Bonne Chance!
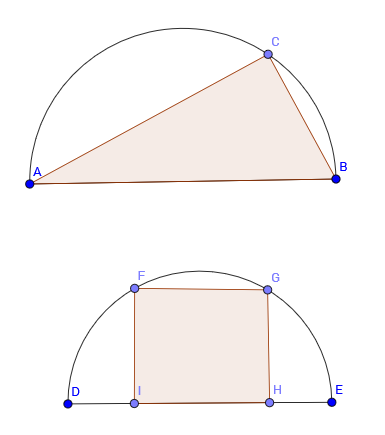
A triangle and a rectangle are in semicircles of radius where two of their vertices are on the diameter, and the rests are on the arc. The angle of vertex of the triangle is equally probable to be any angle between and , while for a rectangle the height is equally probable to be any height between and . If you throw a dart and hit a polygon in the semicircle you will win a prize, but you are blindfolded, and you just have one chance. Which polygon will you choose? Why?
Assume that the dart has an equal chance of landing anywhere on the semicircle.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
We can calculate the expected area for the two shapes. We want to aim at the one with the largest area to have the highest probability of hitting it. WLOG, let r = 1 and let O be the centre of the circle. We begin with the triangle :
Let ∠ C A B = θ ⇒ ∠ C O B = 2 θ because angle at the centre is twice angle at the circumference.
We calculate the area of [ △ A C B ] = [ △ C O A ] + [ △ C O B ] = 2 1 × 1 × 1 × sin ( 1 8 0 ∘ − 2 θ ) + 2 1 × 1 × 1 × sin ( 2 θ ) = sin ( 2 θ )
So the expected value of the area is 2 π − 0 ∫ 0 2 π sin ( 2 θ ) d θ = 2 π 1 = π 2 .
Now we move on to the rectangle :
If the height of the rectangle is h we have the width of the triangle as 2 1 − h 2 by Pythagoras' theorem on △ F O M where M is the midpoint of F G .
The area of the rectangle therefore is 2 h 1 − h 2 .
The expected value is: 1 − 0 ∫ 0 r 2 h 1 − h 2 d h = 3 2 .
As π > 3 ⇒ π 2 < 3 2 so the expected area of the rectangle is bigger so we want to aim at the rectangle .