Area enclosed by two curves
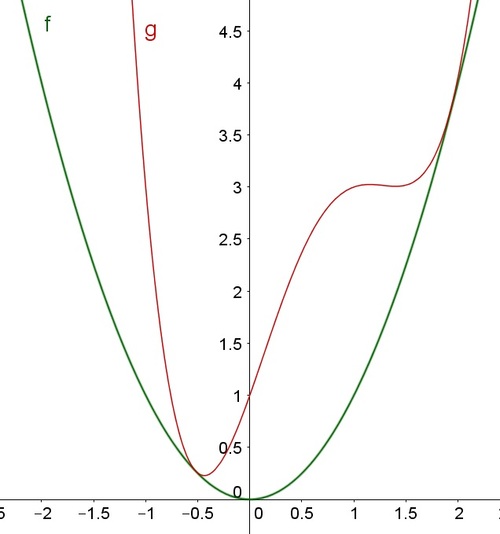 The parabola
is tangent to the graph of
at two distinct points.
The parabola
is tangent to the graph of
at two distinct points.
Given that the area enclosed by these two curves is , where and are coprime positive integers, find the value of .
Remark : The image above shows for the case . The area is the same regardless the parity of .
Bonus : If the parabola is tangent to the graph of at two distinct points, what is the area enclosed by and ?
This problem is part of Curves... cut or touch?
Inspiration .
The answer is 11.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
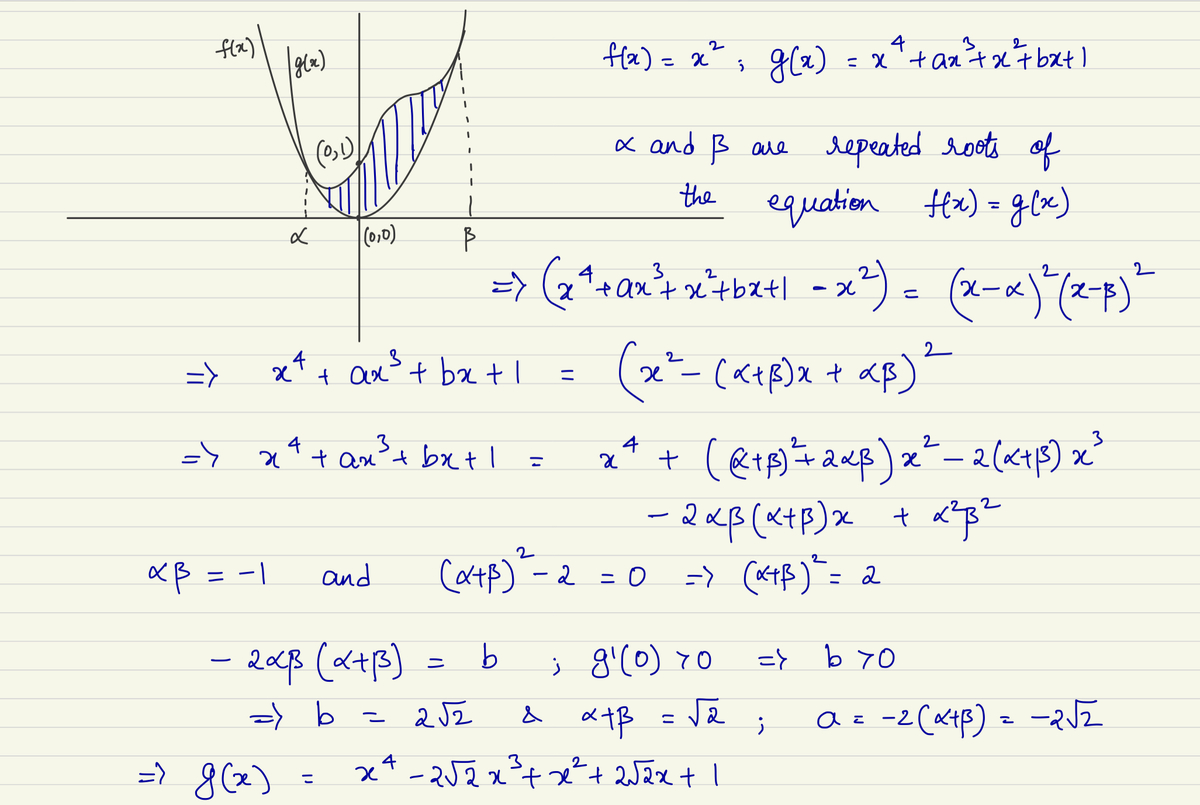
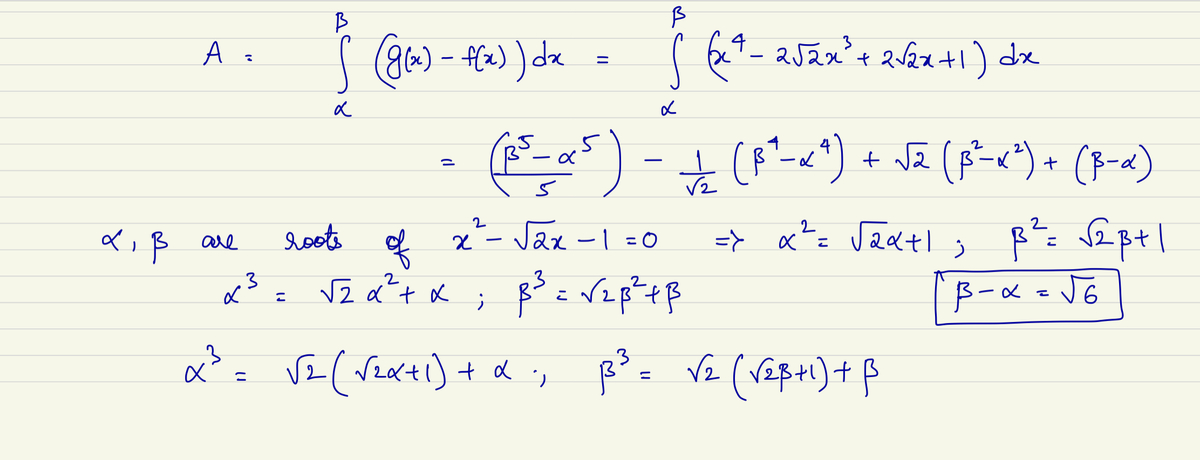
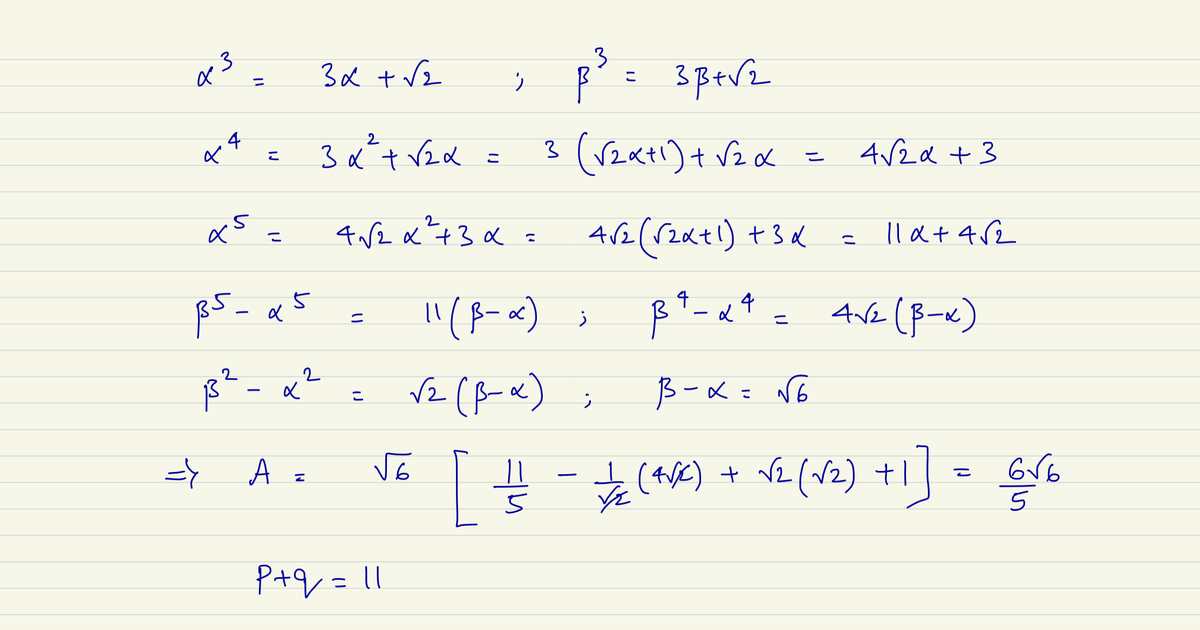
Suppose the x -coordinates of the two intersection point are d and e , where e > d . Then it is possible to write g ( x ) − f ( x ) = x 4 + a x 3 + b x + 1 = ( x − d ) 2 ( x − e ) 2 .
