BID for the angle
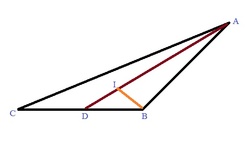 Given in the figure, a
Δ
A
B
C
with sides
A
B
=
3
2
−
6
,
A
C
=
3
2
+
6
and
B
C
=
6
units.
A
D
is the angle bisector of
∠
B
A
C
, with
D
on
B
C
.
I
is the in-center of
Δ
A
B
C
.
Given in the figure, a
Δ
A
B
C
with sides
A
B
=
3
2
−
6
,
A
C
=
3
2
+
6
and
B
C
=
6
units.
A
D
is the angle bisector of
∠
B
A
C
, with
D
on
B
C
.
I
is the in-center of
Δ
A
B
C
.
∠ B I D = cot − 1 ( P + Q − R − S )
where P , Q , R , S are integers with P , Q , R being square free. Find the value of P + Q + R + S .
Clarification : cot − 1 ( x ) = arccot ( x ) .
The answer is 13.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Please correct your diagram. Angle BID=A/2+B/2=82.5 from your calculations. Tan82.5=root2+root3+root4+root6. It's reciprocal gives the answer directly.
Also tan(C/2) also gives the answer, no need of incenter.
Log in to reply
The diagram is correct, whats the problem. I took incenter so as to apply m-n cot theorem.
Log in to reply
Sorry. Since it was a portion of the triangle , I was mislead . The diagram IS correct.
and in exams we are not allowed to use calculator so its basically a JEE approach
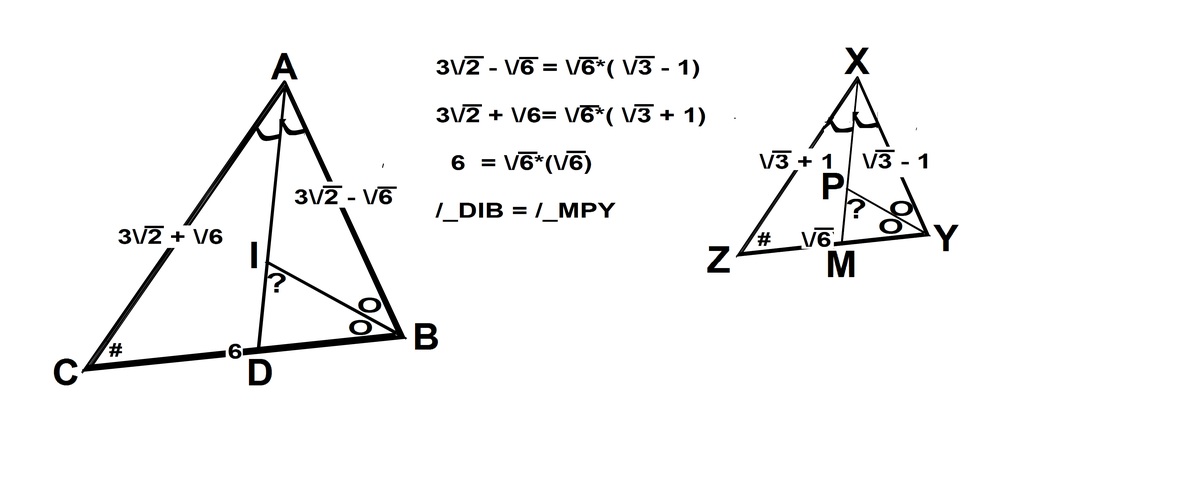
There are three steps to the solution of this problem on triangle.
-
Finding out Δ X Y Z ≅ Δ A B C so that converted data of Δ X Y Z is simpler than that of Δ A B C .
-
The acute angle between angle bisector from X and Y = 2 π − Z .
-
Use Cos Rule to find 2 Z , and relate it to the answer reqired.
1.. Dividing all three sides of the △ A B C b y 6 , w e g e t a s i m i l a r Δ X Y Z . M ≅ D , a n d P ≅ I . S o ∠ B I D = ∠ Y P M . X Y = 3 − 1 , Y Z = 6 , X Z = 3 + 1 . 2 . e x t e r n a l ∠ Y P M = i n t e r n a l ∠ s 2 X + 2 Y . 2 X + 2 Y + 2 Z = 2 π , ⟹ 2 π − ∠ Y P M = 2 Z . ∴ C o t B I D = C o t Y P M = C o t { 2 π − 2 Z } = T a n 2 Z . 3 . C o s Z = 2 ∗ 6 ∗ ( 3 + 1 ) ( 6 ) 2 + ( 3 + 1 ) 2 − ( 3 − 1 ) 2 = 2 ∗ ( 3 + 1 ) 3 + 2 B u t C o c Z = 2 ∗ C o s 2 2 Z − 1 , ⟹ C o s 2 2 Z = 2 C o s Z + 1 ∴ C o s 2 2 Z = 2 ∗ 2 ∗ ( 3 + 1 ) 3 + 2 + 6 + 2 . ∴ T a n 2 2 Z = C o s 2 2 Z 1 − 1 = 3 + 2 + 6 + 2 2 ∗ 2 ∗ ( 3 + 1 ) − 1 . O n r a t i o n a l i s i n g C o t B I D = T a n 2 Z = 6 + 2 − 3 − 2 = P + Q − R − S . ∴ P + Q + R + S = 1 3
Using cosine rule
∠ B A C = 6 0 ∘ ; ∠ B C A = 1 5 ∘
∠ D A B = 3 0 ∘ as AD is angle bisector.
∠ A D B = ∠ I D B ( o f c o u r s e ) = 4 5 ∘ , exterior angle property.
Now, we know in-center divides the angle bisector in the ratio excluded side sum of sides excluding the side opposite to the vertex from which the angle bisector is drawn
I D A I = 6 3 2 + 6 + 3 2 − 6 = 1 2 = n m
Using m-n cot theorem
( 2 + 1 ) k cot ( ∠ B I D ) = k cot ( 3 0 ∘ ) − 2 k cot ( 4 5 ∘ )
∠ B I D = cot − 1 ( 6 + 2 − 3 − 2 )