Broken Bamboo
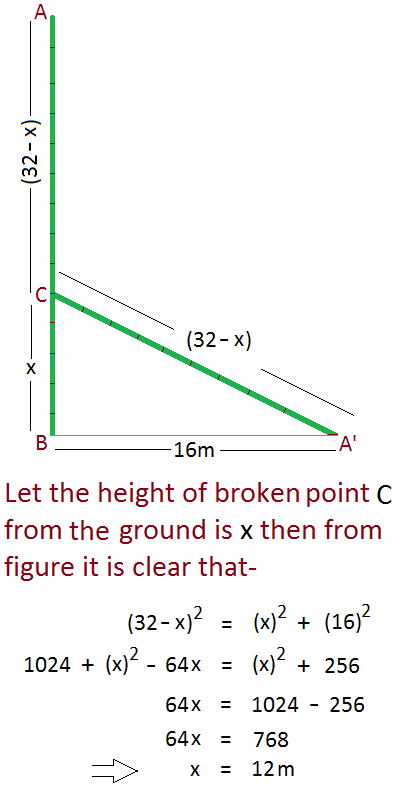
A vertical 32-meter bamboo stick was broken by the wind, such that the tip meets the ground at a point 16 meters from the base. At what height above the ground (in meters) was it broken?

The answer is 12.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
15 solutions
youu explain this question perfectly
Hi, I don't get why AC equals to A'C. I assumed that AB+A'C equals 32m
Log in to reply
i also dont understand that
Ac turn into A'C
The question was not phrased properly if you ask me
Its the broken point of the bamboo. Its like you take a bamboo and break it at point C. So AC and A'C both are the same part of the bamboo. So we are just calling it with different names.
me too, so got it wrong :\
Nice question
Why is it squared
Can anyone explain the where "-64x" came from?
Log in to reply
Expand (32-x)(32-x) = 32.32 -32x-32x + x.x = 1024-64x+x.x
The wording of the problem is confusing. I believed the stick was 32 meters tall then the wind broke off segment AC so the remaining height of the stick would be 32-AC
Log in to reply
It looks like you interpreted the question correctly and you can certainly solve the problem using your proposed method. Notice that in Banti's diagram, the remaining height of the stick (x) is indeed 32 - AC. That is, x = 32 - (32-x)
If the height of the stick is 32-AC and the hypotenuse of the right triangle is AC then you'd use the Pythagorean theorem to get AC=20, which makes the height 32-20=12.
This question was not phrased properly :(
I agree with a previous comment. The problem makes it sound like the stick was 32m BEFORE it broke. If worded correctly, this is simple.
Log in to reply
The stick was 32 meters before it broke. The drawing is a bit confusing but the question was clear.
Hi, I don’t get why (32-x)^2 would equal x^2 + 16^2 / what that has to do with the problem. Wouldn’t it be as simple as, if it fall the length of 16ft , the part that fell would =16, therefore 32-16= 16, however that doesn’t make sense with the diagram?
Here, AC+BC=32
From triangle, A C 2 - B C 2 = A B 2 = 1 6 2
→ (AC+BC) (AC-BC) = 256
→ 32 (AC-BC) = 256
→ AC-BC = 8
From above two equation we can calculate BC = 12
This is the one I employed
Set BC is x and AC is y, AC=A'C, so A'C =y x=32-y 16squared+xsquared=ysquared (pythagorean theorem) Then use x to find y 256+(32-y)squared=ysquared 256+1024-64y+ysquared=ysquared 256+1024=64y 1280=64y 20=y Then, 32-20=12
Well done Albert. One thing, to express 16 squared, you can write as 16^2. ^ is the standard way to express power. Keep up and Have fun.
