Areas and Alternating Series Reposted.
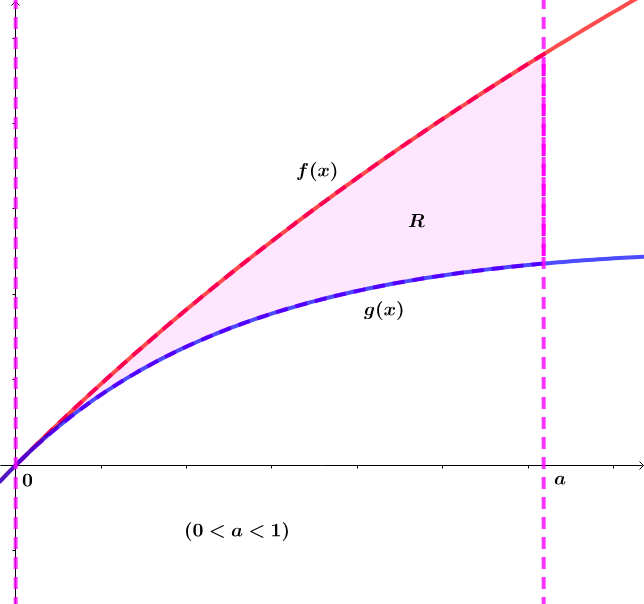
Let and .
If and and the region bounded by and on has area , find the real value of and express the answer as the value of to six decimal places.
The answer is 0.061337.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Let ∣ x ∣ < 1 and ( 0 < a < 1 ) .
Let f ( x ) = ∑ n = 1 ∞ ( − 1 ) n + 1 n x n .
⟹ d x d ( f ( x ) ) = ∑ n = 1 ∞ ( − 1 ) n + 1 x n − 1 = 1 + x 1 ⟹ f ( x ) = ∫ 0 x 1 + x 1 d x = ln ( 1 + x ) .
For ∫ 0 a ln ( 1 + x ) d x
∫ 0 a ln ( 1 + x ) d x = ( x ln ( 1 + x ) + ln ( 1 + x ) − x ) ∣ 0 a = ( x + 1 ) ln ( 1 + x ) − x ∣ 0 a = ( a + 1 ) ln ( a + 1 ) − a .
∑ n = 1 ∞ n x n = ∑ j = 1 ∞ ∑ n = j ∞ x n = 1 − x 1 ∑ j = 1 ∞ x j = 1 − x 1 ( x ) 1 − x 1 = ( 1 − x ) 2 x
⟹ g ( x ) = ∑ n = 1 ∞ ( − 1 ) n + 1 n x n = − ∑ n = 1 ∞ n ( − x ) n = ( 1 + x ) 2 x .
Let u = 1 + x ⟹ d u = d x ⟹ ∫ 0 a g ( x ) d x = ∫ 1 a + 1 u 1 − u 2 1 d u = ( ln ( u ) + u 1 ) ∣ 0 a + 1 = ln ( a + 1 ) + a + 1 1 − 1
⟹ ∫ 0 a f ( x ) − g ( x ) d x = a ln ( a + 1 ) − a + 1 a 2 = a ln ( a + 1 ) − ( 2 a − 1 ) ⟹ a 2 + a − 1 = 0 ⟹ a = 2 − 1 ± 5 ( 0 < a < 1 ) ⟹ a = 2 5 − 1 ⟹ ∫ 0 2 5 − 1 f ( x ) − g ( x ) d x = 2 5 − 1 ln ( 2 1 + 5 ) − 5 + 1 3 − 5 ≈ 0 . 0 6 1 3 3 7 .