Then the the desired area, A is ∫ d e ( g ( x ) − f ( x ) ) d x = ∫ d e ( x − d ) 2 ( x − e ) 2 d x
Let r = 2 e − d and u = x − 2 d + e . Then the area is
A = ∫ − r r ( u − r ) 2 ( u + r ) 2 d u = ∫ − r r ( u 2 − r 2 ) 2 d u = 2 ∫ 0 r ( u 2 − r 2 ) 2 d u = … = 1 5 1 6 r 5
In order to obtain the value of r , By comparing each of the coefficient of x k of f − g respectively, one can obtain
− 2 ( d + e ) d 2 + 4 d e + e 2 − 2 d e ( d + e ) d 2 e 2 = = = = a 0 b 1
From the last equation, d e = ± 1 . If d e = 1 , then from the second equation, d 2 + 4 d e + e 2 = 0 , a contradiction. Hence, d e = − 1 . From second equation again, d 2 + e 2 = − 4 d e = 4 , which means that ( d − e ) 2 = 4 − 2 d e = 6 . As e > d , e − d = 6 . Now, r = 2 e − d = 2 6 and hence A = 1 5 1 6 × 3 2 3 6 6 = 5 6 6 .
Bonus : If the parabola f ( x ) = x 2 is tangent to the graph of g ( x ) = x 4 + a x 3 + c x 2 + b x + 1 at two distinct points, what is the area by f and g ?
The answer is 3 0 ( c + 5 ) 2 c + 5