Bad Karma is a Consequence of Guessing
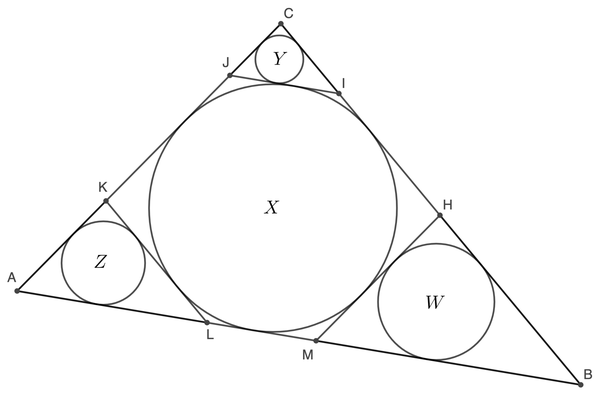
△ A B C contains four inscribed circles. Seqments J I , K L , and M H are parallel to the sides of △ A B C which they do not intersect. Compare the radius of circle X to the sum of the radii of circles Y , Z , and W .
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Well done!
The triangles A B C , A L K , M B H and J I C are all similar, and so we deduce that Z = h a h a − 2 X X W = h b h b − 2 X X Y = h c h c − 2 X X where h a , h b , h c are the lengths of the altitudes of the triangle A B C from the vertices A , B , C respectively. This is because the length of the altitude from A in the triangle A L K is h a − 2 X , and so on. Thus Y + Z + W = 3 X − 2 X 2 ( h a − 1 + h b − 1 + h c − 1 ) = 3 X − Δ X 2 ( a + b + c ) = 3 X − Δ 2 X 2 s = 3 X − 2 X = X where Δ , s are the area and semiperimeter of the triangle A B C .
Since J I ∥ A B , H M ∥ C A and K L ∥ C B , △ A B C ∼ △ J I C ∼ △ M B H ∼ △ A L K ⟹ A B M B = X W , A B J I = X Y , A B A L = X Z ( 1 ) Observe, △ A B C ∼ △ J I C ∼ △ M F L Also, △ J I C and △ M F L have the same exradius ( X ) , so we have, △ J I C ≅ △ M F L ⟹ J I = L M ( 2 ) Using ( 1 ) and ( 2 ) , A B M B + A B J I + A B A L ⟹ A B M B + L M + A L ∴ X = W + Y + Z = X W + X Y + X Z = X W + Y + Z