Can you solve this without calculator attack ( Part 2)?
sin 1 8 ∘ = ?
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
10 solutions
Moderator note:
I'm speechless, well done!
i dnt quite get it :(
wow! take a bow Sir!
This is sublime. :)
The best one
This is outstanding! Simple n elegant!
Out of the world..!
We can make use of the identities sin ( 3 x ) = 3 sin ( x ) − 4 sin 3 ( x ) and cos ( 2 x ) = 1 − 2 sin 2 ( x ) . With x = 1 8 ∘ and letting t = sin ( 1 8 ∘ ) we have that sin ( 5 4 ∘ ) = sin ( 3 ∗ 1 8 ∘ ) = 3 t − 4 t 3 and cos ( 3 6 ∘ ) = 1 − 2 t 2 .
But sin ( 5 4 ∘ ) = cos ( 3 6 ∘ ) , so
3 t − 4 t 3 = 1 − 2 t 2 ⟹ 4 t 3 − 2 t 2 − 3 t + 1 = 0 ⟹ ( t − 1 ) ( 4 t 2 + 2 t − 1 ) = 0 .
Now clearly t = 1 , so t must be a root of 4 t 2 + 2 t − 1 , i.e.,
t = 8 − 2 ± 4 + 1 6 = 4 − 1 ± 5 .
Now clearly t = sin ( 1 8 ∘ ) > 0 , so we must have sin ( 1 8 ∘ ) = 4 − 1 + 5 .
Moderator note:
Nicely done! You made a simple connection by setting up sin ( 5 4 ∘ ) = cos ( 3 6 ∘ ) .
clear and nice solving
use the formulas: sin(x) = cos(90°-x) cos(2x) = 1 - 2 sin²(x) cos²(x) = 1 - sin²(x) sin(2x) = 2 sin(x) cos(x)
so,
sin(18°) = cos(90°-18°) sin(18°) = cos(72°) sin(18°) = cos(2(2 18°)) sin(18°) = 1 - 2sin²(2 18°) sin(18°) = 1 - 2(sin(2*18°))² sin(18°) = 1 - 2(2 sin(18°) cos(18°))² sin(18°) = 1 - (8sin²(18°) cos²(18°)) sin(18°) = 1 - (8sin²(18°)(1 - sin²(18°))) sin(18°) = 1 - 8sin²(18°) + 8sin⁴(18°) 8sin⁴(18°) - 8sin²(18°) -sin(18°) + 1 = 0
suppose sin(18°) = x
8x⁴ - 8x² - x + 1 = 0 the roots are:
x 1 = 1 x 2 = -½ x 3 = -¼ (1 + √5) x 4 = ¼ (-1 + √5)
so;
sin(18°) = 1 ............................(false) sin(18°) = -½ ........................(false) sin(18°) = -¼ (1 + √5)......... (false. must positive) sin (18°) = ¼ (-1 + √5)...........(true)
U have given an excellent explanation than that of others.,good.,keep going.,
I used Chebyshev Polynomials .
sin ( 1 8 ∘ ) = cos ( 7 2 ∘ ) . With T 5 ( x ) = 1 6 x 5 − 2 0 x 3 + 5 x which could be easily verified. Letting x = 7 2 ∘ ⇒ 5 x = 3 6 0 ∘ ⇒ cos ( 5 x ) = 1 and let y = cos ( x ) :
We have 1 6 y 5 − 2 0 y 3 + 5 y = − 1 . By Rational Root Theorem, we can factor out ( y + 1 ) , leaving: 1 6 y 4 − 1 6 y 3 − 4 y 2 + 4 y + 1 = ( 4 y 2 − 2 y − 1 ) 2 . By quadratic formula and taking only the positive root: sin ( 1 8 ∘ ) = cos ( 7 2 ∘ ) = 4 − 1 + 5 .
Moderator note:
Impractical but correct.
cos 5x = 1 not -1
@Trevor Arashiro , does this interest you?
Let x = 18
Then 5 x = 90
Then
sin 2 x = cos 3 x .................. .....................(1)
sin 2 x = 2 sin x cos x ............................. (2)
cos 3 x = cos (2 x + x) = cos 2 x cos x - sin 2 x sin x =
[1 - 2 (sin x)^2] cos x - 2 cos x (sin x)^2
Then
cos 3 x = cos x[1 - 4 (sin x)^2] ............. (3)
Substitute from (2) , (3) in (1)
4 (sin x)^2 + 2 sin x - 1 = 0
Solving for sin x, we get the solution
Consider the equation x 5 − 1 = 0 .
