Tricky Calculus Question I
∫ 6 π 3 π 1 + tan 2 0 1 8 ( x ) 1 d x = k π
Given the above, find the value of k .
The answer is 12.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
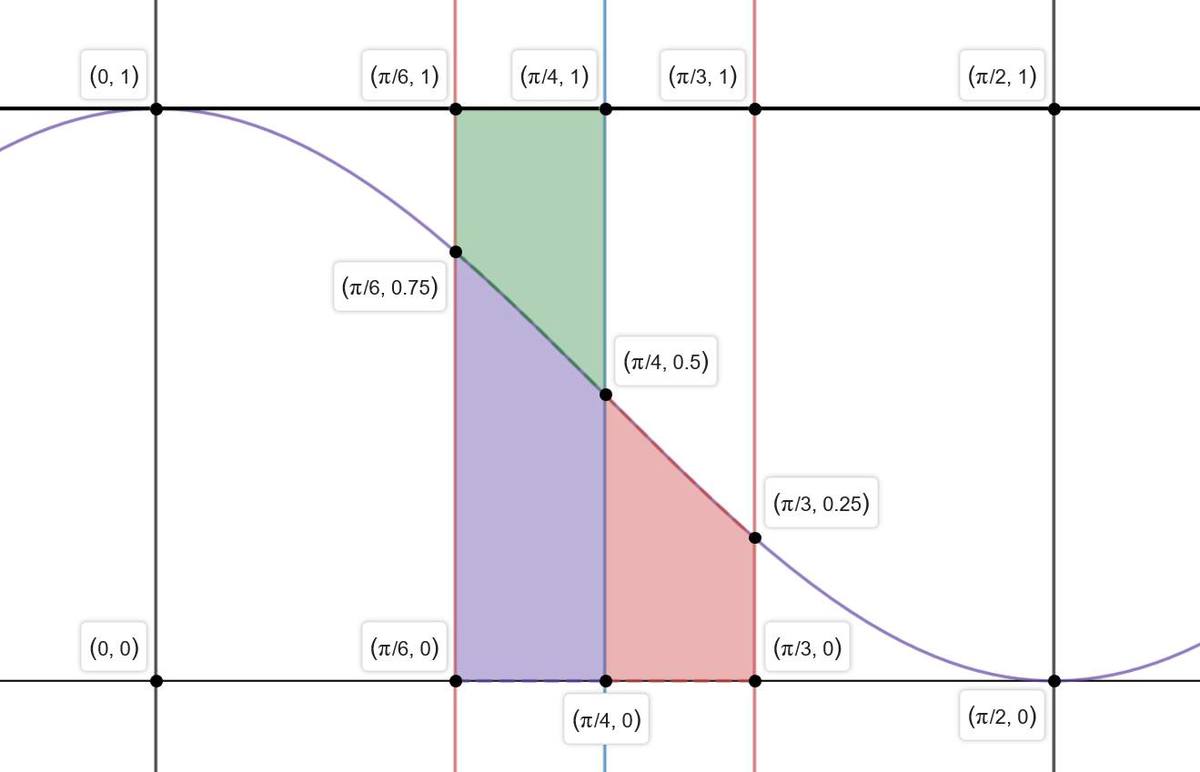
First, we need to prove that the graph of f ( x ) is symmetry about a point between 0 ≤ x ≤ 2 π .
0 ≤ x ≤ 2 π ,
f ( 2 π − x ) = 1 + t a n k ( 2 π − x ) 1 = 1 + c o t k ( x ) 1
f ( x ) + f ( 2 π − x ) = 1 + t a n k ( x ) 1 + 1 + c o t k ( x ) 1 = 1
0 ≤ x ≤ 4 π ,
f ( 4 π − x ) = f ( 2 π − ( 4 π + x ) ) = 1 − f ( 4 π + x )
f ( 4 π − x ) + f ( 4 π + x ) = 1
Thus, we found that the graph of f ( x ) is symmetry about a point ( 4 π , 2 1 ) between 0 ≤ x ≤ 2 π .
∫ 6 π 3 π 1 + t a n k ( x ) 1 d x = Area of purple region + Area of red region = Area of purple region + Area of green region (based on symmetric) = ( 4 π − 3 π ) ⋅ ( 1 ) = 1 2 π
Substitute k = 2 0 1 8 ,
∫
6
π
3
π
1
+
t
a
n
2
0
1
8
(
x
)
1
d
x
=
1
2
π
You don't need to key in text in LaTex in you problem question. It is difficult and not the standard practice of Brilliant.org. Just like function such as \int, \frac, and \pi you need a "\" for \tan. Note that when you enter tan x t a n x , all tan and x are in italic and there is no space between tan and x even though we enter a space. Note that now enter \tan x tan x , tan is not in italic because it is a function. Italic is for variables and constants. Numbers re also not in italic. Also note that there is a space between tan and x. Similarly it is \sin, \cos, \csc, \sec, \ln, \log etc.
Log in to reply
Hi, thanks for teaching me about the coding style of latex, I've start learning latex since last week and it's quite fun!
Log in to reply
You can see the codes by placing your mouse cursor on the formulas or click the pull-down menu " ⋯ More" at the bottom of the answer section and select "Toggle LaTex". You can also use this Daum Equation Editor to learn the codes.
I = ∫ 6 π 3 π 1 + tan 2 0 1 8 x 1 d x = 2 1 ∫ 6 π 3 π ( 1 + tan 2 0 1 8 x 1 + 1 + tan 2 0 1 8 ( 2 π − x ) 1 ) d x = 2 1 ∫ 6 π 3 π ( 1 + tan 2 0 1 8 x 1 + 1 + cot 2 0 1 8 x 1 ) d x = 2 1 ∫ 6 π 3 π ( 1 + tan 2 0 1 8 x 1 + 1 + tan 2 0 1 8 x 1 1 ) d x = 2 1 ∫ 6 π 3 π ( 1 + tan 2 0 1 8 x 1 + tan 2 0 1 8 x + 1 tan 2 0 1 8 x ) d x = 2 1 ∫ 6 π 3 π d x = 2 x ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ 6 π 3 π = 1 2 π Using ∫ a b f ( x ) d x = ∫ a b f ( a + b − x ) d x
Therefore, k = 1 2 .