Area of infinite circles
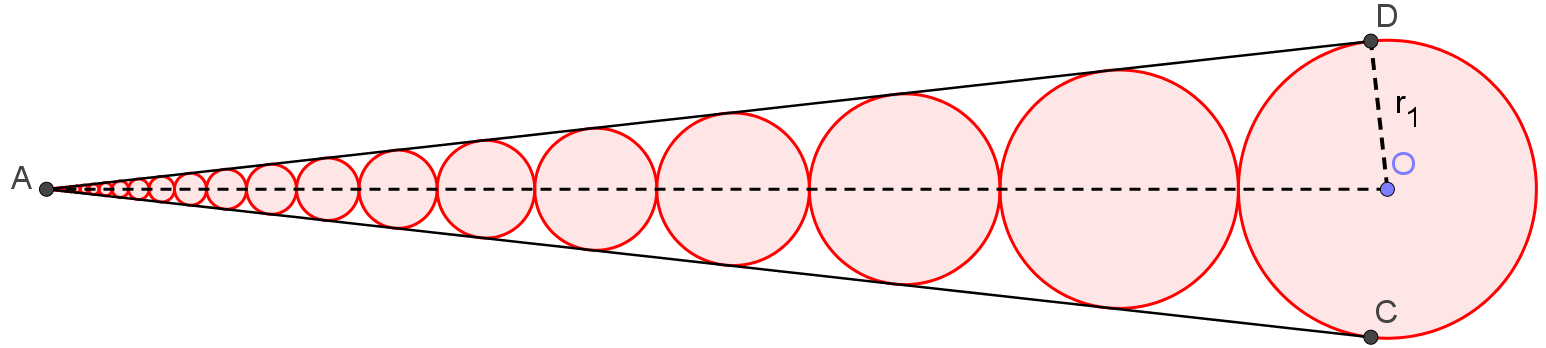
In the figure above :
-
A D and A C are tangent to all circles
-
the radius of circle O is 2
-
A O is 9
-
the shaded area can be written as b a π where a and b are coprime integer
find a+b ?
The answer is 139.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
It should be A G 2 unless you mean the whole fraction has been squared.

In my diagram above △ A O D ∼ △ A P Q . Then we have the following relation:
r 2 r 1 = A P A O
r 2 2 = 9 − 2 − r 2 9
Solving for r 2 :
r 2 2 = 7 − r 2 9
9 r 2 = 1 4 − 2 r 2
1 1 r 2 = 1 4
r 2 = 1 1 1 4
Since all the circles are tangent two by two, and they are also tangent to the segment A D , all the radii of adjacent circles starting from r 1 are decreasing in the same ratio. This ratio is 2 1 1 1 4 = 1 1 7 .
The ratio of the areas of two circles is the same as the ratio of their radii squared. Then the area of echa circle starting from the circle with radius r 1 is decreasing in the ratio of 1 2 1 4 9 .
The sum of the areas of all circles will be the sum of the infinite terms of an Geometric Progression with first term 4 π and common ratio 1 2 1 4 9 . The sum will be:
S = 1 − 1 2 1 4 9 4 π
S = 1 2 1 7 2 4 π
S = 7 2 4 8 4 π = 1 8 1 2 1 π
Then the sum is 1 8 1 2 1 π , and the answer for this question is a + b = 1 2 1 + 1 8 = 1 3 9
if we take any adjacent circle like above we will get a similar triangles
△ a b c ∼ △ A C O
⇒ a c A O = b c C O
⇒ r n + r n + 1 9 = r n − r n + 1 2 since { a c = r n + r n + 1 b c = r n − r n + 1
⇒ r n + 1 = 1 1 7 r n
Now
r 1 = 2 , r 2 = 2 ( 1 1 7 ) 1 , r 2 = 2 ( 1 1 7 ) 2 , . . . . . , r n = 2 ( 1 1 7 ) n − 1
the Area of a circle A n = π ( r n ) 2 = 4 π ( 1 2 1 4 9 ) n − 1
the sum of all circles
∑ n = 1 ∞ A n = 4 π ∑ n = 1 ∞ ( 1 2 1 4 9 ) n − 1 = 1 − 1 2 1 4 9 4 π = 1 8 1 2 1 π
a+b = 121 + 18 = 139
another Solution
△ A P R ∼ △ A S N
so the Area of the shaded Area is similar
⇒ a r e a o f c i r c l e i n △ A N S a r e a o f c i r c l e i n △ A P R = ( A G A J ) 2
let the area of circles in △ A N S = α
so the area of circles in △ A P R = α − 4 π
⇒ α α − 4 π = 1 1 2 7 2 ⇒ α = 1 8 1 2 1 π
a+b = 121 + 18 = 139