Bridge to Nowhere
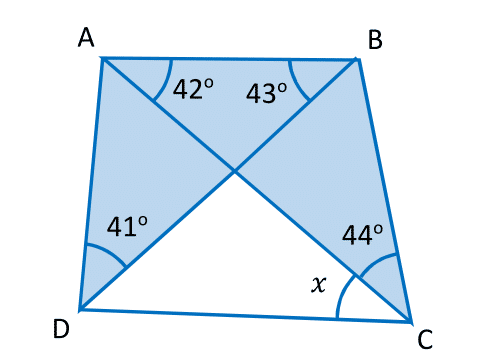 In a quadrilateral
,
, and
. Find
to 2 decimal places.
In a quadrilateral
,
, and
. Find
to 2 decimal places.
The answer is 45.55.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
sin ( 4 1 ) A E = sin ( 5 4 ) 1 , sin ( 4 2 ) B E = sin ( 4 3 ) A E , sin ( 5 1 ) C E = sin ( 4 4 ) B E
C E = sin ( 4 4 ) sin ( 5 1 ) × sin ( 4 3 ) sin ( 4 2 ) × sin ( 5 4 ) sin ( 4 1 ) = 0 . 8 9 0 1 1
In the △ C D E the ∠ C E D = 9 5 ∘ and the sides next to it are 1 and 0.89011. C D can be obtained from the law of cosines as
C D = 1 + 0 . 8 9 0 1 1 2 − 2 × 0 . 8 9 0 1 1 × cos ( 9 5 ) = 1 . 3 9 5 5
The law of sines applied to the △ C D E provides x as
x = arcsin ( 1 . 3 9 5 5 sin ( 9 5 ) ) = 4 5 . 5 5 ∘