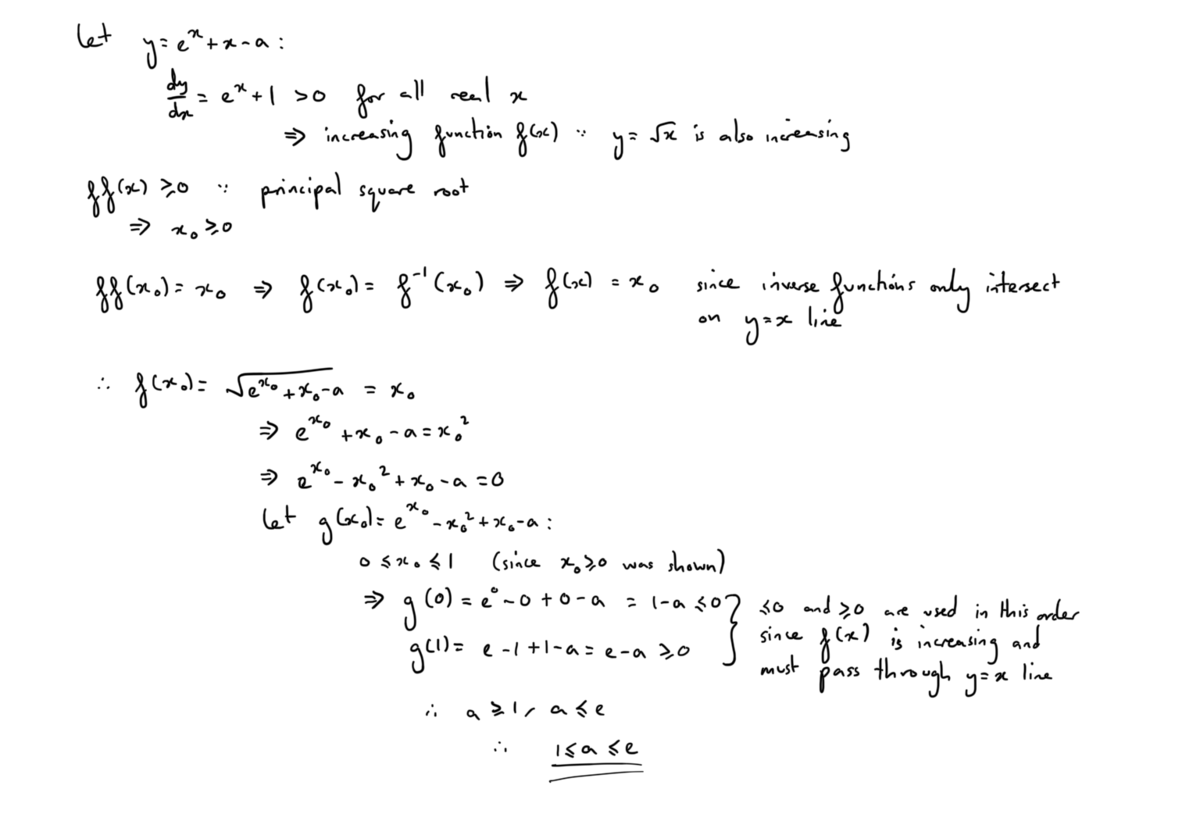Another fixed-point theorem
Let function for . If there exists such that , what is the range of ?
Note: This problem requires a little-known and trivial fixed-point theorem. Can you find and prove it?
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.