The complex roots of the above equation are the roots of x 4 + x 3 + x 2 + x + 1 = 0
Hence, x 2 + x 2 1 + x + x 1 + 1 = 0
Letting, z = x + x 1 the equation becomes z 2 + z − 1 = 0 giving z = 2 − 1 − + 5
The values of x are c o s ( 5 2 r π ) − + i s i n ( 5 2 r π ) for r = 1 , 2
Hence, the values of z are 2 c o s ( 5 2 π ) and 2 c o s ( 5 4 π )
Now, c o s ( 5 4 π ) = − c o s ( 5 π ) .
Hence, c o s ( 5 π ) = c o s 3 6 ( d e g r e e s ) = 4 5 + 1 .
Now using the formula, c o s 2 A = 1 − 2 s i n 2 A one can easily find the value of s i n 1 8
Moderator note:
Nice use of roots of unity!
This could be solved geometrically, but I solved it with the small angle approximation. First convert to radians 1 8 ∘ = 1 8 0 1 8 π = 1 0 π ≈ . 3 1 4 1 0 π is a sufficiently small angle, so by the small angle approximation, sin 1 0 π ≈ 1 0 π Note that 4 × . 3 1 4 = 1 . 2 5 6 ≈ 5 − 1 . So a possible closed form is 4 − 1 + 5
Moderator note:
This solution has been marked wrong. Your solution only shows that it approximately equals to 4 − 1 + 5 and you did not mention the error term. You are not advised to post an antisolution. If you did post one, you should post something like this:
Because 0 ∘ < 1 8 ∘ < 3 0 ∘ with sin ( 3 0 ∘ ) = 2 1 , then the only possible solution from the given choices is positive and less than 2 1 is 4 − 1 + 5 .
Since sin 1 8 ∘ = cos 7 2 ∘ , we will determine value of cos 7 2 ∘
Set z = cos 7 2 ∘ + i sin 7 2 ∘ , we have then z + z 1 = 2 cos 7 2 ∘
Now, using De Moivre's Therome, we obtain
z 5 = cos 3 6 0 ∘ + i sin 3 6 0 ∘ = 1 ( z − 1 ) ( z 4 + z 3 + z 2 + z + 1 ) = 0
It gives two condition. First, z − 1 = 0 ⟹ z = 1 , for z = 1 , then z + z 1 = 1 + 1 = 2 cos 7 2 ∘ or cos 7 2 ∘ = 1 . This result is obviously wrong since 1 = cos 0 ∘ .
Second,
z 4 + z 3 + z 2 + z + 1 ) = 0 ( z 2 + z 2 1 ) + ( z + z 1 ) + 1 = 0 ( z + z 1 ) 2 + ( z + z 1 ) − 1 = 0 ( z + z 1 ) = 2 − 1 ± 5 2 cos 7 2 ∘ = 2 − 1 ± 5 cos 7 2 ∘ = 4 − 1 ± 5 .
We know that cos 7 2 ∘ is positive, then the required answer is cos 7 2 ∘ = 4 − 1 + 5
Note that sin 1 8 ∘ = sin 1 0 π = cos ( 2 π − 1 0 π ) = cos 5 2 π . Using the following identity:
cos 5 2 π + cos 5 4 π cos 5 2 π + 2 cos 2 5 2 π − 1 4 cos 2 5 2 π + 2 cos 5 2 π − 1 ⟹ cos 5 2 π sin 1 8 ∘ = − 2 1 = − 2 1 = 0 = 8 − 2 + 2 2 + 1 6 = 4 − 1 + 5 Note that cos 5 2 π > 0
Sin 18 always positive ,,,1-√5\4&1-√5\2 are wrong answers,,,,assume a right angle triangle ,assume sin 18=(-1+√5)\4=opposite \hypotenuse, so adjacent side to angle =√(16-(-1+√5)^2)=√(10+2√5),so cos(18)=√(10+2√5)\4,sin^2(18)+cos^2(18) must be =1,sin^2(18)=(-1+√5)^2\16=6-2√5\16,,,cos^2(18)=√(10+2√5)^2\16=10+2√5\16,sin^2(18)+cos^2 (18)=6-2√5+10+2√5\16=16\16=1###-1+√5\4 is the right answer .
