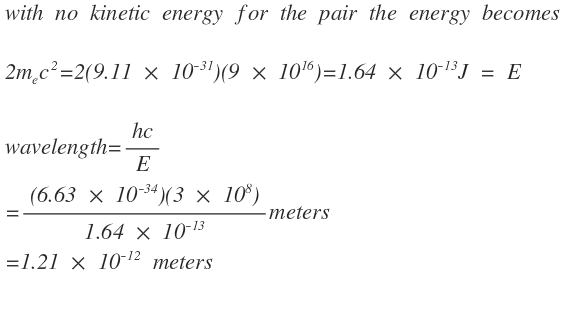Pair Production
Calculate the wavelength of the least energetic photon capable of producing an electron-positron pair in meters.

The answer is 1.21E-12.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
E = h v
v = λ c
Minimum energy
= 2 m e v 2
= 2 ( 9 . 1 ∗ 1 0 − 3 1 k g ) ( 3 ∗ 1 0 8 m / s ) 2
= 1 . 6 3 8 ∗ 1 0 − 1 3 J
= 1 . 0 2 2 M e V
Minimum frequency
= h 2 m e v 2
= 6 . 6 2 6 ∗ 1 0 − 3 4 J s 2 ( 9 . 1 ∗ 1 0 − 3 1 k g ) ( 3 ∗ 1 0 8 m / s ) 2
= 2 . 4 7 2 ∗ 1 0 2 0 H z
Minimum wavelength
= f r e q u e n c y c
= 2 . 4 7 2 ∗ 1 0 2 0 H z 3 ∗ 1 0 8 m / s
= 1 . 2 ∗ 1 0 − 1 2 m
This is the threshold wavelength of an incoming photon in pair production. Simply use the photoelectric effect formula of hv and set it equal to two electron (neglecting nuclear recoil)...and solve in terms of wavelength! :)