Arccotangent Sum
Evaluate cot ( cot − 1 ( 7 ) + cot − 1 ( 1 3 ) + cot − 1 ( 2 1 ) + cot − 1 ( 3 1 ) )
The answer is 3.25.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
4 solutions
More easy way is to generalising the sum,
S
=
cot
(
2
∑
n
cot
−
1
(
n
2
+
n
+
1
)
)
[
n
=
5
]
S
=
cot
(
2
∑
n
tan
−
1
(
1
+
n
(
n
+
1
)
n
+
1
−
n
)
)
Now, rest is your's...
Log in to reply
Great observation, Akhil. I was wondering why those specific numbers were chosen. So following your lead, we now have that
n = 2 ∑ 5 tan − 1 ( 1 + n ( n + 1 ) n + 1 − n ) = n = 2 ∑ 5 ( tan − 1 ( n + 1 ) − tan − 1 ( n ) ) ,
which telescopes to tan − 1 ( 6 ) − tan − 1 ( 2 ) = tan − 1 ( 1 + 6 ∗ 2 6 − 2 ) = tan − 1 ( 1 3 4 ) = cot − 1 ( 4 1 3 ) ,
and so S = cot ( cot − 1 ( 4 1 3 ) ) = 4 1 3 .
S = cot ( arctan ( 7 1 ) + arctan ( 1 3 1 ) + arctan ( 2 1 1 ) + arctan ( 3 1 1 ) )
Let a = 7 + i , b = 1 3 + i , c = 2 1 + i and d = 3 1 + i . Then:
S = cot ( ar g ( a ) + ar g ( b ) + ar g ( c ) + ar g ( d ) ) )
S = cot ( ar g ( a b c d )
S = cot ( ar g ( ( 7 + i ) ( 1 3 + i ) ( 2 1 + i ) ( 3 1 + i ) ) )
S = cot ( ar g ( ( 1 0 ) ( 9 + 2 i ) ( 2 6 ) ( 2 5 + 2 i ) ) )
We can ignore the 1 0 and the 2 6 , since they don't affect the argument:
S = cot ( ar g ( 2 2 1 + 6 8 i ) )
S = 6 8 2 2 1 = 4 1 3
I used similar methods as others here, but first derived cot α = x , cot β = y ⟹ cot ( α + β ) = x + y x y − 1 ; or, with fractions, cot α = u x , cot β = v y ⟹ cot ( α + β ) = x v + y u x y − u v .
Applying this to the given values in pairs, cot ( cot − 1 ( 7 ) + cot − 1 ( 1 3 ) ) = 7 + 1 3 7 ⋅ 1 3 − 1 = 2 0 9 0 = 2 9 ; cot ( cot − 1 ( 2 1 ) + cot − 1 ( 3 1 ) ) = 2 1 + 3 1 2 1 ⋅ 3 1 − 1 = 5 2 6 5 0 = 2 2 5 ; cot ( cot − 1 ( 2 9 ) + cot − 1 ( 2 2 5 ) ) = 9 ⋅ 2 + 2 5 ⋅ 2 9 ⋅ 2 5 − 2 ⋅ 2 = 6 8 2 2 1 = 4 1 3 = 3 . 2 5 .
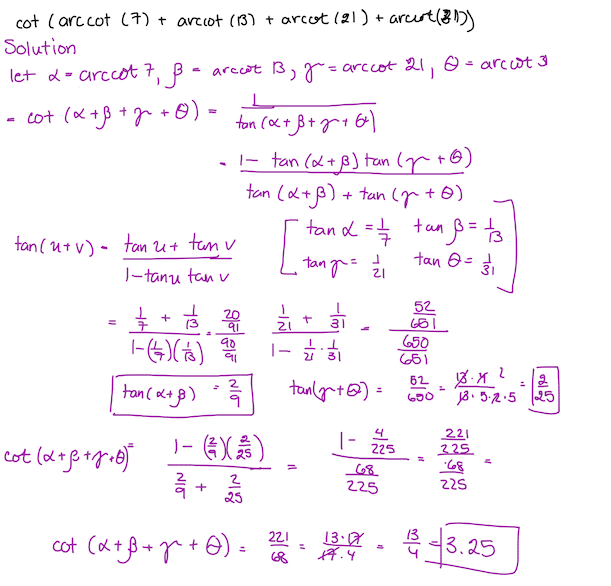
Using the arctan sum formula, we have that
cot − 1 ( 7 ) + cot − 1 ( 1 3 ) = tan − 1 ( 7 1 ) + tan − 1 ( 1 3 1 ) = tan − 1 ( 1 − 7 1 ∗ 1 3 1 7 1 + 1 3 1 ) = tan − 1 ( 9 2 ) .
Similarly, cot − 1 ( 2 1 ) + cot − 1 ( 3 1 ) = tan − 1 ( 1 − 2 1 1 ∗ 3 1 1 2 1 1 + 3 1 1 ) = tan − 1 ( 2 5 2 ) .
Since tan − 1 ( 9 2 ) + tan − 1 ( 2 5 2 ) = tan − 1 ( 1 − 9 2 ∗ 2 5 2 9 2 + 2 5 2 ) = tan − 1 ( 2 2 5 6 8 ) = tan − 1 ( 1 3 4 ) = cot − 1 ( 4 1 3 ) ,
the given expression comes out to cot ( cot − 1 ( 4 1 3 ) ) = 4 1 3 = 3 . 2 5 .