At the crossroads of algebra and geometry
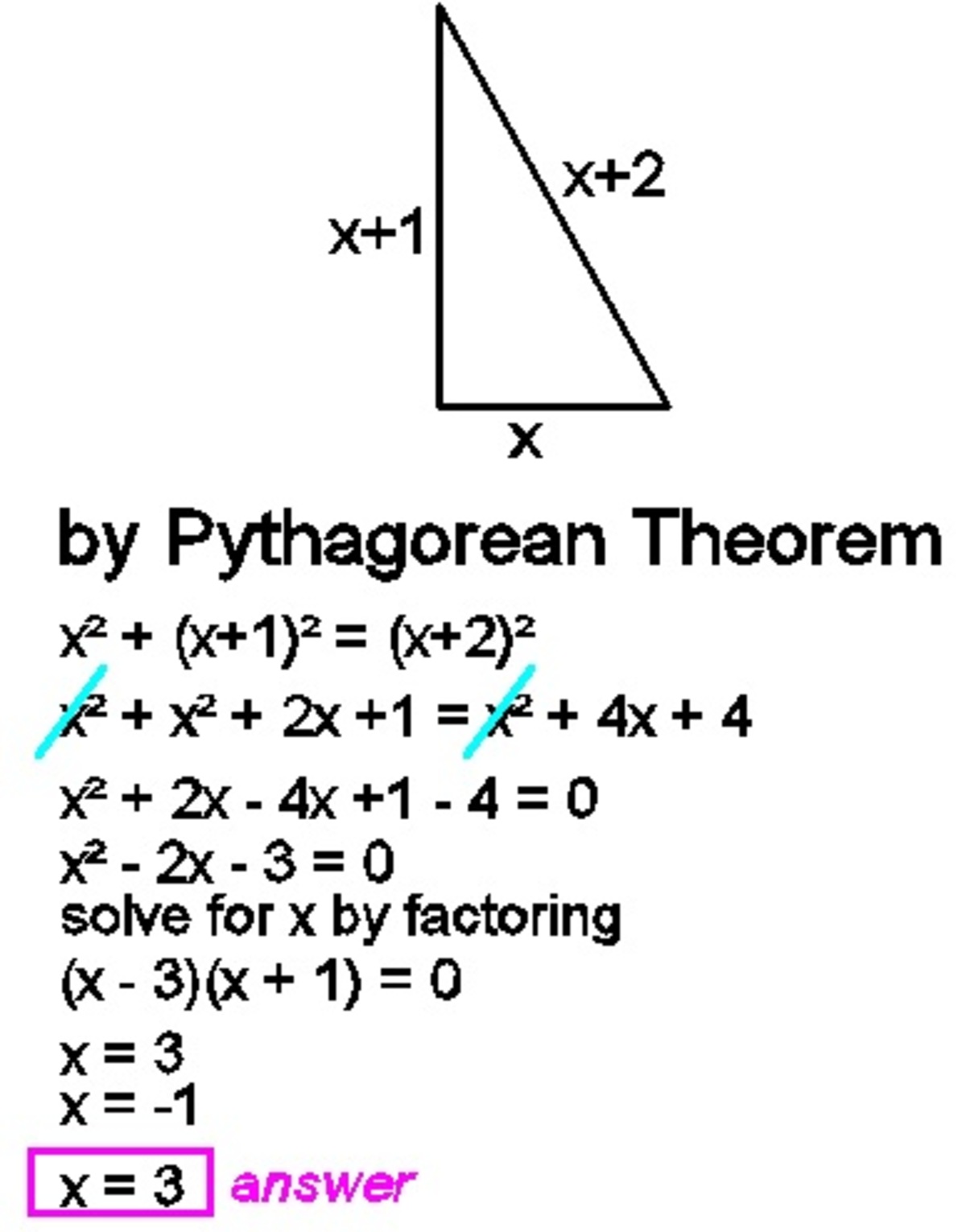
The lengths of the sides of a triangle are cm, cm, and cm. Determine so that this triangle is a right-angled triangle.
The answer is 3.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Relevant wiki: Pythagorean Theorem
According to Pythagorean Theorem,
x 2 + ( x + 1 ) 2 = ( x + 2 ) 2
x 2 = ( x + 2 ) 2 − ( x + 1 ) 2
x 2 = ( x + 2 + x + 1 ) ( x + 2 − x − 1 )
x 2 = 2 x + 3
You end up with a quadratic equation:
x 2 − 2 x − 3 = 0
Split the middle term:
x 2 − 3 x + x − 3 = 0
Solve for x by factoring:
( x − 3 ) ( x + 1 ) = 0
∴ x = 3 or x = − 1
As length cannot be negative, the second solution is not applicable.
So, the answer must be x = 3 .