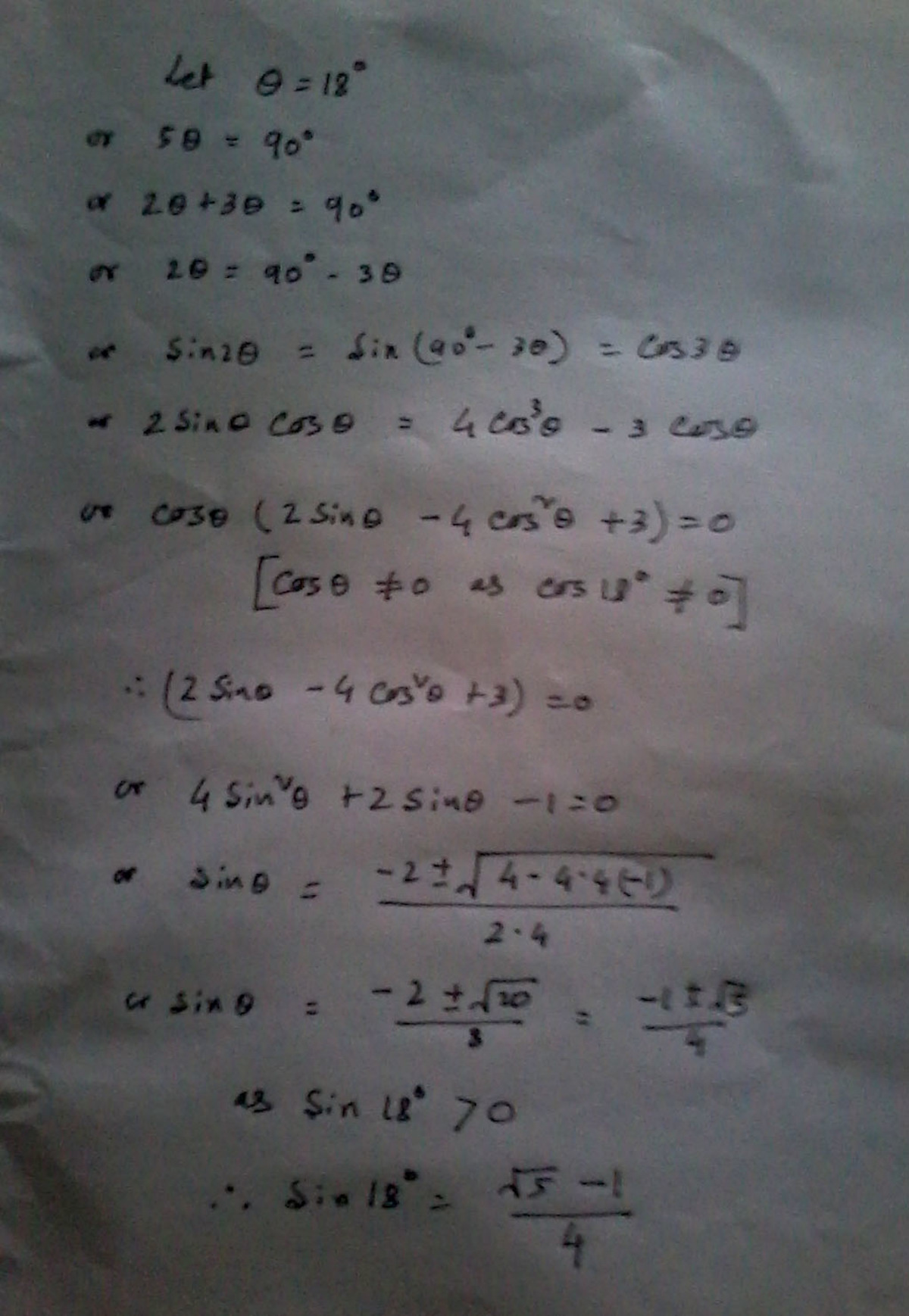
The attached figure almost offers a "proof without words." By similar triangles we have 1 x = x x + 1 , so that x = ϕ , the golden section. Bisecting the angle at point A , we see that sin ( 1 8 o ) = ϕ 2 1 = 5 + 1 1 = 4 5 − 1