Going round in circles
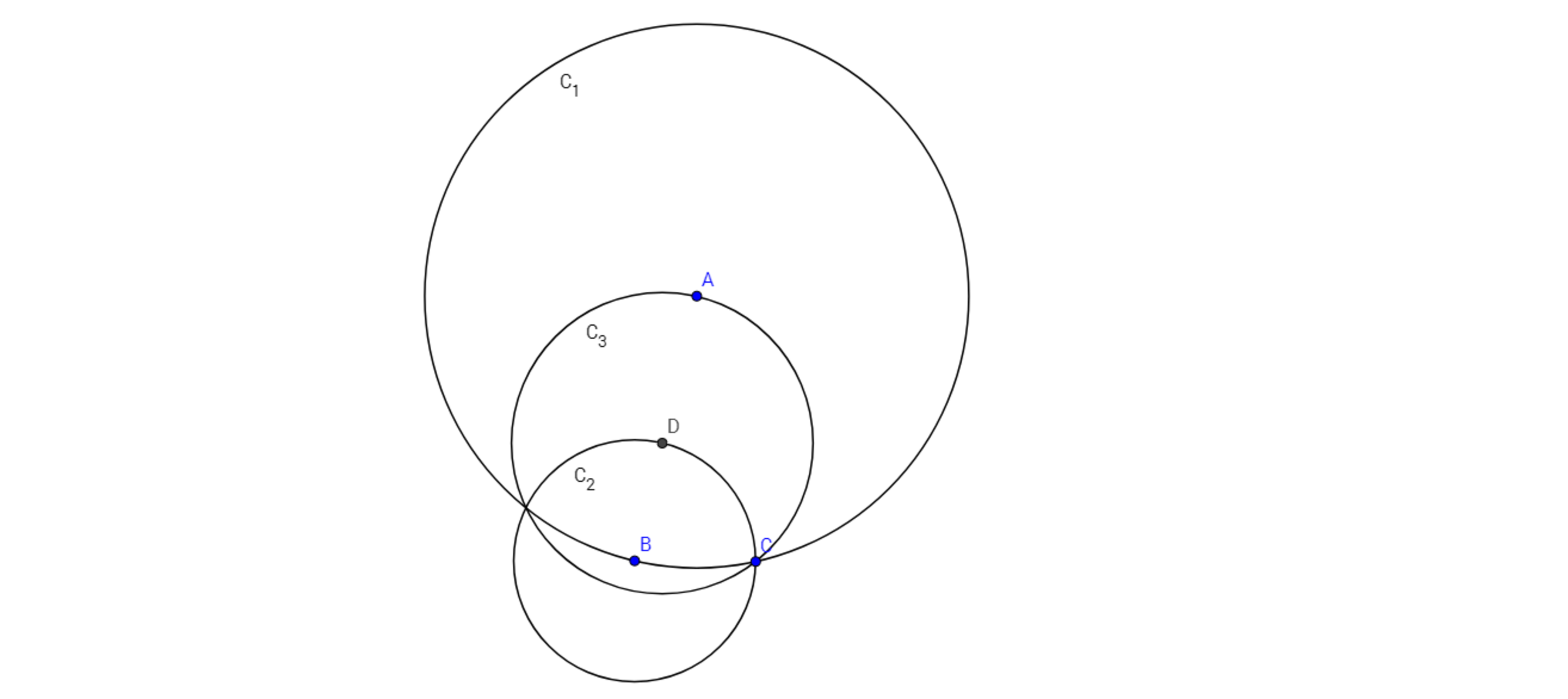
In the above diagram, a circle centred at point is constructed and two points and on the circumference are chosen. Next, another circle centred at with radius is constructed and point is where intersects . Interestingly, if I were to construct a third circle centred at with radius , point would also lie on this circle.
Let be the circumference of circle while be the length of arc . Then,
The answer is 14.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Let ∠ C A D = x . Then considering circle C 3 where A D = C D = r C 3 , , we see that ∠ A C D = ∠ C A D = x . It then follows that ∠ B D C = ∠ A C D + ∠ C A D = x + x = ( 1 + 1 ) x = 2 x . Similarly, considering circle C 2 where B C = B D , we have ∠ B C D = ∠ B D C = 2 x .
Next, we also deduce that ∠ B C A = ∠ B C D + ∠ A C D = 2 x + x = ( 2 + 1 ) x = 3 x . Considering circle C 1 where A B = A C , we have ∠ A B C = ∠ B C A = 3 x . To solve for x :
∠ C B D + ∠ B C D + ∠ B D C = π
3 x + 2 x + 2 x = π
( 3 + 4 ) x = π
7 x = π
x = 7 π
Alternatively,
∠ A B C + ∠ A C B + ∠ B A C = π
3 x + 3 x + x = π
( 6 + 1 ) x = π
7 x = π
x = 7 π
Yet another method is:
∠ A D C = ∠ C B D + ∠ B C D = 3 x + 2 x = ( 3 + 2 ) x = 5 x
∠ A D C + ∠ A C D + ∠ C A D = π
5 x + x + x = π
( 5 + 2 ) x = π
7 x = π
x = 7 π
Therefore, Y X = 7 π 2 r C 1 2 π 2 r C 1 = 7 1 2 = 2 × 7 = 1 4