G i v e n
A B = 3 2 m
A ′ B = 1 6 m
L e t : A C = b , C B = a
T h e n : b = 3 2 − a
A s s u m p t i o n : the bamboo stick is perpendicular on the ground
U s i n g P y t h a g o r a s
b 2 = a 2 + 1 6 2
( 3 2 − a ) 2 = a 2 + 1 6 2
3 2 2 + a 2 − 2 × 3 2 a = a 2 + 1 6 2
2 1 0 − 2 6 a = 2 8
a = 2 6 2 2 × 2 8 − 2 8
a = 2 6 2 8 × ( 2 2 − 1 )
a = 2 8 − 6 × ( 2 2 − 1 ) = 4 × 3 = 1 2 m
It's pretty easy to guess; since the distance 1 6 shown in the diagram is one of the legs of the right triangle, the triangle has to satisfy one of the Pythagorean triples (the answer has to be an integer). In this case, the triplets are 6 , 8 , 1 0 , multiplying by 2 gives 1 2 , 1 6 , 2 0
The answer is 1 2
Why is it required that the answer be an integer? Nowhere in the problem is that requirement stated. You got lucky that it happened to work out that way. Be careful about assumptions.
Some times math is just a game , luck has a great deal with that. I like this solution
While it is not a requirement, the assumption that the solution may be related to a 3-4-5 triplet is easily checked. If 12 is the answer, then 20 must result from the hypotenuse for the total length to be 32. That is the case here. So what started as a guess ended up being verifiable rather quickly.
lets x be the height above the ground,BC=x,AC=(32-x)A'C=(32-x), we have from right angle triangle x^2+16^2=(x-32)^2, by solving the above equation we get x=12
