Another Triangle Problem
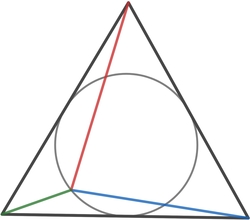
Let the distances between the vertices of a unit equilateral triangle and a point on its incircle be a , b , and c .
If a , b , and c are in a geometric progression , then b = q p , where p and q are coprime positive integers. Find p + q .
The answer is 27.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Analytic approach:
Let A = ( − 6 3 , − 2 1 ) , B = ( − 6 3 , + 2 1 ) , C = ( + 3 3 , 0 ) - three points forming a unit equilateral triangle. We need to find point X on the incircle so that a = A X , b = B X , c = C X were in a geometric progression. Let X = ( 6 3 cos α , 6 3 sin α ) , where α ∈ [ 0 ; 2 π ] .
Now let's derive the distances:
a = ∣ ∣ ∣ A X ∣ ∣ ∣ = ∣ ∣ ∣ ( 6 3 cos α + 6 3 , 6 3 sin α + 2 1 ) ∣ ∣ ∣ = ( 6 3 cos α + 6 3 ) 2 + ( 6 3 sin α + 2 1 ) 2 a = 1 2 1 cos 2 α + 6 1 cos α + 1 2 1 + 1 2 1 sin 2 α + 6 3 sin α + 4 1 = 1 2 5 + 6 1 cos α + 6 3 sin α a = 1 2 5 + 2 cos α + 2 3 sin α
b = ∣ ∣ ∣ B X ∣ ∣ ∣ = ∣ ∣ ∣ ( 6 3 cos α + 6 3 , 6 3 sin α − 2 1 ) ∣ ∣ ∣ = ( 6 3 cos α + 6 3 ) 2 + ( 6 3 sin α − 2 1 ) 2 b = 1 2 1 cos 2 α + 6 1 cos α + 1 2 1 + 1 2 1 sin 2 α − 6 3 sin α + 4 1 = 1 2 5 + 6 1 cos α − 6 3 sin α b = 1 2 5 + 2 cos α − 2 3 sin α
c = ∣ ∣ ∣ C X ∣ ∣ ∣ = ∣ ∣ ∣ ( 6 3 cos α − 3 3 , 6 3 sin α ) ∣ ∣ ∣ = ( 6 3 cos α − 3 3 ) 2 + ( 6 3 sin α ) 2 c = 1 2 1 cos 2 α − 3 1 cos α + 3 1 + 1 2 1 sin 2 α = 1 2 5 − 3 1 cos α c = 1 2 5 − 4 cos α
Since a , b , c are in a geometric progression, the following is true:
b a = c b a ⋅ c = b ⋅ b a 2 ⋅ c 2 = b 2 ⋅ b 2
Now let's use the derived expressions:
1 2 5 + 2 cos α + 2 3 sin α ⋅ 1 2 5 − 4 cos α = 1 2 5 + 2 cos α − 2 3 sin α ⋅ 1 2 5 + 2 cos α − 2 3 sin α 2 5 + 1 0 cos α + 1 0 3 sin α − 2 0 cos α − 8 cos 2 α − 8 3 sin α cos α = 2 5 + 4 cos 2 α + 1 2 sin 2 α + 2 0 cos α − 2 0 3 sin α − 8 3 sin α cos α 0 = 3 0 cos α − 3 0 3 sin α + 1 2 cos 2 α + 1 2 sin 2 α 2 cos α − 2 3 sin α = − 5 4
Finally now we can recall the expression of b and find the value:
b = 1 2 5 + 2 cos α − 2 3 sin α b = 1 2 5 − 5 4 = 6 0 2 5 − 4 = 6 0 2 1 = 2 0 7
Thus, p = 7 , q = 2 0 and the answer is 2 7
Let the unit equilateral triangle be △ A B C and its incenter be the origin O ( 0 , 0 ) ; and A ( − 2 1 , − 2 3 1 ) , B ( 0 , 3 1 ) , and C ( 2 1 , − 2 3 1 ) . Let the point on the incircle be P ( x , y ) and A P = a , B P = b , and C P = c . Then the incircle is given by x 2 + y 2 = 1 2 1 and by Pythagorean theorem :
⎩ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎨ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎪ ⎧ a 2 = ( x + 2 1 ) 2 + ( y + 2 3 1 ) 2 = x 2 + x + 4 1 + y 2 + 3 y + 1 2 1 = 1 2 5 + x + 3 y b 2 = ( x − 0 ) 2 + ( y − 3 1 ) 2 = x 2 + y 2 − 3 2 y + 3 1 = 1 2 5 − 3 2 y c 2 = ( x − 2 1 ) 2 + ( y + 2 3 1 ) 2 = x 2 − x + 4 1 + y 2 + 3 y + 1 2 1 = 1 2 5 − x + 3 y
For geometric progression, we have a c = b 2 . Therefore,
a 2 c 2 ( 1 2 5 + x + 3 y ) ( 1 2 5 − x + 3 y ) ( 3 y + 1 2 5 ) 2 − x 2 3 y 2 + 6 3 5 y + 1 4 4 2 5 − 1 2 1 + y 2 2 3 5 y ⟹ y ⟹ b 2 ⟹ b = b 4 = ( 1 2 5 − 3 2 y ) 2 = 3 4 y 2 − 3 3 5 y + 1 4 4 2 5 = 3 4 y 2 − 3 3 5 y + 1 4 4 2 5 = 1 2 1 = 3 0 3 = 1 2 5 − 3 2 × 3 0 3 = 2 0 7 = 2 0 7
Therefore p + q = 7 + 2 0 = 2 7 .