Arc Again And Tangent Again!
arctan 3 1 + arctan 4 1 + arctan 5 1 + arctan n 1 = 4 π
Find the positive integer n such that the above equality is true.
The answer is 47.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
Moderator note:
More generally, we can just combine all of the known terms onto one side as follows:
( n + i ) = R ( 3 + i ) ( 4 + i ) ( 5 + i ) ( 1 + i ) = R 2 2 2 0 4 7 + i
which shows directly that n = 4 7 . You can apply this to any tan − 1 angles that you want to sum / subtract.
See this for a quick review of Inverse-Trigonometric-Functions.
arctan 3 1 + arctan 4 1 + arctan 5 1 = 4 π − arctan n 1 Taking tan on both sides and using:- tan ( A + B + C ) = 1 − tan A tan B − tan B tan C − tan C tan A tan A + tan B + tan C − tan A tan B tan C arctan ( tan A ) = A and tan ( A + B ) = 1 − tan A tan B tan A + tan B
(For the above identities see Tangent of Sums here )
1 − 3 ⋅ 4 1 − 4 ⋅ 5 1 − 5 ⋅ 3 1 3 1 + 4 1 + 5 1 − 3 ⋅ 4 ⋅ 5 1 = 1 + n 1 1 − n 1 4 8 4 6 = n + 1 n − 1 4 7 + 1 4 7 − 1 = n + 1 n − 1 ∴ n = 4 7
Since we are dealing with acute angles, tan ( arctan a ) = a
Note that, tan ( arctan a + arctan b ) = 1 − a b a + b , by tangent addition. Thus, arctan a + arctan b = arctan 1 − a b a + b
Applying this to first two terms, we get arctan 3 1 + arctan 4 1 = arctan 1 1 7 .
Now, arctan 1 1 7 + arctan 5 1 = arctan 2 4 2 3 .
We now have arctan 2 4 2 3 + arctan n 1 = 4 π = arctan 1 .
Thus, 1 − 2 4 n 2 3 2 4 2 3 + n 1 and simplifying ;
2 3 n + 2 4 = 2 4 n − 2 3 → n = 4 7
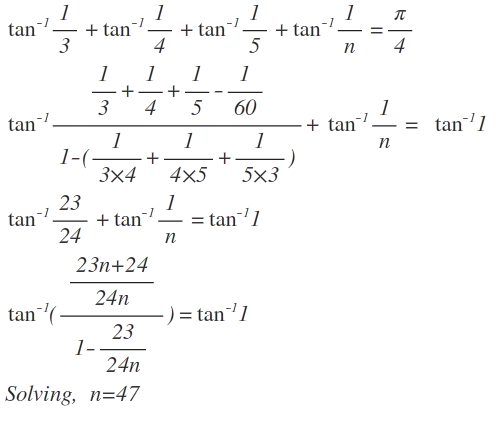
Relevant wiki: Complex Plane
Note that tan − 1 n 1 is the argument of n + i , and adding angles is essentially like multiplying the arguments. Note that ( 3 + i ) ( 4 + i ) ( 5 + i ) ( n + i ) = ( 4 8 n − 4 6 ) + ( 4 8 + 4 6 n ) i .
Since the RHS is 4 π , the real and imaginary parts of the result above must be equal. Setting 4 8 n − 4 6 = 4 8 + 4 6 n gives 2 n = 9 4 , so n = 4 7 .