Let the distance from the base to the breaking point be x meter, hence the remaining is (32-x) meter. Therefore, the distance from the tip to the cracking point is equivalent to 32-x. This satisfies the phytagorean theorm of x^2+y^2=z^2. Substituting the hypothenuse with 32-x, adjacent side with x, and the other one with 16, thus we get x =12.
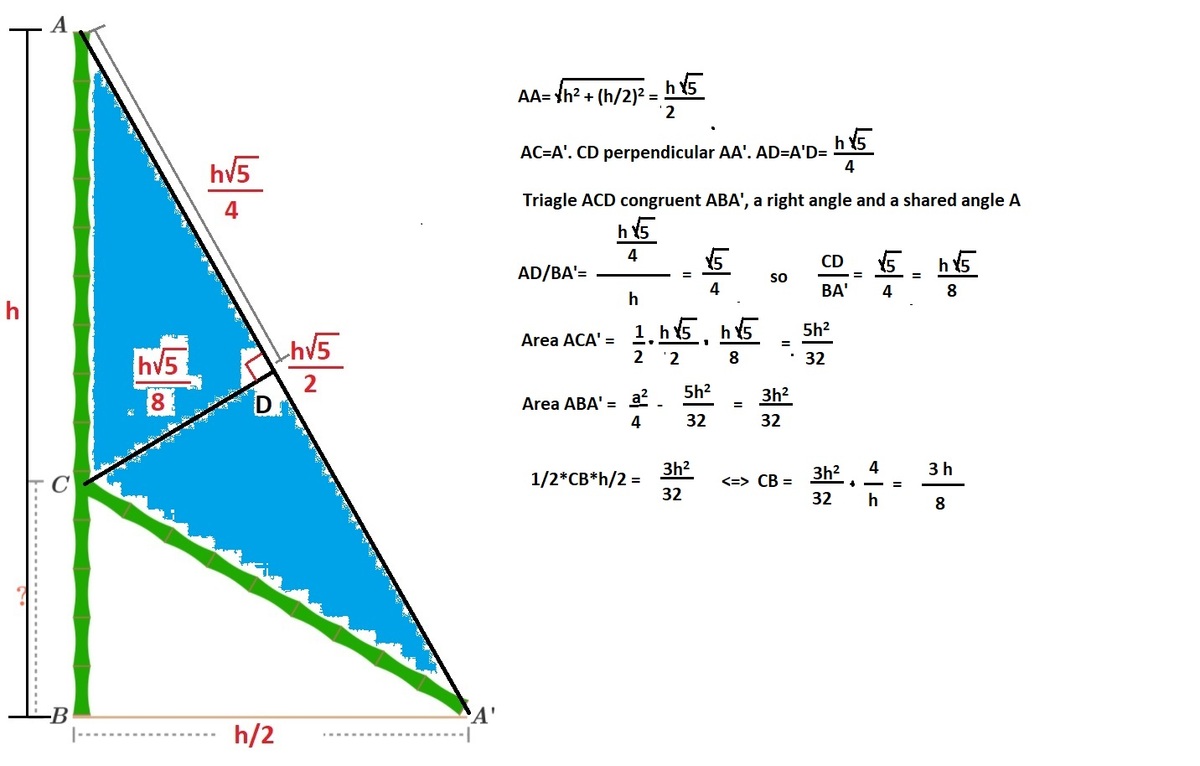
I have figured out a formula. If the height of a bamboo is "h" and the distance between its root and the point at which its vertex touches, when broken, is "h\2". Then the formula for calculating the remaining height is: h(r) = 3h/8.
Let's check it. When h=32, then h(r) = 3*32/8 = 12.
My strategy: Calculating the total area ABA', the subtracting the area shaded blue. Calculating the line CB based on the remaining area.
in pythagorus there is combination as 3,4,5 .in this they are multiply by 4,logical answer 12
The question is asking as to resolve the length of BC
We know that AC = A´C, and from here we can create a couple of equations with two variables each to help us resolve the problem:
-
we know that AC + BC = 32;
-
according to Pythagoras theorem, AC2 = BC2 + 162 => AC2 - BC2 = 256. This can also be written as: (AC – BC) x (AC + BC) = 256;
We know from the first equation the value of AC + BC, which we can substiture in the second equation: (AC – BC) x 32 = 256 => AC – BC = 256 / 32 => AC – BC = 8
