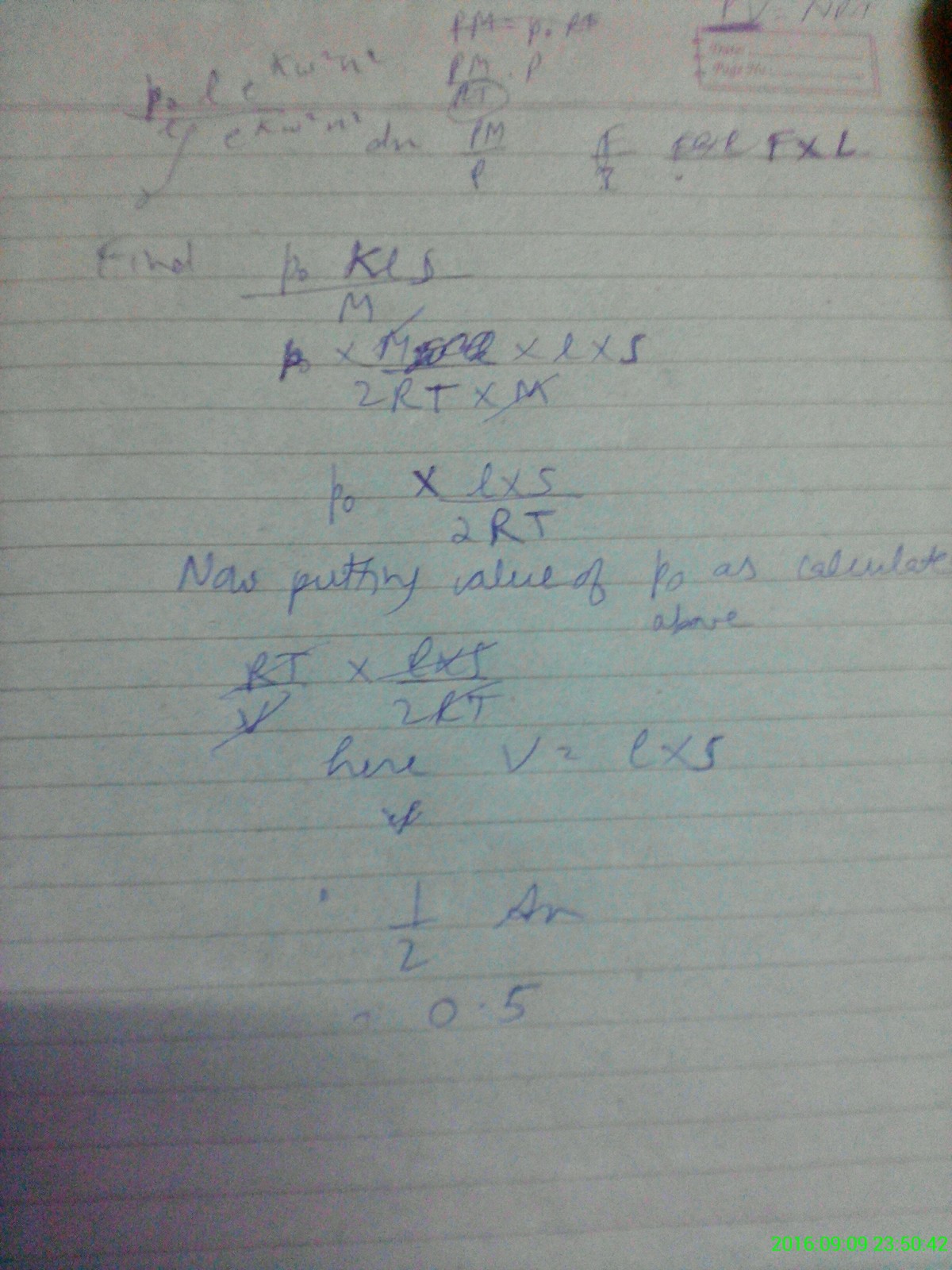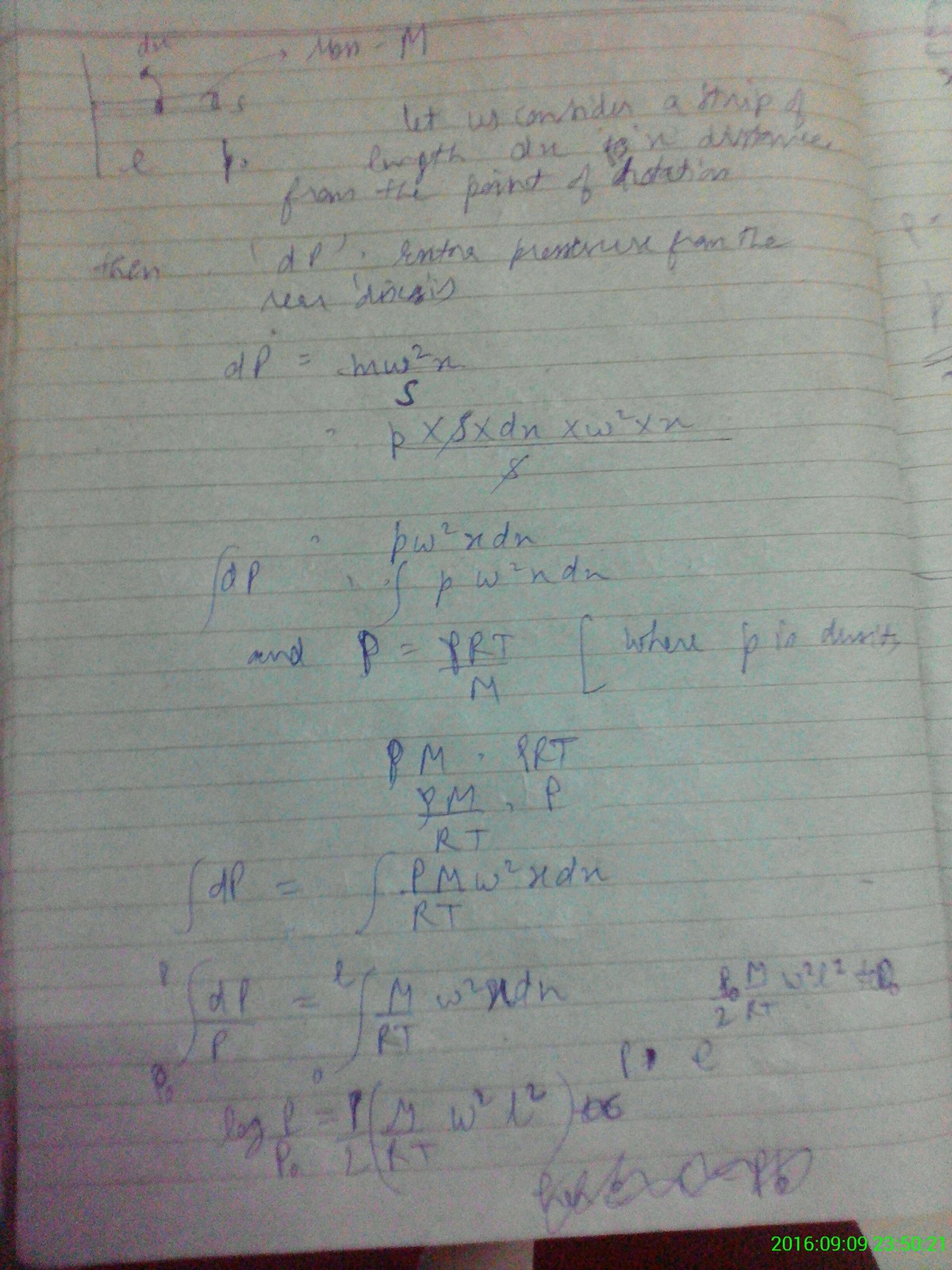Can it be practically evaluated?
A narrow horizontal cylindrical tube is filled with a gas. The tube rotates in a horizontal plane with an angular velocity about a perpendicular axis through one of its ends A. The length of the tube is and cross sectional area is . Total mass of contained gas is . When the tube was at rest initially, it had a pressure and a temperature .
Assuming that the temperature remained constant, find the Pressure in the tube as a function of distance x from the end A.
If for some constant , find
We've got more for you at the set
The answer is 0.5.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.