Area of a triangle
In triangle X Y Z , X E divides ∠ Y X Z into two equal parts such that point E lies on Y Z . Point D lies on X Z such that D X = D Z . Point Q is the intersection of Y D and X E . Point F lies on X Y such that Z F passes through point Q . If F Y = 1 9 . 2 , E Y = 2 4 and E Z = 3 6 , find the area of triangle X F E rounded to the nearest integer.
The answer is 343.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
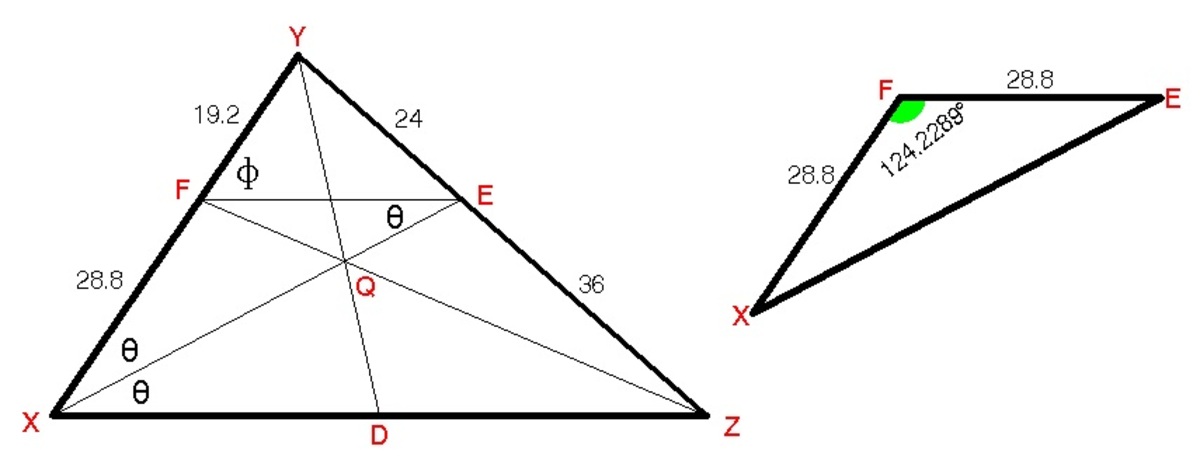 By Ceva’s Theorem, we have
By Ceva’s Theorem, we have
( F X F Y ) ( D Z D X ) ( E Y E Z ) = 1
Because D X = D Z , we have
F X F Y = E Z E Y
F X 1 9 . 2 = 3 6 2 4
F X = 2 4 3 6 ( 1 9 . 2 ) = 2 8 . 8
Since F X F Y = E Z E Y , F E ∣ ∣ X Z
Because X E bisects ∠ Y X Z , ∠ E X Z = ∠ X E F .
Therefore triangle X F E is isosceles, so F E = F X = 2 8 . 8 .
We let ∠ Y F E = ϕ , by cosine law, we obtain
2 4 2 = 1 9 . 2 2 + 2 8 . 8 2 − 2 ( 1 9 . 2 ) ( 2 8 . 8 ) c o s ϕ
ϕ = 5 5 . 7 7 1 1 ∘
It follows that
∠ X F E = 1 8 0 − ϕ = 1 2 4 . 2 2 8 9 ∘
Finally the area of triangle X F E is
A X F E = 2 1 ( 2 8 . 8 ) ( 2 8 . 8 ) ( s i n 1 2 4 . 2 2 8 9 ) = 3 4 3
Suppose that D X = D Z = x and F X = y . Then Ceva's Theorem tells us that 1 9 . 2 y × 3 6 2 4 × x x = 1 and hence y = 2 4 3 6 × 1 9 . 2 = 2 8 . 8 Using the Angle Bisector Theorem, we have 4 8 2 4 = 2 x 3 6 and hence x = 3 6 Thus triangle X Y Z has sides 4 8 , 6 0 and 7 2 , and hence has area ∣ X Y Z ∣ = 9 0 × 4 2 × 3 0 × 1 8 = 5 4 0 7 Hence triangle X Y E has area ∣ X Y E ∣ = 6 0 2 4 ∣ X Y Z ∣ = 2 1 6 7 and so triangle X F E has area ∣ X F E ∣ = 4 8 y ∣ X Y E ∣ = 5 6 4 8 7 = 3 4 2 . 8 8 9 3 6 9 9 . . . . . . To the nearest integer, this is 3 4 3 .