We have now ended up with two equations that are solved easily:
AC + BC = 32 and AC – BC = 8
Which takes us to conclude that BC = 12
Using the 3 - 4 - 5 triangle, we find that 4 x 4 = 16, and thus that the other two are 3 x 4 = 12, and 5 x 4 = 20. Since we need the opposite side of the triangle, we fins that the answer is 12 meters
Relevant wiki: Pythagorean Theorem
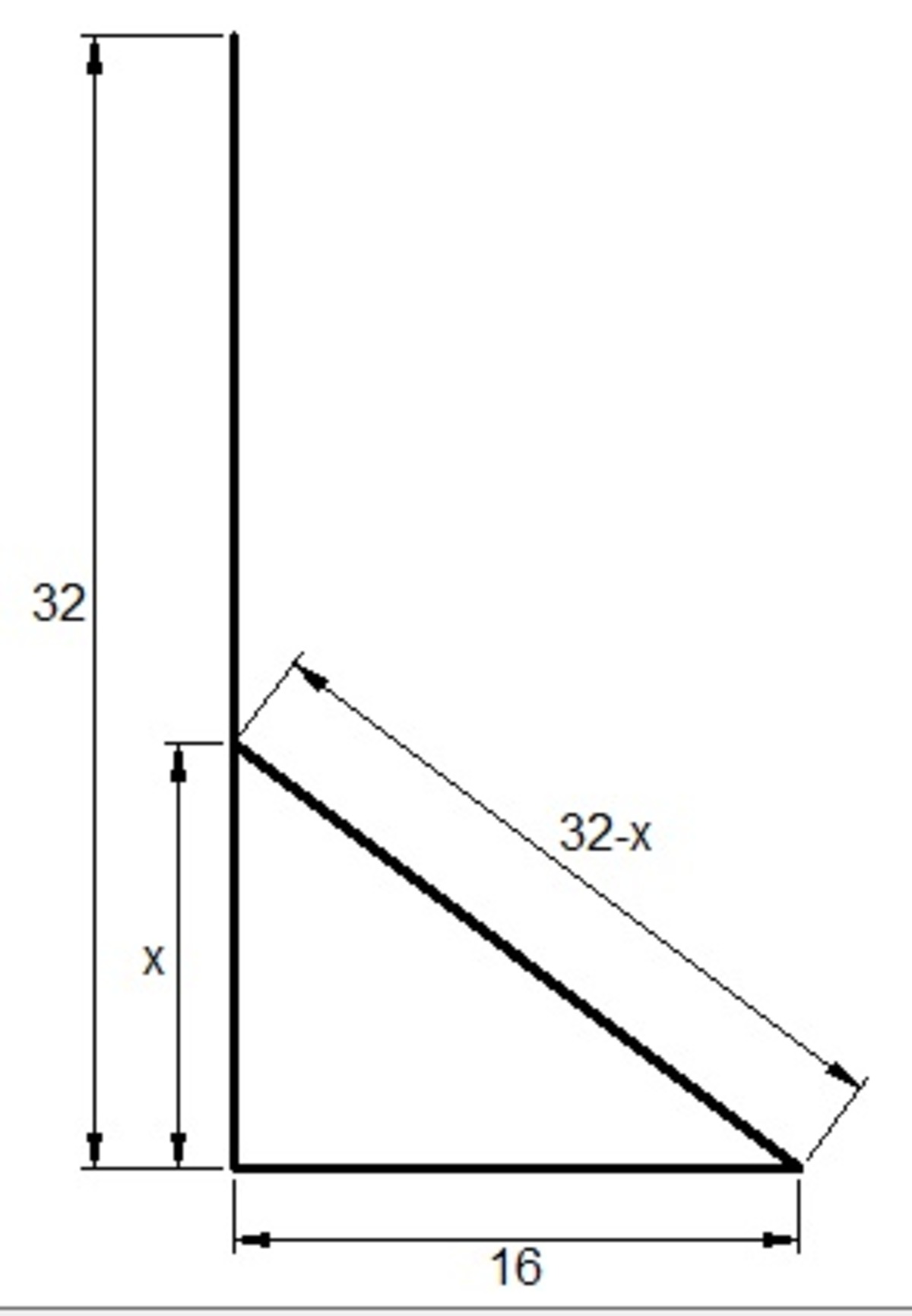 Consider the diagram. Using
pythagorean theorem
, we have
Consider the diagram. Using
pythagorean theorem
, we have
( 3 2 − x ) 2 = x 2 + 1 6 2
1 0 2 4 − 6 4 x + x 2 = x 2 + 2 5 6
7 6 8 = 6 4 x
x = 1 2
From the problem:
B C + A C = 3 2
We can solve for A C :
A C = 3 2 − B C
From the Pythagorean Theorem:
A B 2 + B C 2 = A C 2
Substituting in data from the problem we get:
1 6 2 + B C 2 = A C 2
∴ 2 5 6 + B C 2 = A C 2
Now we have two ways to express A C 2
A C 2 = ( 3 2 − B C ) 2
A C 2 = B C 2 + 2 5 6
so we can set those equal to each other and solve for B C .
( 3 2 − B C ) 2 = B C 2 + 2 5 6
∴ 1 0 2 4 − 6 4 B C + B C 2 = B C 2 + 2 5 6
∴ 1 0 2 4 − 6 4 B C = 2 5 6
∴ − 6 4 B C − 7 6 8
∴ B C = 1 2
The no of squares in side cb = 5x The no of squares in side c a' = 8x By pathagorus Therefore, CB equal 12 cm
I took the clever way out. The black lines dividing up the piece of bamboo look more or less even. So I counted them up (14 total). 32/14=2.28 .. 2.28 * 5 = 11.39 .. Round up .. Boom 12. ;)