Area Of A Shaded Region.

In the diagram above, P is the center of the circle. If the area of the shaded region can be represented as b a π − b c , where a , b and c are coprime positive integers, find a + b + c .
The answer is 248.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Let the radius of the circle be r and the angle ∠ P B C be α . Then
2 r cos ( 3 0 ° + α ) = 1 0 ⟹ r ( 3 cos α − sin α ) = 1 0
2 r cos ( 3 0 ° − α ) = 1 2 ⟹ r ( 3 cos α + sin α ) = 1 2
From these we get r 2 = 3 1 2 4 , tan α = 1 1 3 .
Hence tan ( 3 0 ° − α ) = 3 3 2 and tan ( 3 0 ° + α ) = 5 3 7 .
Total area of bottom two regions is 2 × ( 6 π r 2 − 4 3 r 2 ) = 3 π r 2 − 2 3 r 2 = 3 π r 2 − 3 6 2 .
Area of top left region is 2 r 2 ( 3 2 π − 2 α ) − 2 5 tan ( 3 0 ° + α ) .
Area of top right region is 2 r 2 ( 3 2 π + 2 α ) − 3 6 tan ( 3 0 ° − α ) .
Sum of these two is 3 2 π r 2 − 3 5 9 .
Therefore the total area is π r 2 − 3 1 2 1 = 3 1 2 4 π − 3 1 2 1 .
So a = 1 2 4 , b = 3 , c = 1 2 1 and a + b + c = 2 4 8 .

m ∠ A B C = 3 0 ∘ = m ∠ C B D ⟹ m ( A C ⌢ ) = 6 0 ∘ = m ( C D ⌢ ) ⟹ A C ≅ C D .
⟹ 1 0 0 + x 2 − 1 0 3 x = 1 4 4 + x 2 − 1 2 3 x ⟹ 2 3 x = 4 4 ⟹ x = 3 2 2 .
h 1 = 1 0 sin ( 3 0 ∘ ) = 5 and h 2 = 1 2 sin ( 3 0 ∘ ) = 6 ⟹ A 1 = 2 1 ( 3 2 2 ) ( 5 ) = 3 5 5 and
A 2 = 3 6 6 ⟹ A T = A 1 + A 2 = 3 1 2 1 .
