Catch It!
A car travelling at overtakes another car traveling at . Assuming each car to be long, find the total road distance in metre used for the overtake.
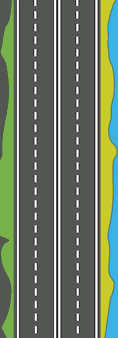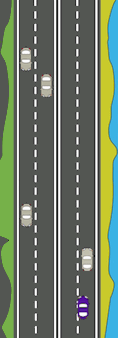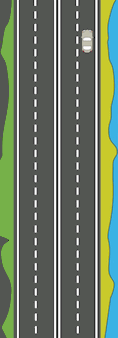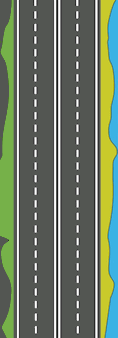
Note : Define the period of overtaking to start when the fast car is completely behind the slow car and ends when the slow car is completely behind the fast car.
The answer is 33.333333333.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
Relative velocity of the cars
= 6 0 − 4 2 = 1 8 k m p h = 5 m s − 1
For simplicity ;
⇒ We can imagine a frame where the car travelling at 4 2 k m p h is at rest & the car travelling at 6 0 k m p h overtakes it with a speed of 5 m s − 1 .
Now , since each car is 5 m long , Therefore , in our frame ,
⇒ The overtaking car travels a 'relative' distance of 5 + 5 = 1 0 m with the relative speed of 5 m s − 1 for overtaking.
Hence, Time taken = 5 1 0 = 2 s .
Now , coming back to the original frame ,
This car travels for 2 s with a speed of 6 0 k m p h or 3 5 0 m s − 1 .
Hence ,
Total road distance used for overtaking
= 3 5 0 × 2
= 3 3 . 3 3 m