Atmospheric physics 9: Atmospheric stability
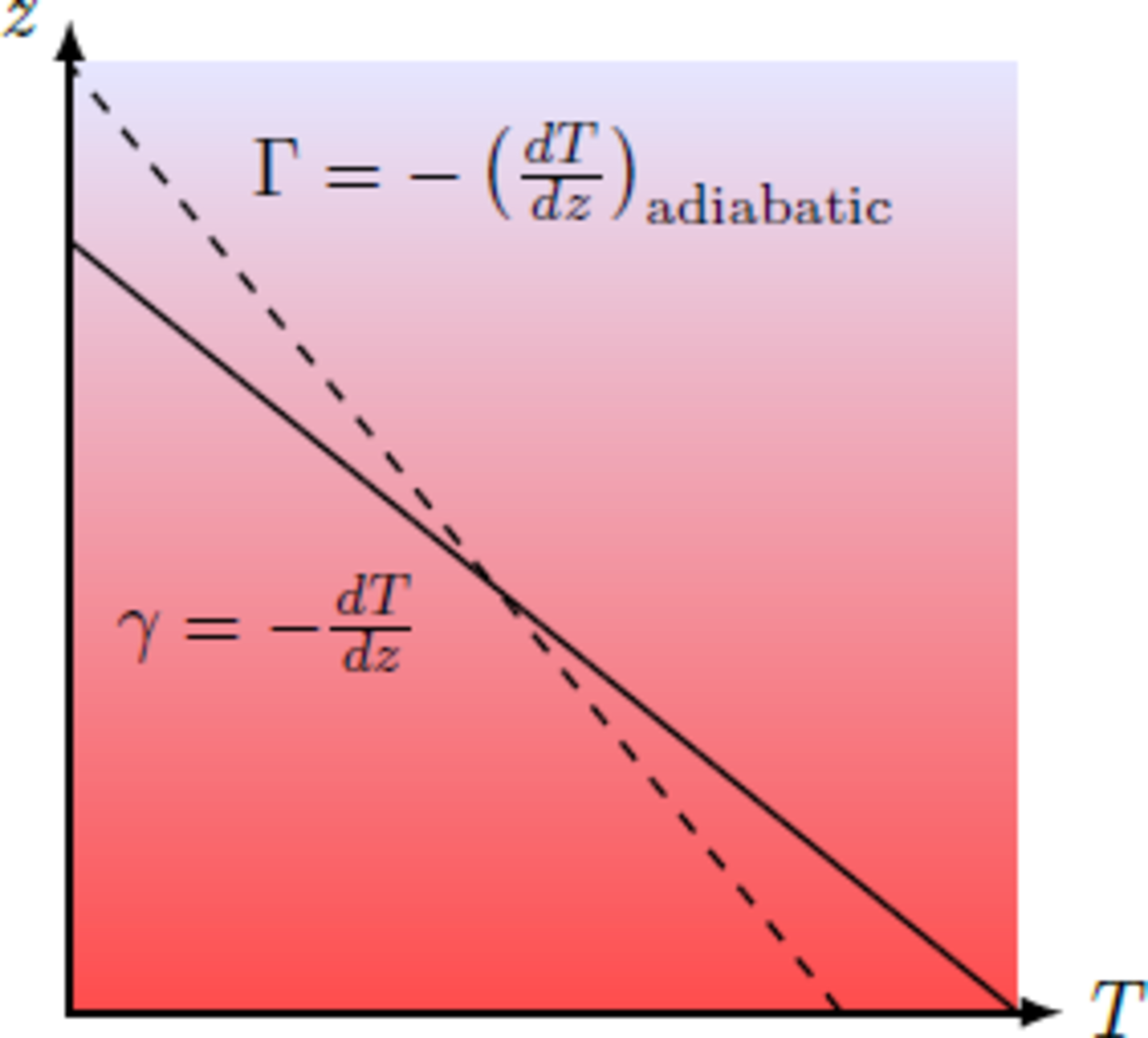
Due to the current weather conditions, there is a linear temperature profile in the lowest layers of the atmosphere with where the temperature gradient is much larger than the adiabatic temperature gradient , which we determined in the previous section. Thus, the air temperature decreases very rapidly with increasing altitude. Which statement can be made about the atmospheric layers?
Hints: To estimate the stability of the atmosphere, consider an air parcel, that is displaced from its alititude up or down. Due to the change in pressure, it adiabatically changes its temperature. What is the direction of net buoyancy acting on the air parcel in the new enviroment?
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
If an air parcel is displaced from the height z by the value ± Δ z , its temperature changes by the adiabatic process by the value delta Δ T = ∓ Γ Δ z . The new states of the air parcel lie on the dashed line, which corresponds to the adiabatic temperature gradient Γ . The temperature change of the air parcel is, however, less than the temperature change in the surrounding air.
If the air parcel is deflected upwards, it is warmer than the environment. Due to the lower density of the parcel, a net buoyancy force then acts to further accelerate the deflected air. So there is a positive feedback, so that the air parcel rises more and more in the atmosphere
If the air parcel is deflected down, the reverse process happens. The air package heats up more slowly than the surrounding atmosphere, so that the deflected air is colder than the environment. Because the air is denser than the environment, a net gravity acts to accelerate the package downwards so that the air continues to sink.
Even small fluctuations thus ensure that air parcels rise and fall, so that there is an atmospheric instability. It therefore comes to spontaneous up and downdraft, so that the air layers are mixed by the convection.