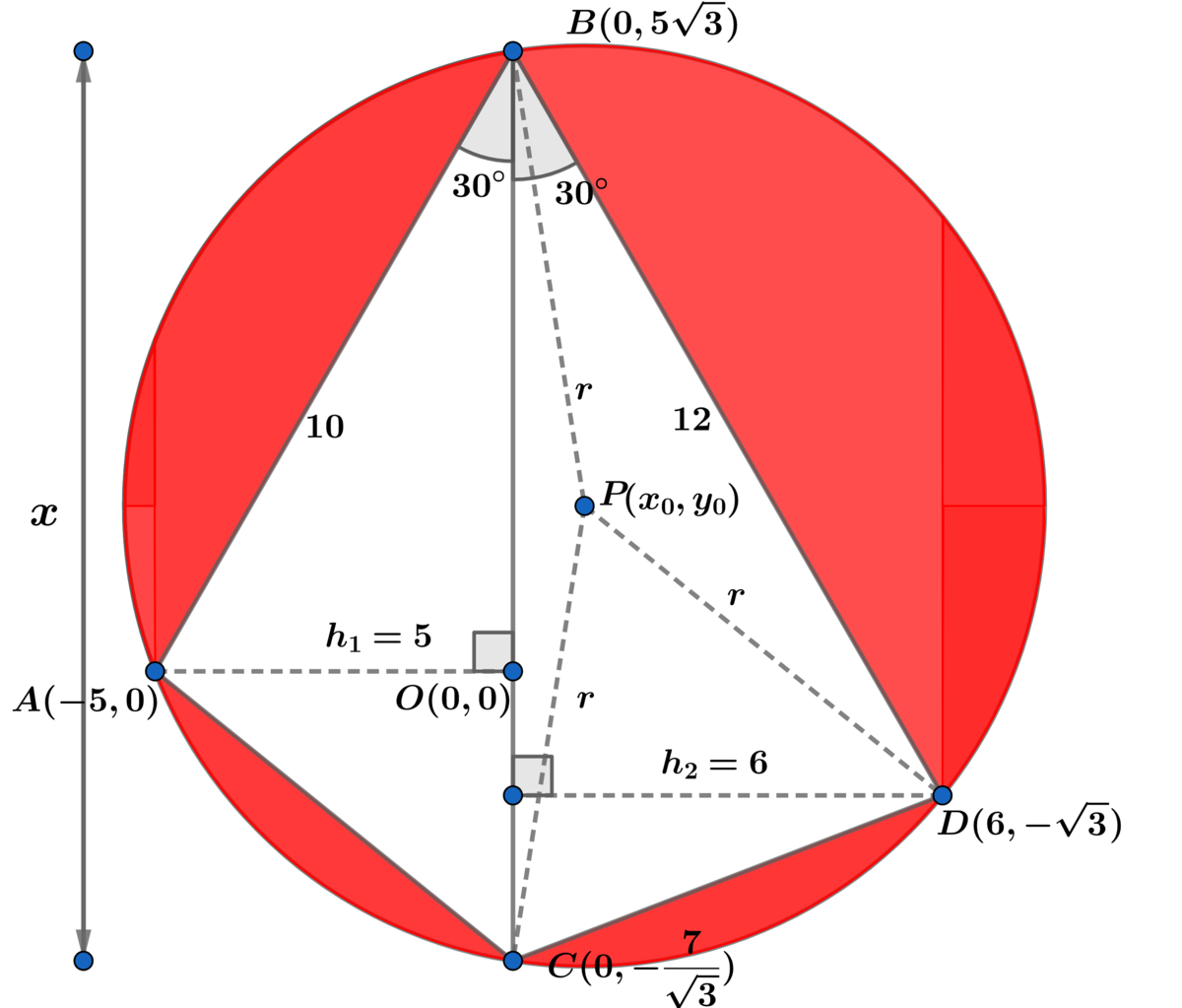
Assigning coordinates we have:
r 2 = x 0 2 + ( y 0 − 5 3 ) 2
r 2 = x 0 2 + ( y 0 + 3 7 ) 2
⟹ 3 4 4 y 0 = 3 1 7 6 ⟹ y 0 = 3 4
and
r 2 = ( x 0 − 6 ) 2 + ( y 0 + 3 ) 2
r 2 = x 0 2 + ( y 0 + 3 7 ) 2
using y 0 = 3 4 ⟹
x 0 2 − 1 2 x 0 + 3 6 + 3 4 9 = r 2
x 0 2 + 3 1 2 1 = r 2
⟹ − 1 2 x 0 + 1 2 = 0 ⟹ x 0 = 1 ⟹ P ( 1 , 3 4 ) ⟹ r 2 = 3 1 2 1 + 1 = 3 1 2 4
⟹ r = 2 3 3 1 ⟹ Area of the circle A c = 3 1 2 4 π and A T = 3 1 2 1 ⟹
The desired shaded area A = A c − A T = 3 1 2 4 π − 3 1 2 1 = b a π − b c ⟹
a + b + c = 2 4 8
Since A B D C is a cyclic quadrilateral , ∠ A D C = ∠ A B C = 3 0 ∘ and ∠ C A D = ∠ C B D = 3 0 ∘ , therefore △ A C D is isosceles and A C = C D = a . Also the angle at the center is twice at at the circumference, then ∠ A P D = 2 ∠ A B C = 1 2 0 ∘ , therefore △ A P D is an isosceles triangle congruent to △ A C D , implying that the radius of the circle is a .
To find a , we note that A D = 2 a cos 3 0 ∘ = 3 a . By cosine rule ,
( 3 a ) 2 3 a 2 ⟹ a = 1 0 2 + 1 2 2 − 2 ( 1 0 ) ( 1 2 ) cos 6 0 ∘ = 1 2 4 = 2 3 3 1
Area of the shaded region is given by:
A = A ◯ − A △ A B D − A △ A C D = π a 2 − 2 1 ( 1 0 ) ( 1 2 ) sin 6 0 ∘ − 2 1 a 2 sin 1 2 0 ∘ = 3 1 2 4 π − 3 0 3 − 3 3 1 3 = 3 1 2 4 π − 3 1 2 1
Therefore a + b + c = 1 2 4 + 3 + 1 2 1 = 2 4 8 .