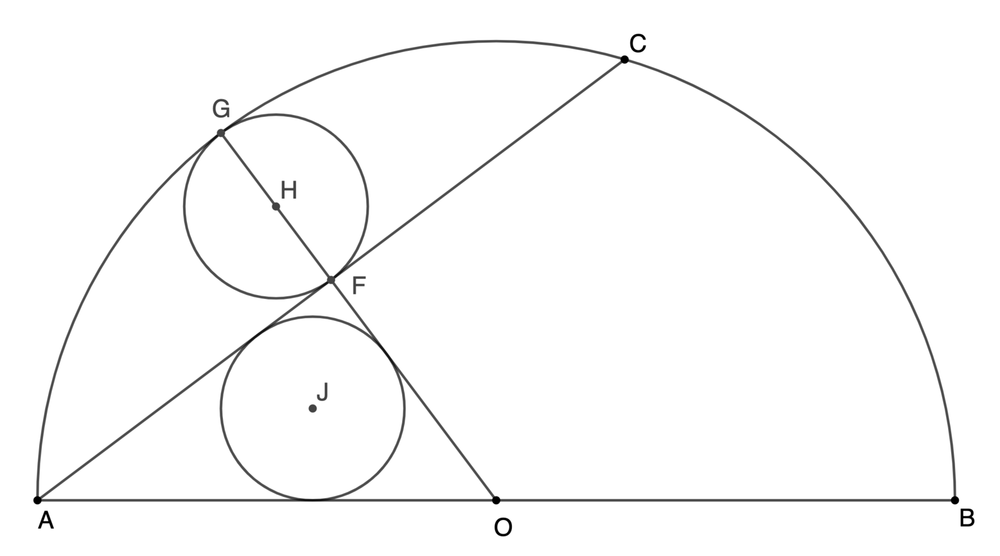
The radius of the semicircle is R and the radius of the two congruent circles is r . The lower circle is the incircle of △ A O F . The upper circle is tangent to the semicircle at G and segment A C at F . Find R r = b a , where a and b are coprime integers, and submit a + b .
The answer is 6.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
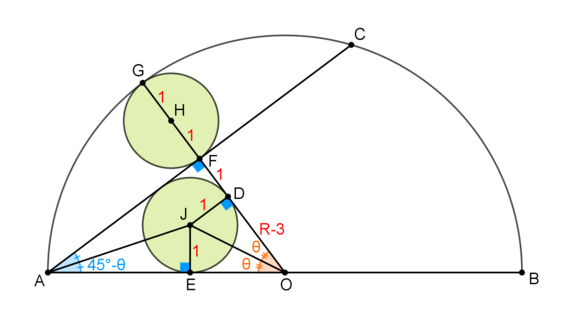 WLOG, we set
r
=
1
. Let
E
,
D
be the points of tangency of the lower circle with
O
A
and
O
F
respectively. Denote
∠
J
O
D
by
θ
.
WLOG, we set
r
=
1
. Let
E
,
D
be the points of tangency of the lower circle with
O
A
and
O
F
respectively. Denote
∠
J
O
D
by
θ
.
O
J
is the angle bisector of
∠
E
O
D
, hence
∠
E
O
J
=
∠
D
O
J
=
θ
Since
A
C
is tangent to the upper circle,
O
H
is perpendicular to
A
C
, thus
△
A
F
O
is a right angled triangle.
Hence,
∠
O
A
F
=
9
0
∘
−
∠
A
O
F
=
9
0
∘
−
2
θ
Since
A
J
is the angle bisector of
∠
O
A
F
,
∠
O
A
J
=
2
∠
O
A
F
=
4
5
∘
−
θ
On right
△
O
D
J
,
cot
θ
=
J
D
O
D
=
J
D
O
F
−
F
D
=
1
(
R
−
2
)
−
1
⇒
cot
θ
=
R
−
3
(
1
)
Furthermore,
O
E
=
O
D
=
R
−
3
and on right
△
J
A
E
,
cot ( 4 5 ∘ − θ ) = J E A E = 1 A E ⇒ A E = cot ( 4 5 ∘ − θ ) = cot θ − cot 4 5 ∘ cot θ ⋅ cot 4 5 ∘ + 1 = cot θ − 1 cot θ + 1 ⇒ ( 1 ) A E = ( R − 3 ) − 1 ( R − 3 ) + 1 ⇒ A E = R − 4 R − 2 ( 2 ) Finally, A O = A E + E O ⇒ ( 2 ) R = R − 4 R − 2 + R − 3 ⇔ R ( R − 4 ) = R − 2 + ( R − 4 ) ( R − 3 ) ⇔ R 2 − 4 R = R − 2 + R 2 − 7 R + 1 2 ⇔ R = 5
This gives R r = 5 1 For the answer, a = 1 , b = 5 , thus a + b = 6 .
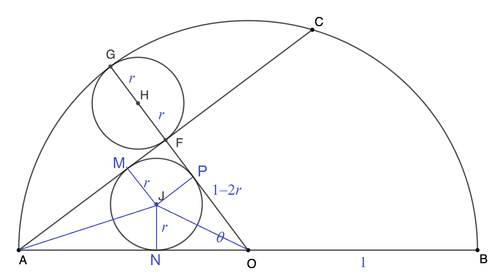
Let R = 1 , the radius of the two congruent circles be r , J M , J N , and J P be perpendicular to A F , A O , and F O respectively, and ∠ F O A = θ . Since radius O G is perpendicular to chord A C , ∠ A F O = 9 0 ∘ and ∠ F A O = 9 0 ∘ − θ . Considering the radius A O :
A N + N O J N cot 2 ∠ F A O + J N cot 2 ∠ F O A r cot ( 4 5 ∘ − 2 θ ) + r cot 2 θ ( 1 − t 1 + t ) t + t r ⟹ r = A O = A O = 1 = 1 = 1 − t 1 + t + t 1 1 Let t = tan 2 θ . . . ( 1 )
We note that F O = 1 − 2 r . Similarly,
F P + P O r + r cot 2 θ ⟹ r = F O = 1 − 2 r = 3 + t 1 1 . . . ( 2 )
From ( 1 ) = ( 2 ) :
1 − t 1 + t + t 1 1 ⟹ 1 − t 1 + t 1 + t = 3 − 3 t ⟹ t ⟹ R r = 3 + t 1 1 = 3 = 2 1 = r = 3 + t 1 1 = 5 1
Therefore a + b = 1 + 5 = 6 .
Let the radius of the semi-circle be R = 1 .
From O G , F O = O G − G F = 1 − 2 r .
By the Pythagorean Theorem on △ A F D , A F = A O 2 − F O 2 = 1 2 − ( 1 − 2 r ) 2 = 2 r − r 2 .
As an inradius of a right triangle, r = 2 1 ( A F + F O − A O ) = 2 1 ( 2 r − r 2 + 1 − 2 r − 1 ) , which solves to r = 5 1 for r > 0 .
Therefore, R r = 1 5 1 = 5 1 , so a = 1 , b = 5 , and a + b = 6 .