Brightness of bulb
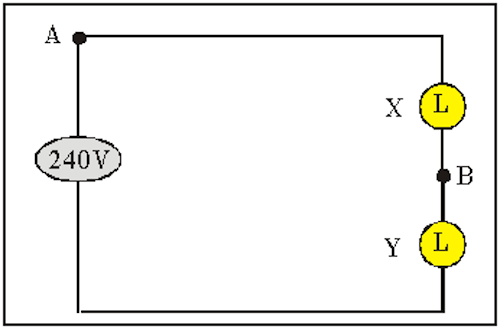 Two identical light bulbs
and
, which are rated at
;
are connected in series to a
source, as shown in the above diagram. If point
A
in the circuit is now connected to point
B
by a piece of copper wire with very low resistance, how will the brightness of each bulb change?
Two identical light bulbs
and
, which are rated at
;
are connected in series to a
source, as shown in the above diagram. If point
A
in the circuit is now connected to point
B
by a piece of copper wire with very low resistance, how will the brightness of each bulb change?
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
By creating an alternative pathway of lower resistance from A to B , the current induced by the e.m.f. source bypasses the route that contains bulb X . This results in almost negligible current passing through bulb X and hence would not light up. Since all the current mainly goes through bulb Y , bulb Y will receive the same voltage as that of the e.m.f. source. Thus, burning the brightest.